Sesame is a time-honored seed used both as a culinary staple and as a potent herbal remedy. Renowned for its rich nutrient profile and bioactive compounds, sesame offers impressive antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cardioprotective benefits. Packed with lignans like sesamin, sesamolin, sesamol, and a myriad of essential minerals and vitamins, sesame plays a crucial role in supporting digestion, skin health, and immune function. Additionally, its oil is prized for its skin-nourishing qualities and for balancing body chemistry. This article explores sesame’s botanical identity, detailed phytochemistry, broad spectrum of health benefits, diverse applications, supporting scientific research, and provides answers to frequently asked questions.
Table of Contents
- Botanical Characterization and Identification
- Phytochemical Profile and Active Compounds
- Health Promoting Attributes and Key Benefits
- Practical Uses and Safety Guidelines
- Research Insights and Study Highlights
- Frequently Asked Questions about Sesame
Botanical Characterization and Identification
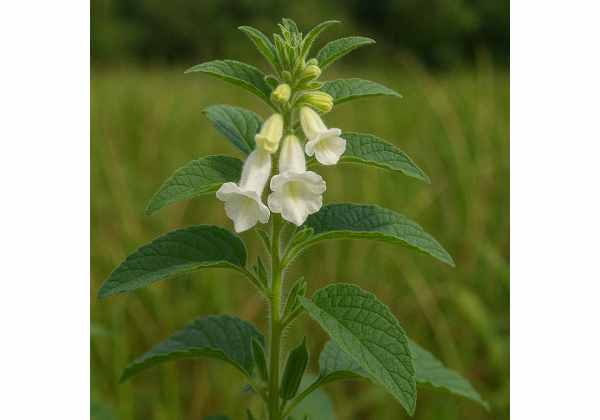
Sesame (Sesamum indicum) is an ancient annual herbaceous plant belonging to the Pedaliaceae family, although it is sometimes classified under its own family, Sesamaceae. Cultivated for thousands of years, sesame is recognized for its tiny, oil-rich seeds and its hardy, drought-resistant nature. Native to Africa and parts of Asia, it now thrives in tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate regions around the globe.
Morphological Traits and Taxonomy
Sesame plants typically grow to heights of 60–150 centimeters. They have slender, erect stems with a somewhat bushy appearance and a deep, extensive taproot that enables survival in arid conditions. The leaves are simple, arranged alternately, and range from ovate to lanceolate, with a rough surface texture. In summer, the plant produces tubular, pale yellow or white flowers that are held in clusters along the stem; these flowers subsequently develop into capsule-like fruits containing numerous tiny, flat seeds.
The taxonomic classification of sesame is as follows:
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Clade: Angiosperms
- Order: Lamiales
- Family: Pedaliaceae (or Sesamaceae)
- Genus: Sesamum
- Species: Sesamum indicum
Growing Conditions and Geographic Distribution
Sesame is particularly valued for its resilience in challenging growing conditions. It prefers well-drained, sandy soils and thrives in environments that receive abundant sunlight. The plant exhibits notable drought tolerance due to its extensive root system, which accesses deep soil moisture. This adaptability has made sesame a critical crop in regions with limited water resources.
Cultivation practices for sesame have evolved over millennia. Today, it is grown on large-scale farms as well as in smallholder gardens across Asia, Africa, and Latin America. Modern agricultural techniques, including improved irrigation and organic cultivation methods, are used to optimize yield and maintain the quality of its nutrient-dense seeds.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Sesame has long been revered in many cultures for its culinary, medicinal, and even ritualistic value. Ancient civilizations in India, Egypt, and Mesopotamia prized sesame seeds for their remarkable oil content and nutritional benefits. In traditional Ayurvedic medicine, sesame oil is used for wound healing and as a carrier oil in massage therapies. Moreover, its seeds have been incorporated into a variety of dishes—from savory breads to sweet confections—underscoring its versatile role as both food and remedy.
