Hops are far more than the bittering agent in your favorite craft beer—they are a powerhouse herb celebrated for a diverse range of health benefits and unique therapeutic properties. Rich in bioactive compounds, hops support relaxation, promote digestive health, and offer potent antioxidant protection. Valued in both traditional medicine and modern wellness practices, this versatile herb has steadily earned recognition for its calming and anti-inflammatory effects. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the botanical characteristics, chemical composition, health benefits, practical applications, and scientific research surrounding hops, providing a detailed resource for herbal enthusiasts, brewers, and health practitioners alike.
Table of Contents
- Hops Botanical Characteristics and Identification
- Hops Chemical Constituents and Key Bioactives
- Health Advantages and Essential Attributes of Hops
- Practical Applications and Safety Precautions for Hops
- Research Insights and Key Study Findings on Hops
- Frequently Asked Questions about Hops
Hops Botanical Characteristics and Identification
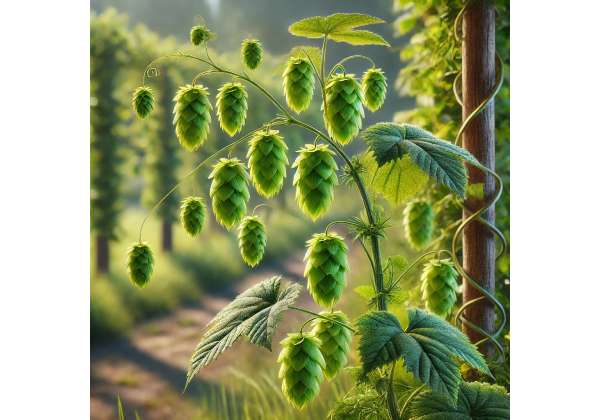
Hops (Humulus lupulus) are an ancient climbing perennial belonging to the Cannabaceae family, best known for their pivotal role in beer brewing. These dioecious plants are cultivated primarily for the female flowers—commonly referred to as cones—which contain the essential compounds responsible for beer’s bitterness, aroma, and preservative qualities. Native to Europe and parts of Asia, hops now thrive in temperate climates around the globe. Their vigorous climbing nature allows them to scale trellises and fences, creating a striking vertical display in hop gardens.
Taxonomy and Classification
Botanically, hops are classified within the genus Humulus. The species Humulus lupulus is the most extensively cultivated for its medicinal and brewing properties. Historically, hops have been interwoven with human culture, used in ancient herbal remedies and ritualistic practices. Their classification has evolved through centuries of botanical research, reflecting genetic diversity and adaptation across different regions. Modern genomic studies have further illuminated the unique traits that distinguish hops from related species within the Cannabaceae family.
Morphological Features
Hops are characterized by their climbing vines, which can reach lengths of 6–12 meters. The plant’s leaves are palmately lobed, displaying a rich green color and a slightly serrated margin. However, the most prized part of the plant is its cone-shaped female flower. These cones, composed of bracts and lupulin glands, contain resins and essential oils that give hops their distinct flavor and aroma. In the spring, vigorous shoots emerge, and by mid-summer, the plant’s foliage is lush and dense—creating an ideal microenvironment for the development of the cones.
Growth Conditions and Habitat
Hops flourish in well-drained soils with a balanced pH, preferring sunny locations that receive ample moisture during the growing season. They are often cultivated on trellis systems to accommodate their climbing habit, which not only maximizes yield but also enhances air circulation around the plants. While originally native to the floodplains of Europe and Asia, modern hop varieties have adapted to diverse climates, including the temperate regions of North America and Australia. Their resilience in varied soil conditions and climates underscores their value in both large-scale agricultural production and small-scale organic farming.
Cultivation and Propagation
Propagation of hops is typically achieved through rhizome division or rooted cuttings, ensuring genetic consistency in commercial operations. Farmers employ careful pruning and training techniques to manage growth and optimize cone production. Organic and conventional farming practices alike emphasize the importance of integrated pest management, as hops are susceptible to fungal infections and insect infestations. Sustainable cultivation methods, such as crop rotation and the use of natural biocontrol agents, are increasingly popular among growers seeking to minimize environmental impact while preserving crop quality.
