Scalp Odor: Causes (Yeast, Sweat, Buildup) and How to Fix It
A persistent scalp odor can be surprisingly distressing. It often appears as a sour, musty, oily, or even “cheesy” smell that seems to return...
Scalp Oiling: Benefits, Risks, and Who Should Avoid It
Scalp oiling sits at an interesting crossroads between tradition, comfort, and modern hair care. For some people, it is a soothing pre-wash ritual that...
Scalp Pain (Trichodynia): Why Your Scalp Hurts and What Helps
A painful scalp can feel confusing and surprisingly distressing. You may notice soreness when brushing your hair, a burning sensation at the roots, or...
Scalp pH Explained: Why It Matters for Flakes, Oil, and Itch
Scalp problems often look simple from the outside. You see flakes, feel itch, notice greasy roots, and assume the scalp is either too dry...
Scalp Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
A persistently flaky scalp is easy to dismiss as dandruff, especially when the first signs are scattered scale and itching. Scalp psoriasis is different....
Scalp Rosacea: Symptoms, Triggers, and Treatment Options
Persistent scalp redness, burning, or unusual sensitivity can be frustrating, especially when it appears without obvious dandruff, infection, or product irritation. In some cases,...
Scalp Serums for Hair Growth: Popular Ingredients and What to Expect
Hair growth products have evolved far beyond basic oils and shampoos. Today, scalp serums occupy a rapidly expanding space in hair care routines, promising...
Scalp Sunburn: Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
The scalp is one of the most frequently overlooked areas when it comes to sun protection. Even people who carefully apply sunscreen to their...
Scalp Sunscreen: Best SPF Formats for Part Lines, Braids, and Thinning Hair
The scalp is one of the easiest places to miss with sun protection and one of the easiest places to burn. A neat center...
Seasonal Hair Shedding: Why It Peaks in Fall and How to Reduce It
Most people notice hair in the shower year-round. What makes fall different is the sudden sense that the amount has doubled: more strands on...
Seborrheic Dermatitis: Symptoms, Triggers, and the Best Shampoos
Seborrheic dermatitis often starts quietly: a dusting of flakes on a dark top, an itchy patch near the hairline, or a scalp that feels...
Secretome Therapy for Hair Growth: Exosomes, Growth Factors, and What’s Real
Hair loss treatment is entering a new phase where clinics no longer sell only minoxidil, finasteride, PRP, and surgery. Now the language is “regenerative,”...
Selenium and Hair Loss: Brazil Nuts, Safe Upper Limits, and Deficiency Signs
Selenium sits in an unusual place in hair health. It is essential, yet the gap between “enough” and “too much” is narrower than many...
Silica for Hair: Best Forms, Evidence, and Who Should Avoid It
Silica shows up in many “hair, skin, and nails” supplements, often surrounded by glossy promises about stronger strands and faster growth. The reality is...
Silicones in Hair Products: Are They Bad or Actually Protective?
On a label, names like dimethicone, amodimethicone, and cyclopentasiloxane can make a product look suspicious. Online, silicones are often blamed for dullness, dryness, limp...
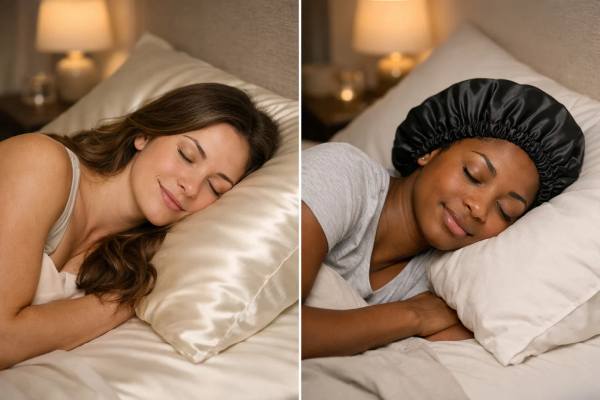
Silk Pillowcase vs Satin Bonnet: Which Protects Hair Better Overnight?
Nighttime hair care looks simple until you wake up with flattened curls, frizz at the crown, or snapped ends along the nape. A surprising...
Skinification of Haircare: Skincare Ingredients in Scalp Products Explained
The scalp used to be treated as a narrow strip of skin hidden under hair. Now it is being treated more like facial skin:...
Sleeping With Wet Hair: Breakage, Frizz, and Scalp Problems
Sleeping with wet hair is one of those habits that feels harmless until the effects start to show up in small, repeatable ways: more...
Smoking and Hair Loss: Circulation, Oxidative Stress, and What Changes Fastest
Smoking affects hair in a way many people notice before they fully understand it. The crown looks thinner. The temples seem to creep back...
Spearmint Tea for PCOS Hair: Hormone Claims, Benefits, and Safety
PCOS hair changes can feel especially frustrating because they often move in two directions at once. You may notice more facial hair, more body...
Spironolactone for Female Hair Loss: Benefits, Side Effects, and Results Timeline
For many women, hair thinning does not arrive as a dramatic event. It shows up quietly: a wider part, more scalp at the crown...
Spironolactone vs Oral Minoxidil for Women: Which Works Better and Why?
For many women, hair loss treatment does not begin with one simple question. It begins with several at once. Is the thinning hormonal, genetic,...
Split Ends: Causes, Prevention, and What Actually Helps
Split ends can make healthy hair look older, rougher, and thinner than it really is. They are often treated like a cosmetic annoyance, but...
Starting Minoxidil: Best Routine, Common Mistakes, and How to Reduce Irritation
Starting minoxidil often comes with a strange mix of hope and second-guessing. You may have read that it is one of the few hair-loss...