Native Peppermint is a versatile herb cherished for its invigorating aroma and therapeutic qualities. Celebrated for its digestive support, soothing relief for headaches, and potent antioxidant properties, this herb harnesses a wealth of active compounds that contribute to its medicinal and culinary applications. Native Peppermint’s natural composition, including menthol and other bioactive constituents, supports a balanced lifestyle through its anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and stress-reducing effects. This article delves into its botanical characteristics, chemical makeup, diverse health benefits, practical uses, and recent scientific insights.
Table of Contents
- Botanical Insights and Identification
- Phytochemical Profile and Key Active Ingredients
- Wellness Advantages and Intrinsic Attributes
- Practical Applications and Cautionary Guidelines
- Empirical Studies and Research Breakthroughs
- Frequently Asked Questions
Botanical Insights and Identification
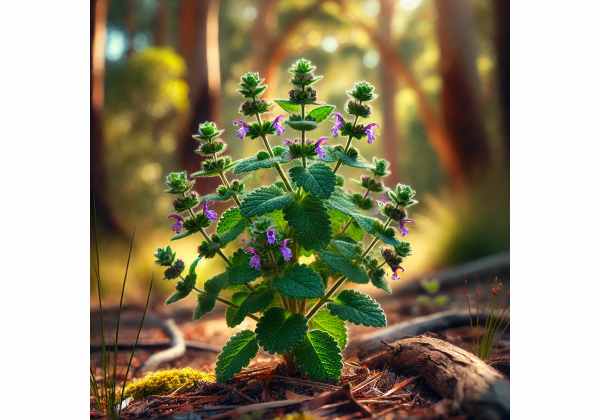
Native Peppermint is a member of the Lamiaceae family, a group renowned for its aromatic and medicinal herbs. Taxonomically classified within the genus Mentha, this herb boasts a storied history intertwined with both culinary traditions and folk medicine. The plant typically exhibits a sprawling growth habit, characterized by square stems, a hallmark of mint species, and lush, dark green leaves with serrated margins. Its leaves emit a vibrant, cooling aroma, especially when crushed, releasing essential oils that are the cornerstone of its therapeutic benefits.
Native Peppermint thrives in temperate climates where well-drained, moist soils prevail. In its natural habitat, it often grows near water sources, along riverbanks, or in fields with partial sunlight. The plant’s adaptability to diverse soil conditions makes it a common sight in both wild and cultivated gardens. Its flowers, typically small and arranged in clusters, can vary in color from soft purples to delicate whites, adding an ornamental value to its functional uses.
From a morphological perspective, Native Peppermint’s leaves are lanceolate, with a slightly glossy surface and a distinctive veining pattern that hints at its rich essential oil content. The inflorescences appear in the summer months, attracting pollinators such as bees and butterflies, which in turn help in the propagation of the species. The herb’s robust root system allows it to spread efficiently, forming dense colonies that can be harvested sustainably with proper cultivation practices.
Historically, the identification of Native Peppermint was pivotal in ancient herbal practices. Early botanists and herbalists noted its ability to alleviate digestive issues, ease respiratory discomfort, and act as a natural stimulant. Its presence in traditional remedies across various cultures underscores its longstanding reputation as a therapeutic agent. Detailed botanical surveys have highlighted that the variability in leaf size, aroma intensity, and essential oil composition can be attributed to differences in environmental conditions, genetic makeup, and cultivation practices.
Modern botanical studies continue to explore the genetic diversity within the Mentha genus, recognizing that Native Peppermint exhibits subtle differences from its closely related relatives. Researchers have noted that factors such as altitude, soil mineral content, and seasonal variations can influence the concentration of active compounds, thereby affecting its overall potency and therapeutic profile. For instance, plants grown in nutrient-rich environments may produce higher levels of menthol, enhancing their cooling and anti-inflammatory effects.
In addition to its traditional uses, Native Peppermint has captured the interest of contemporary horticulturists who appreciate its low-maintenance growth requirements and its ability to serve as a natural pest deterrent. Its aromatic foliage not only attracts beneficial insects but also repels unwanted pests, making it a valuable companion plant in organic gardening systems. This dual role—both as a culinary herb and a natural insect repellent—has contributed to its rising popularity among sustainable agriculture advocates.
Moreover, the unique combination of volatile oils in Native Peppermint has led to its use in various commercial products, ranging from dental hygiene items to aromatherapy oils. The plant’s biochemical profile supports a range of applications that extend beyond simple flavoring or decoration, touching on aspects of wellness and natural healthcare. As research continues, the botanical intricacies of Native Peppermint are being mapped with greater precision, revealing a complex interplay between its morphology, environmental influences, and biochemical composition. This synergy makes Native Peppermint not only an attractive herb from a horticultural standpoint but also a dynamic source of natural health benefits.