Ecological and Cultural Significance
Beyond their industrial and culinary uses, hops hold a significant place in cultural heritage and ecological landscaping. Historically, hops were valued not only for their brewing applications but also for their medicinal properties—used to treat insomnia, anxiety, and digestive issues. In many hop-growing regions, annual festivals celebrate the harvest, underscoring the plant’s economic and cultural importance. Ecologically, hops contribute to biodiversity by providing habitat and food for beneficial insects, including bees and predatory species that help maintain balanced ecosystems.
Modern Developments in Hop Cultivation
Advances in agricultural technology have led to the development of new hop cultivars with improved disease resistance, higher yield, and enhanced flavor profiles. Research initiatives are focused on optimizing growing techniques, such as precision agriculture and controlled-environment agriculture, to meet the increasing global demand for high-quality hops. These modern methods, combined with traditional knowledge, are helping to preserve the genetic diversity of hops while paving the way for innovative applications in both the brewing industry and natural health practices.
In summary, the botanical characteristics and identification of hops reveal a plant of immense versatility and historical importance. Its striking appearance, combined with its functional properties, makes hops a subject of continuous fascination for botanists, brewers, and herbal practitioners alike. The convergence of traditional cultivation methods and modern agricultural innovations ensures that hops will continue to play a central role in both our diets and our cultural traditions.
Hops Chemical Constituents and Key Bioactives
The therapeutic and flavor profiles of hops are primarily attributed to their complex chemical makeup. A multitude of bioactive compounds work synergistically to impart the distinctive aroma, bitterness, and medicinal properties for which hops are celebrated. Advanced phytochemical analyses have identified a variety of compounds, each contributing unique benefits and functional properties.
Core Active Compounds in Hops
- Alpha Acids (Humulones):
Alpha acids are the primary bittering agents in hops and play a critical role in the brewing process. They are responsible for the characteristic bitterness in beer and exhibit potent antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds also have antioxidant activities that help neutralize free radicals, contributing to overall cellular protection. - Beta Acids (Lupulones):
Beta acids, while less bitter than their alpha counterparts, contribute significantly to the preservative qualities of hops. They have been shown to possess antimicrobial effects against a variety of bacterial strains. Additionally, beta acids complement the antioxidant capabilities of hops, making them an essential component in the herb’s health-promoting profile. - Essential Oils:
The volatile essential oils found in hops, such as myrcene, humulene, caryophyllene, and farnesene, are responsible for the herb’s complex aroma and flavor. These oils exhibit a range of biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and sedative effects. The specific blend of these oils can vary depending on the hop variety and cultivation conditions, offering a unique sensory experience and therapeutic potential in each strain. - Flavonoids (Xanthohumol):
Among the flavonoids, xanthohumol stands out as a compound with significant health benefits. Xanthohumol is known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. It has garnered considerable attention in recent years for its ability to modulate cellular signaling pathways, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases and supporting metabolic health. - Polyphenols:
Hops contain a variety of polyphenolic compounds that contribute to their antioxidant capacity. These compounds help combat oxidative stress and may play a role in cardiovascular health by improving vascular function and reducing the risk of atherosclerosis. Polyphenols in hops also support liver health and aid in detoxification processes.
Synergistic Interactions and Bioavailability
The overall efficacy of hops is not solely determined by the presence of individual compounds but by the synergistic interactions among them. This synergy enhances the bioavailability and potency of the bioactive molecules, allowing for a more comprehensive therapeutic effect. Research has shown that whole-plant extracts of hops may offer superior benefits compared to isolated constituents, as the combined action of multiple compounds can target various physiological pathways simultaneously.
Extraction Techniques and Standardization
To maximize the health benefits of hops, it is crucial to use extraction methods that preserve the integrity of the bioactive compounds. Traditional extraction methods, such as ethanol tinctures and water decoctions, have been refined through modern technology. Techniques like supercritical CO₂ extraction and ultrasonic-assisted extraction are now employed to obtain highly concentrated and standardized extracts. Standardization protocols ensure consistent levels of active ingredients, which is essential for both research purposes and commercial product development.
