Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia, remnant cholesterol, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment
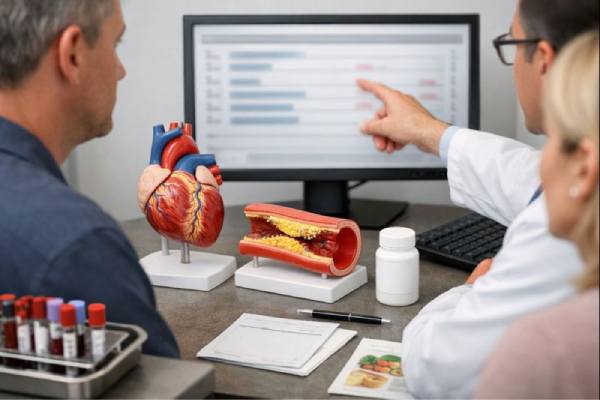
Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia is an inherited lipid disorder where the body has trouble clearing certain cholesterol- and triglyceride-carrying particles from the bloodstream. The result is...
Familial hypercholesterolemia, symptoms, diagnosis, and effective management
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is an inherited condition that raises cholesterol from birth and quietly increases the chance of early heart and blood-vessel disease. The...
Familial hyperchylomicronemia, pancreatitis risk, warning signs, and prevention steps
Familial hyperchylomicronemia is a rare inherited condition in which the body cannot clear fat from the bloodstream after eating. The result is extremely high...
Familial hyperlipoproteinemia: Risk Factors, Complications, Testing, and Family Screening
Familial hyperlipoproteinemia is a family-linked tendency to have unusually high levels of blood fats that travel through the body. These fats are carried in...
Familial hypertension: Causes, Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Long-Term Care
Familial hypertension means high blood pressure that shows up repeatedly in a family. Sometimes this is because relatives share many small genetic traits that...
Familial hypertriglyceridemia: Causes, Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Plan
Familial hypertriglyceridemia is an inherited tendency to run higher blood triglycerides—fats that circulate in your blood—often across several relatives. Many people discover it after...
Familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Family Screening
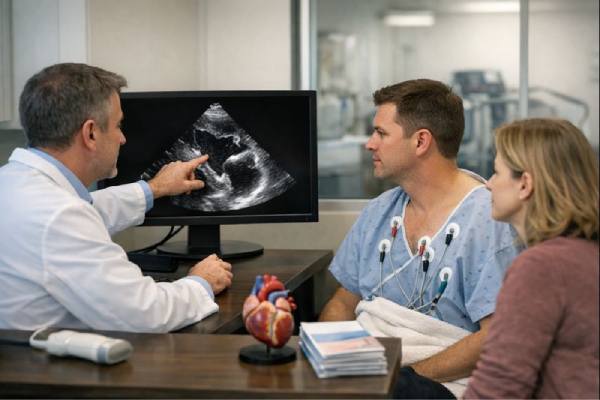
Familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a condition where the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick, and that tendency runs in families. It often appears without warning:...
Familial restrictive cardiomyopathy: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Modern Treatment Options
Familial restrictive cardiomyopathy is a rare inherited heart condition where the heart becomes unusually stiff. A stiff heart may still squeeze well, yet it...
Familial thrombophilia: Causes, Genetics, and Family Screening Decisions
Familial thrombophilia means you inherit a higher tendency to form blood clots. Most often, these clots develop in deep veins—usually in the leg—and can...
Familial ventricular tachycardia: Diagnosis, ECG Testing, and Family Screening
Familial ventricular tachycardia is a pattern of fast, abnormal heart rhythms that can run in families. Ventricular tachycardia (VT) means “fast rhythm from the...
Fat embolism: Diagnosis Criteria, Imaging Clues, and Key Differentials
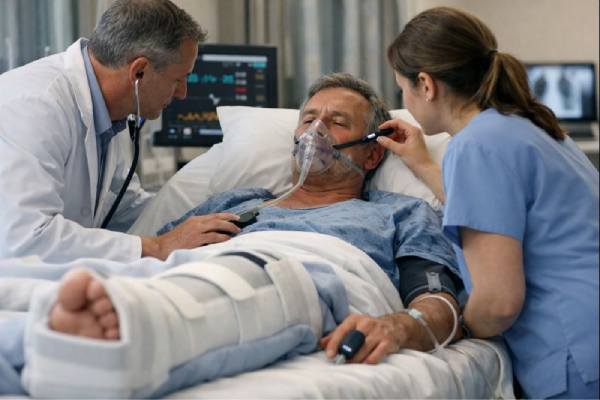
Fat embolism happens when droplets of fat enter the bloodstream and travel to small blood vessels, most often in the lungs and sometimes in...
Fatty heart: What It Means, Causes, Symptoms, and Management
“Fatty heart” is a common phrase, not a single medical diagnosis. People use it to describe extra fat around the heart, fat within the...
Femoral artery aneurysm: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Imaging, and Treatment Options
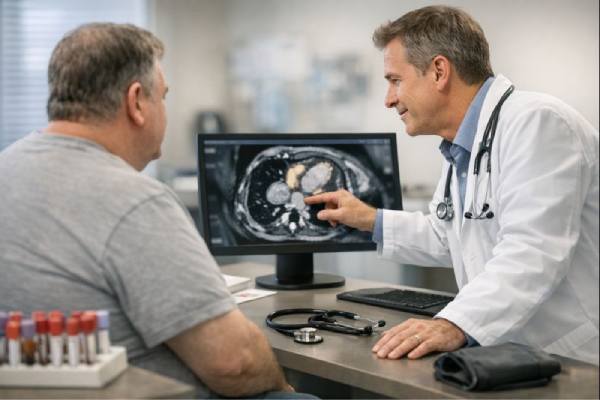
A femoral artery aneurysm is a bulging, weakened section of an artery in the upper thigh or groin. Many people first notice a new,...
Femoral artery embolism: Treatment With Heparin, Embolectomy, and Thrombectomy
Femoral artery embolism is a sudden blockage in a major thigh artery caused by material that traveled from elsewhere in the body. Most often,...
Femoral artery occlusion: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Recovery
A femoral artery occlusion is a blockage in one of the main arteries that supplies blood to your leg. When that flow slows or...
Femoral artery thrombosis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Emergency Treatment Options
A clot in the femoral artery can turn an ordinary day into an emergency. The femoral artery is the main “highway” vessel that carries...