Ecological Role
Beyond its agricultural importance, sesame contributes significantly to sustainable farming practices. Its adaptability to low-fertility soils and drought conditions helps maintain soil health and prevent erosion. When cultivated responsibly, sesame can be an environmentally friendly crop that supports local ecosystems and biodiversity.
In summary, the botanical characterization of sesame reveals an ancient, adaptable, and multipurpose plant with both significant cultural heritage and modern-day relevance. Its impressive physical attributes and resilience in diverse growing conditions form the foundation for its widespread use in culinary and medicinal applications.
Phytochemical Profile and Active Compounds
The health-promoting properties of sesame can be largely attributed to its rich phytochemical composition. Modern analytical techniques have identified a wide array of bioactive compounds that work together synergistically to deliver potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cardioprotective effects. Here, we explore the primary chemical constituents of sesame in detail:
- Sesamin and Sesamolin:
These lignans are among the most celebrated compounds found in sesame. Sesamin and sesamolin exhibit strong antioxidant properties, neutralizing free radicals that cause cellular damage. Moreover, they have been associated with lipid-lowering effects and improved cardiovascular function by influencing blood cholesterol levels and promoting arterial health. - Sesamol:
A phenolic compound that forms during the roasting of sesame seeds, sesamol is a powerful antioxidant. It not only scavenges free radicals but also protects against oxidative stress and inflammation. Research suggests that sesamol may have neuroprotective effects and aid in reducing the risk of age-related diseases. - Phytosterols:
Sesame seeds contain various phytosterols, such as beta-sitosterol, which contribute to maintaining healthy cholesterol levels by inhibiting cholesterol absorption in the digestive tract. These compounds support cardiovascular health and promote a balanced lipid profile. - Tocopherols:
Vitamin E in the form of tocopherols is present in sesame seeds and plays a significant role in protecting cell membranes against oxidative damage. Tocopherols work in tandem with other antioxidants to bolster the body’s defense mechanisms and support skin health as well as general immunity. - Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs):
Sesame seeds are notably high in both omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids, which are essential for maintaining cell structure and regulating inflammatory processes. These fatty acids contribute significantly to the nutritional value of sesame oil, making it a prized ingredient in both culinary and therapeutic applications. - Phenolic Acids and Flavonoids:
A variety of phenolic acids (such as ferulic acid and caffeic acid) and flavonoids are found in sesame seeds. These compounds provide robust antioxidant effects, help reduce chronic inflammation, and may lower the risk of certain cancers through their ability to modulate cell signaling pathways. - Minerals and Vitamins:
Beyond its phytochemicals, sesame is a rich source of minerals including calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and iron. It is also an excellent source of B vitamins, which are critical for energy metabolism and overall vitality. The combination of these micronutrients with bioactive compounds makes sesame a superfood with wide-ranging health benefits.
The synergy of these compounds is what makes sesame an exceptionally potent nutritional and medicinal resource. Research using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry has enabled scientists to quantify these bioactives precisely, ensuring that sesame extracts and oils retain their maximum therapeutic potential. Standardization of sesame products is essential for ensuring consistent efficacy, particularly in clinical settings.
In summary, the diverse phytochemical profile of sesame is central to its health benefits. The active compounds present in sesame work in concert to deliver antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cardioprotective effects while also providing essential nutrients that support overall health.
Health Promoting Attributes and Key Benefits
Sesame is highly regarded for its multifaceted health benefits, which span from cardiovascular protection to skin nourishment. This section details the various therapeutic attributes of sesame and explains how its unique blend of nutrients and bioactive compounds supports overall wellness.
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Benefits
One of the standout benefits of sesame is its potent antioxidant activity. The lignans (such as sesamin and sesamolin), sesamol, and tocopherols work synergistically to combat oxidative stress by neutralizing harmful free radicals. This protective action is critical in preventing cellular damage that can lead to chronic diseases like cancer and heart disease. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory properties of sesame help to reduce inflammation in the body, which is beneficial for conditions such as arthritis, digestive disorders, and even skin irritations.