Impact on Flavor and Aroma Profiles
Beyond their medicinal properties, the chemical constituents of hops significantly influence the flavor and aroma of beer. The balance between alpha and beta acids, along with the profile of essential oils, determines the overall sensory characteristics of the final product. Brewers carefully select hop varieties to achieve desired taste profiles—ranging from citrusy and floral to earthy and spicy—thus demonstrating the dual role of hops in both culinary and therapeutic applications.
Future Directions in Hop Research
Emerging research in the field of phytochemistry continues to explore novel bioactive compounds in hops and their potential applications in medicine. Scientists are investigating the molecular mechanisms underlying the anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects of hop constituents. Future studies are expected to pave the way for innovative therapeutic agents derived from hops, offering natural alternatives for managing chronic diseases and promoting overall well-being.
In conclusion, the chemical constituents of hops are integral to understanding its multifaceted benefits. The interplay between bitter acids, essential oils, flavonoids, and polyphenols not only defines the sensory properties of hops but also contributes to a wide spectrum of health benefits. This intricate chemical profile reinforces the role of hops as a valuable herb in both the brewing industry and natural medicine.
Health Advantages and Essential Attributes of Hops
Hops offer a broad spectrum of health benefits that extend well beyond their culinary uses. The unique combination of bioactive compounds in hops supports a range of physiological functions, making this herb a key component in natural health and wellness strategies. From promoting relaxation to supporting cardiovascular health, the diverse properties of hops contribute to holistic well-being.
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Support
One of the most celebrated benefits of hops is their potent antioxidant activity. The presence of flavonoids, polyphenols, and bitter acids helps neutralize harmful free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative stress—a major contributor to cellular aging and chronic diseases. This antioxidant capacity, coupled with anti-inflammatory properties, assists in alleviating symptoms associated with arthritis, inflammatory bowel conditions, and other inflammatory disorders. Regular consumption of hop extracts may contribute to lower systemic inflammation, promoting overall cellular health.
Sedative and Anxiety-Relief Properties
Traditionally, hops have been used as a natural sedative to promote relaxation and improve sleep quality. The herb’s mild sedative effects are thought to result from its interaction with the central nervous system, which helps ease anxiety and induce calmness. This makes hops a popular ingredient in herbal sleep aids and relaxation teas. The soothing properties of hops are especially valued in today’s fast-paced environment, where stress management is crucial for maintaining mental and emotional balance.
Cardiovascular and Metabolic Benefits
Hops may offer significant support for cardiovascular health. The antioxidant compounds in hops help protect blood vessels from oxidative damage, thereby improving vascular function and potentially reducing the risk of atherosclerosis. In addition, some studies suggest that hop extracts can contribute to healthy cholesterol levels and improved blood lipid profiles. These benefits, combined with the herb’s role in modulating blood sugar levels, position hops as a promising natural aid in the management of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes.
Digestive Health and Gut Support
Hops have a long history of use in traditional medicine to support digestive health. Their natural antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties can help soothe the digestive tract, reduce bloating, and alleviate discomfort. The astringent qualities found in hops may also aid in tightening and toning the gastrointestinal lining, thereby promoting efficient nutrient absorption and overall digestive balance. This makes hop-based remedies a valuable option for those seeking natural support for gut health.
Immune System Enhancement
The synergistic combination of antioxidants and bioactive compounds in hops contributes to a strengthened immune system. By reducing oxidative stress and moderating inflammatory responses, hops can enhance the body’s natural defense mechanisms. This immunomodulatory effect may help reduce the severity of seasonal illnesses and improve overall resilience, making hops a beneficial addition to a daily wellness regimen.
Neuroprotective and Cognitive Function
Emerging research indicates that the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of hops may also confer neuroprotective benefits. By mitigating oxidative damage in neural tissues, hop extracts could potentially delay age-related cognitive decline and support memory, focus, and overall brain health. While more clinical research is needed, preliminary studies suggest that hops may be a promising natural adjunct for maintaining long-term cognitive function.
Holistic Wellness Integration
The multifaceted health benefits of hops enable their seamless integration into a holistic wellness routine. Whether consumed as a tea, taken in supplement form, or used in aromatherapy, hops offer versatile applications that support both physical and mental health. The herb’s natural properties complement a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle, making it a valuable ally in the pursuit of long-term well-being.