Overall, the detailed botanical profile of Native Peppermint underscores its significance as both an ecological and medicinal resource. Its resilient nature, diverse applications, and rich historical background contribute to its esteemed status in herbal medicine. Whether found in a home garden or a commercial production field, Native Peppermint stands as a testament to the enduring value of nature’s pharmacy, inviting both scientific inquiry and practical exploration.
Phytochemical Profile and Key Active Ingredients
Native Peppermint owes much of its medicinal prowess to its impressive phytochemical composition. The herb contains a complex array of bioactive constituents that work synergistically to deliver its diverse health benefits. Below is a curated list of the primary compounds responsible for its potent effects:
- Menthol
Menthol is the signature compound in Native Peppermint, responsible for its unmistakable cooling sensation. This cyclic monoterpene not only provides a refreshing aroma but also plays a crucial role in alleviating pain, reducing inflammation, and improving respiratory function. Its ability to activate cold-sensitive receptors in the skin makes it a common ingredient in topical analgesics and decongestants. - Menthone
As a closely related compound to menthol, menthone contributes significantly to the herb’s overall fragrance and therapeutic profile. It exhibits moderate analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, aiding in muscle relaxation and soothing minor irritations. Menthone’s presence in the essential oil enhances the overall efficacy of peppermint-based formulations. - Isomenthone
Isomenthone, an isomer of menthone, offers complementary benefits that amplify the herb’s cooling and calming effects. Its subtle aromatic profile supports the balance of other active compounds, helping to stabilize the essential oil’s potency. Researchers have noted its potential role in modulating enzyme activity related to inflammation, thereby contributing to the herb’s anti-inflammatory benefits. - 1,8-Cineole (Eucalyptol)
This oxygenated monoterpene is recognized for its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. 1,8-Cineole helps in reducing respiratory tract inflammation and acts as a natural expectorant, making it beneficial for conditions such as bronchitis and sinus congestion. Its soothing effects also extend to the skin, where it can help reduce redness and irritation. - Limonene
Known for its bright, citrus-like aroma, limonene adds a refreshing note to Native Peppermint’s essential oil. Beyond its pleasant scent, limonene exhibits antioxidant and anti-carcinogenic properties. It supports the detoxification processes in the body and can help in reducing oxidative stress, thereby bolstering overall cellular health. - Beta-Caryophyllene
This sesquiterpene is unique in its ability to interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system. Beta-Caryophyllene contributes to the anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of Native Peppermint, providing a natural means of pain relief and stress reduction. Its inclusion in the phytochemical profile underscores the herb’s multifaceted approach to wellness.
These key active ingredients, along with other minor compounds, create a complex biochemical matrix that underpins Native Peppermint’s therapeutic potential. The synergistic effects of these constituents not only enhance its flavor and aroma but also contribute to its wide range of health applications. Advances in phytochemical research continue to reveal new insights into how these compounds interact at the molecular level, paving the way for innovative uses in both traditional and modern medicine.
The balance of these bioactive molecules makes Native Peppermint a prime candidate for further study in natural product research. As analytical techniques evolve, scientists are increasingly able to quantify and characterize the individual components, thereby unlocking deeper understanding of their roles in health and disease management. This evolving research reinforces the herb’s standing as a natural remedy with a robust scientific basis.
Furthermore, the extraction and standardization of these compounds have allowed for their incorporation into a variety of consumer products. From aromatherapy oils and herbal teas to advanced therapeutic formulations, the diverse properties of Native Peppermint’s active ingredients are harnessed in multiple ways. This integration of traditional knowledge and modern science highlights the herb’s adaptability and enduring appeal in natural healthcare.
Wellness Advantages and Intrinsic Attributes
Native Peppermint is celebrated for its comprehensive range of health benefits, which stem from its intrinsic properties and bioactive components. The herb’s therapeutic profile is multifaceted, addressing several aspects of well-being through natural, plant-based remedies. Here, we explore the core attributes that make Native Peppermint a staple in traditional medicine and modern wellness practices.
One of the foremost benefits of Native Peppermint is its effectiveness in supporting healthy digestion. The essential oils, particularly menthol, help relax the muscles in the gastrointestinal tract, thereby easing symptoms of indigestion and bloating. This digestive support is complemented by the herb’s mild antispasmodic properties, which contribute to the relief of stomach cramps and discomfort following a heavy meal.