Cardiovascular Support
Research has consistently shown that sesame plays an important role in promoting cardiovascular health. Sesamin and sesamolin contribute to maintaining healthy cholesterol levels by reducing the oxidation of low-density lipoproteins (LDL). The phytosterols in sesame further support heart health by inhibiting the absorption of dietary cholesterol. Regular intake of sesame seeds or oil has been linked to lower blood pressure and improved arterial function, making it a heart-friendly addition to the diet.
Digestive Health and Gut Function
Sesame is rich in dietary fiber, which is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system. The fiber content aids in regular bowel movements and prevents constipation, thereby promoting a healthy gut microbiota. In addition, the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of sesame help soothe the gastrointestinal tract, reduce irritation, and support overall digestive efficiency.
Skin and Hair Nourishment
Sesame oil is widely used in both traditional and modern cosmetic formulations due to its excellent emollient properties. Rich in vitamin E and essential fatty acids, sesame oil moisturizes and protects the skin from environmental damage. It also helps in promoting hair growth and reducing scalp irritations. The oil penetrates deeply into the skin, providing long-lasting hydration and improving overall skin texture and tone.
Bone Health and Mineral Support
Sesame seeds are an outstanding source of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, which are crucial for maintaining strong bones and teeth. This mineral-rich profile not only supports skeletal health but also contributes to proper muscle function and overall metabolic balance. Regular inclusion of sesame in the diet is particularly beneficial for individuals at risk for osteoporosis.
Immune System Enhancement
The combination of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals present in sesame supports a robust immune system. Vitamin E, along with the array of polyphenols, helps protect immune cells from oxidative damage, thereby improving their functionality. Regular consumption of sesame can help fortify the body’s natural defenses against infections and illnesses.
Metabolic and Energy Support
Sesame seeds provide a rich source of healthy fats and proteins, making them an excellent addition to an energy-boosting diet. The balanced composition of essential fatty acids and B vitamins contributes to optimal metabolism and sustained energy levels. This makes sesame beneficial not only for physical activity but also for overall vitality and endurance.
Synergistic Holistic Wellness
When taken as a part of a balanced diet, sesame contributes to holistic well-being by supporting multiple body systems simultaneously. The cumulative effects of its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, cardiovascular, digestive, and skin-nourishing properties establish sesame as a cornerstone of natural health care. Its multifaceted benefits extend beyond isolated functions, promoting comprehensive health and vitality.
In summary, the health-promoting attributes of sesame are rooted in its unique chemical composition. Whether consumed as whole seeds, oil, or supplements, sesame provides extensive benefits that support antioxidant defense, cardiovascular health, digestive function, skin integrity, and overall well-being.
Applications and Precautions
Sesame is not only celebrated for its health benefits but is also remarkably versatile in its applications. It is employed in culinary, medicinal, and cosmetic domains, each offering unique ways to harness its nutritional and therapeutic potential. In this section, we provide guidance on various uses of sesame along with important precautions for safe consumption and application.
Culinary Applications
- Whole Seeds:
Sesame seeds can be sprinkled on salads, added to baked goods (such as breads, muffins, and crackers), and used as a topping for dishes to enhance flavor and nutrition. Their nutty taste and crunch make them a popular ingredient in both savory and sweet preparations. - Sesame Oil:
Extracted from sesame seeds, this oil is a staple in many Asian cuisines. Its robust flavor is ideal for stir-frying, salad dressings, marinades, and even drizzling over cooked dishes. Sesame oil is also renowned for its stability and long shelf-life due to natural antioxidants. - Sesame Paste (Tahini):
Tahini is made by grinding sesame seeds into a smooth paste and is a key ingredient in Middle Eastern recipes like hummus and baba ganoush. It offers a creamy texture and rich flavor, as well as a concentrated dose of sesame’s beneficial nutrients. - Beverages and Smoothies:
Sesame seeds and sesame oil can be blended into smoothies or added to health drinks to boost their nutritional profile. Their inclusion provides healthy fats and essential vitamins that complement other ingredients.