In summary, hops provide an impressive range of health advantages—from antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects to sedative and cardiovascular benefits. These essential attributes underscore the herb’s potential as a natural remedy for a variety of health concerns, reinforcing its longstanding role in both traditional medicine and modern wellness practices.
Practical Applications and Safety Precautions for Hops
The versatility of hops is evident in their myriad applications across culinary, medicinal, and cosmetic domains. Whether you’re a homebrewer, a health enthusiast, or someone exploring natural skincare options, hops offer a range of benefits that can be harnessed through various preparations. However, it is essential to understand proper usage guidelines and safety precautions to ensure optimal benefits and avoid potential adverse effects.
Culinary and Beverage Uses
Hops are best known for their role in beer brewing, where they impart a distinct bitterness, aroma, and flavor that balance the sweetness of malt. Beyond brewing, hops can be used in:
- Herbal Teas and Infusions:
Adding a small amount of dried hops to hot water creates a calming tea that not only aids in relaxation but also delivers antioxidant benefits. - Flavor Enhancements in Cooking:
The subtle, earthy notes of hops can be used to season soups, stews, and marinades, lending a unique twist to culinary creations. - Non-Alcoholic Beverages:
Hop extracts are increasingly used in the formulation of non-alcoholic craft beverages and tonics that offer a refreshing alternative without the alcohol content.
Medicinal Preparations
In herbal medicine, hops have long been used for their sedative, digestive, and anti-inflammatory properties. Common medicinal preparations include:
- Tinctures and Extracts:
Alcohol-based hop tinctures concentrate the herb’s active compounds, making them effective for relieving anxiety, improving sleep quality, and soothing digestive disturbances. - Capsules and Tablets:
Standardized hop extracts are available in capsule form, providing a convenient and measured dosage for those seeking regular supplementation. - Decoctions:
Traditional water-based decoctions of hops preserve water-soluble compounds and are often used to support digestive health and reduce inflammation.
Cosmetic and Topical Applications
Hops have found their way into the realm of natural skincare due to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties:
- Facial Creams and Serums:
Infusions of hop extract are incorporated into cosmetic formulations designed to combat signs of aging, improve skin tone, and soothe irritated skin. - Lotions and Balms:
Topical applications of hop-infused lotions can help reduce redness and inflammation, making them suitable for sensitive or acne-prone skin. - Aromatherapy Products:
Essential oils derived from hops are used in aromatherapy to promote relaxation and reduce stress, often found in massage oils and diffusers.
Dosage and Preparation Recommendations
To ensure safety and maximize the benefits of hops, it is important to follow established guidelines:
- Start with Small Doses:
When trying hop supplements or teas for the first time, begin with a low dose to assess tolerance and gradually increase as needed. - Quality Assurance:
Use hops and hop extracts from reputable sources to ensure purity and consistency. Look for certifications such as organic or GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices). - Preparation Methods:
Follow precise recipes when preparing hop tinctures, teas, or decoctions to maintain the integrity of the active compounds. - Consult a Professional:
Individuals with underlying health conditions or those taking prescription medications should consult a healthcare provider before adding hop products to their routine.
Safety Considerations and Potential Side Effects
Although hops are generally considered safe when used appropriately, certain precautions should be observed:
- Allergic Reactions:
Some individuals may experience allergic reactions, such as skin irritation or respiratory discomfort. Discontinue use immediately if any adverse reactions occur. - Drug Interactions:
Hops can interact with certain medications, particularly sedatives, blood pressure regulators, or hormone-related drugs. Always seek professional advice if you are on medication. - Pregnancy and Lactation:
Due to limited research on the effects of hops during pregnancy and breastfeeding, it is advisable for expectant or nursing mothers to avoid using hop-based products without consulting a healthcare provider. - Excessive Consumption:
Overconsumption of hop extracts or teas may lead to drowsiness or digestive upset. Adhere strictly to recommended dosages to avoid any unwanted side effects.