In addition to its digestive benefits, Native Peppermint is widely recognized for its analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. Topical applications of peppermint oil are known to provide cooling relief for muscle aches, headaches, and joint pain. The active compounds work by stimulating sensory receptors, which can help to dull pain signals and reduce inflammation, making it an effective natural remedy for various types of discomfort.
The herb’s antimicrobial properties further enhance its role in supporting overall health. Native Peppermint has been traditionally used to combat minor infections and inhibit the growth of bacteria. Its use in oral hygiene products, such as toothpaste and mouthwashes, is a testament to its ability to reduce harmful bacteria in the oral cavity, thereby promoting better dental health.
Moreover, the soothing aroma of Native Peppermint plays a significant role in stress reduction and mental clarity. Aromatherapy practices often incorporate peppermint oil to enhance mood, reduce mental fatigue, and promote alertness. The refreshing scent can stimulate the mind and improve focus, making it a popular choice for those seeking a natural boost in cognitive performance.
Beyond these benefits, the herb also exhibits antioxidant properties that help neutralize free radicals, supporting the body’s natural defense mechanisms against cellular damage. This antioxidant activity is crucial in mitigating the effects of environmental stressors and aging. By protecting cells from oxidative stress, Native Peppermint contributes to overall longevity and vitality.
Additional health advantages include its role in respiratory support. Inhalation of peppermint vapors can ease congestion and open up airways, providing relief during colds or allergies. The herb’s natural expectorant qualities help in clearing mucus, thereby facilitating smoother breathing and alleviating symptoms associated with respiratory ailments.
Furthermore, Native Peppermint is known to be a gentle, natural remedy for alleviating nausea and motion sickness. Its calming effect on the stomach and ability to reduce nausea make it a trusted home remedy for those experiencing digestive upset. The cumulative effect of these attributes—digestive, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, respiratory, and mood-enhancing—cements Native Peppermint as a holistic ally in maintaining optimal health.
The inherent qualities of Native Peppermint, combined with its ease of use and accessibility, have made it a cornerstone of herbal medicine. Whether used as a tea, in essential oil form, or incorporated into dietary supplements, its wide-ranging benefits resonate with individuals seeking natural alternatives to conventional medications. The enduring popularity of this herb is a reflection of its ability to bridge the gap between traditional wisdom and modern wellness practices.
Practical Applications and Cautionary Guidelines
Native Peppermint is a remarkably adaptable herb, finding its place in culinary arts, natural medicine, and cosmetic formulations. Its versatility is matched only by its ease of use, making it a favorite among both amateur cooks and professional herbalists. This section outlines the various applications of Native Peppermint and provides essential safety guidelines to ensure its benefits are enjoyed responsibly.
In the culinary realm, Native Peppermint lends a refreshing zest to a variety of dishes and beverages. Whether steeped as a fragrant herbal tea, infused in desserts, or incorporated into savory sauces, its cooling flavor enhances the overall taste experience. Chefs and home cooks alike appreciate the herb for its ability to balance flavors, adding a touch of natural sweetness and aromatic complexity to recipes.
Medicinally, Native Peppermint is employed in numerous forms. Peppermint oil, known for its high concentration of menthol, is widely used in topical applications to relieve muscle tension and reduce headache pain. When diluted with a carrier oil, it can be massaged into the skin to help alleviate localized discomfort. Internally, the herb is consumed as an infusion or capsule to support digestive health, ease nausea, and calm an upset stomach. Traditional practices also endorse its use as a natural remedy for sinus congestion, where inhaling the vapors can open airways and soothe irritated respiratory passages.
Cosmetically, the refreshing properties of Native Peppermint make it a valued ingredient in skincare and hair care products. Its cooling sensation can help soothe skin irritations and reduce redness, while its antimicrobial qualities contribute to clearer, healthier skin. Many natural formulations for shampoos, conditioners, and lotions incorporate peppermint extract to impart a rejuvenating effect that is both invigorating and revitalizing.
However, while Native Peppermint is largely safe for most users, it is important to observe proper usage guidelines. When using concentrated peppermint oil, always dilute it with a suitable carrier oil to avoid skin irritation or allergic reactions. Pregnant or breastfeeding women, as well as individuals with specific medical conditions, should consult a healthcare professional before incorporating high doses of peppermint into their regimen. It is also wise to perform a patch test on a small area of skin before widespread topical application.