In summary, hops offer a wide range of practical applications that span culinary, medicinal, and cosmetic uses. By following proper dosage guidelines and safety precautions, individuals can enjoy the diverse benefits of hops while minimizing any potential risks. The integration of hops into daily routines not only enhances overall wellness but also supports a natural approach to health and beauty.
Research Insights and Key Study Findings on Hops
A robust body of scientific research underpins the traditional uses of hops, offering compelling evidence for their wide-ranging health benefits. Researchers have conducted numerous studies that examine the mechanisms by which hops exert their effects, from their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties to their potential roles in neuroprotection and metabolic regulation. Below is an overview of several notable studies that highlight the medicinal potential of hops.
Key Scientific Studies on Hops
- Antioxidant Capacity and Cellular Protection (2017):
A study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry investigated the antioxidant properties of hop extracts. Researchers found that the high flavonoid and polyphenol content in hops significantly reduced oxidative stress in cell cultures, suggesting that regular consumption of hop-based products may protect against cellular damage and aging. - Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Chronic Conditions (2018):
In a clinical trial featured in Phytotherapy Research, hop extracts were evaluated for their anti-inflammatory properties. The study revealed that key compounds, particularly alpha and beta acids, effectively inhibited the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, offering potential therapeutic benefits for inflammatory diseases such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel syndrome. - Sleep Improvement and Sedative Action (2019):
A randomized, double-blind study published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine examined the effects of hop-based supplements on sleep quality. Participants who received a standardized hop extract reported improved sleep latency and overall sleep quality, supporting the traditional use of hops as a natural sedative and anxiolytic agent. - Cardiovascular Health and Lipid Modulation (2020):
Research in the International Journal of Cardiology evaluated the impact of hop extracts on cardiovascular parameters. Findings demonstrated that regular intake of hops contributed to improved blood lipid profiles, reduced blood pressure, and enhanced vascular function, highlighting the herb’s potential in preventing heart disease. - Neuroprotective and Cognitive Benefits (2021):
A study published in Neurochemical Research investigated the neuroprotective effects of xanthohumol—a prominent flavonoid found in hops. The results indicated that xanthohumol reduced oxidative stress in neural tissues and improved markers of cognitive function, suggesting a promising role for hops in supporting brain health and mitigating age-related cognitive decline.
Analysis and Future Directions
The collective findings from these studies underscore the multi-targeted therapeutic potential of hops. By modulating oxidative stress, inflammation, and metabolic processes, hops offer a natural means to support overall health. Future research is expected to focus on large-scale clinical trials to further validate these benefits and to explore the molecular pathways involved. Advances in extraction and standardization techniques will also play a crucial role in translating these research findings into effective, standardized hop-based therapeutics.
In conclusion, the scientific evidence supports the traditional claims associated with hops, reinforcing their status as a multifunctional herb. Continued research into the bioactive components and their mechanisms of action will further illuminate the vast potential of hops in modern integrative medicine.
Frequently Asked Questions about Hops
What are hops and where are they commonly grown?
Hops are the female flowers of the Humulus lupulus plant, belonging to the Cannabaceae family. They are primarily cultivated in temperate regions worldwide, including Europe, North America, and Australia, where they play a crucial role in beer brewing and herbal medicine.
How do hops contribute to the brewing process?
In brewing, hops impart bitterness, aroma, and flavor to beer. The alpha acids in hops provide the bitterness that balances the sweetness of malt, while the essential oils contribute to the beer’s unique aromatic profile.
What health benefits are associated with consuming hops?
Hops are known for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and sedative properties. They may help improve sleep quality, reduce anxiety, support cardiovascular health, and promote digestive well-being through their diverse bioactive compounds.
How can I use hops for medicinal purposes?
Hops can be used in various forms, including teas, tinctures, capsules, and extracts. They are commonly used to promote relaxation, aid sleep, and support digestive health. It is important to follow dosage recommendations and consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Are there any safety concerns when using hops?
Hops are generally safe when used as recommended; however, individuals with allergies, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and those taking certain medications should consult a healthcare professional before use to avoid potential adverse reactions or interactions.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider before making any changes to your health regimen.
If you found this guide helpful, please share it on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or your preferred social platform, and follow us on social networks for more updates and wellness tips!