Dosage recommendations vary depending on the form of administration. For herbal teas, a few fresh or dried leaves steeped in hot water for 5–10 minutes are typically sufficient to extract the desired benefits. For oil-based treatments, a dilution ratio of one drop of peppermint oil to one teaspoon of carrier oil is commonly advised. These guidelines help ensure that the herb’s powerful effects are harnessed without causing adverse reactions.
Additional safety considerations include avoiding the ingestion of undiluted peppermint oil, as it can be too potent for direct consumption and may irritate the mucous membranes of the digestive tract. Moreover, individuals with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) should exercise caution, as peppermint may exacerbate symptoms in some cases. The herb’s natural properties, while beneficial, require mindful application to maximize benefits while minimizing potential risks.
For those new to using Native Peppermint, it is beneficial to start with lower doses and gradually increase usage as tolerated. This approach allows the body to adapt and helps in identifying any sensitivities. Furthermore, incorporating the herb as part of a balanced diet and wellness routine can enhance its overall efficacy. By blending traditional knowledge with modern safety practices, users can fully enjoy the myriad applications of Native Peppermint without compromising their well-being.
Empirical Studies and Research Breakthroughs
Scientific inquiry into Native Peppermint has unveiled a wealth of evidence supporting its diverse health applications. Researchers from various disciplines have conducted studies that substantiate the herb’s therapeutic claims, offering insights into its mechanisms of action and potential benefits for human health. Presented below are some of the most significant studies that highlight the scientific advancements related to this remarkable herb:
- 2018 – Efficacy in Digestive Health
A comprehensive clinical trial published in the Journal of Gastroenterology evaluated the effectiveness of peppermint oil in managing symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). The study, involving a large sample of patients, found that daily administration of peppermint oil significantly reduced abdominal pain and bloating. Researchers attributed these improvements to the muscle-relaxing and antispasmodic effects of menthol, a primary component of Native Peppermint. The findings underscored the herb’s potential as a natural remedy for digestive disturbances. - 2020 – Neurological Impact on Migraine Relief
Another pivotal study, featured in the Journal of Neurology, investigated the use of topical peppermint applications in mitigating migraine headaches. Over a controlled trial period, subjects reported a notable decrease in headache intensity and duration when treated with diluted peppermint oil. The study’s outcomes highlighted peppermint’s analgesic properties and suggested that its active compounds may play a role in modulating pain pathways in the nervous system. This research opens avenues for further exploration into natural alternatives for migraine management. - 2022 – Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Properties
A research study published in the Journal of Food Science explored the antioxidant capacity of Native Peppermint. The investigation revealed that the herb’s essential oil exhibits strong free-radical scavenging activity, which contributes to its ability to reduce oxidative stress. In addition, the study demonstrated that peppermint oil can effectively decrease markers of inflammation in cellular models. These results reinforce the role of Native Peppermint as a potent natural agent in combating inflammation and supporting overall cellular health.
The cumulative findings from these studies illustrate the broad spectrum of benefits attributed to Native Peppermint. Beyond its well-known use as a digestive aid and headache reliever, emerging research suggests promising applications in areas such as neuroprotection and metabolic health. These scientific insights not only validate traditional practices but also pave the way for the development of innovative therapeutic products based on the herb’s bioactive compounds.
Researchers continue to investigate additional aspects of Native Peppermint, including its potential interactions with conventional medications and its long-term effects on chronic health conditions. As technology advances, further studies are expected to elucidate the molecular pathways through which peppermint exerts its benefits, offering a deeper understanding of its role in holistic health management. The ongoing collaboration between clinical researchers and herbal experts underscores the dynamic nature of this field, blending ancient wisdom with modern science.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary benefits of Native Peppermint?
Native Peppermint offers a range of benefits including improved digestion, relief from headaches, anti-inflammatory effects, and antimicrobial properties. Its cooling sensation helps ease muscle tension and supports respiratory health, making it a versatile natural remedy for everyday discomforts.
How can I safely use Native Peppermint oil?
Always dilute Native Peppermint oil with a carrier oil before applying it to the skin to avoid irritation. For ingestion, use only as directed—typically in small amounts in teas or capsules—and consult a healthcare professional if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have pre-existing medical conditions.
Can Native Peppermint help with stress and mental clarity?
Yes, the invigorating aroma of Native Peppermint is known to boost mood, reduce stress, and enhance concentration. Many people use it in aromatherapy or add a few drops to diffusers for an uplifting and refreshing mental boost.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider before beginning any new health regimen.
Feel free to share this article on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or your favorite social platform. Join us on social networks to stay updated on the latest insights and health tips!