Medicinal Applications
- Dietary Supplements:
Sesame is available in capsule or tablet form as an extract, which concentrates its bioactive compounds for enhanced therapeutic effects. Such supplements aim to support cardiovascular health, boost antioxidant levels, and promote overall vitality. - Herbal Remedies:
Traditional herbalists often prepare decoctions or infusions from toasted sesame seeds to soothe digestive issues and inflammatory conditions. These remedies are usually consumed on a short-term basis to alleviate specific symptoms like indigestion or joint pain. - Topical Applications:
Sesame oil is extensively used in cosmetics and skincare. Applied directly to the skin, it helps moisturize and nourish, reducing dryness and signs of aging. It is also used in massage oils due to its ability to penetrate deeply into the skin and provide long-lasting hydration.
Dosage Guidelines
- Whole Seeds:
A typical serving size is about 1–2 tablespoons per day, either consumed alone or sprinkled on food. - Sesame Oil:
For culinary and health purposes, 1–2 teaspoons per serving is sufficient. For topical use, a small amount applied to the skin is generally effective. - Dietary Supplements:
Always follow the dosage recommended on the product label, as concentrations can vary across different brands. - Herbal Preparations:
If preparing an infusion or decoction, use approximately 1–2 teaspoons of toasted sesame seeds per cup of boiling water, steeped for 10–15 minutes.
Safety Considerations and Precautions
While sesame is widely recognized for its benefits, it is essential to consider the following precautions:
- Allergic Reactions:
Sesame is among the top food allergens. Individuals with known sesame allergies should avoid all forms of sesame. Symptoms can range from mild skin rashes to severe anaphylactic reactions. - Digestive Sensitivity:
In some cases, high intake of sesame seeds or oil might cause gastrointestinal discomfort. Moderation is key, and individuals experiencing adverse effects should reduce their consumption. - Interaction with Medications:
Although sesame is natural, it may interact with certain medications, particularly those affecting blood clotting or cholesterol levels. Consult with a healthcare provider if you are on prescription medications. - Caloric Density:
Sesame seeds and oil are calorie-dense. Overconsumption may lead to an unintended increase in calorie intake, especially if incorporated frequently into the diet.
Integration into a Healthy Lifestyle
To maximize the benefits of sesame while minimizing any risks, consider these tips:
- Balanced Diet:
Incorporate sesame into a varied diet that emphasizes fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. This approach ensures you obtain a broad range of nutrients. - Hydration:
Adequate water intake complements the high fiber content of sesame seeds, aiding digestion and preventing constipation. - Moderation:
Use sesame in moderation as part of a comprehensive nutritional strategy rather than as a sole focus of your diet. - Consultation:
Particularly if you have any underlying health conditions or dietary restrictions, consult a nutritionist or healthcare provider to tailor sesame consumption to your needs.
In conclusion, sesame offers diverse applications that extend from the kitchen to the medicine cabinet and the beauty shelf. By adhering to proper dosage guidelines and taking necessary precautions, you can safely enjoy the extensive health benefits of sesame.
Research Insights and Study Highlights
A robust body of scientific research supports the traditional uses of sesame, underscoring its broad spectrum of health benefits. The following studies highlight key findings regarding sesame’s efficacy and mechanisms of action:
- Antioxidant Capacity and Cellular Protection (2012):
A study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry demonstrated that sesame seed extracts exhibit significant antioxidant activity, primarily attributed to sesamin, sesamolin, and sesamol. The research showed that these compounds protect cells from oxidative damage and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular disorders. - Cardiovascular Health and Lipid Regulation (2014):
Research featured in Nutrition Research investigated the effects of sesame oil on lipid profiles and blood pressure. Results indicated that regular consumption of sesame oil significantly lowered LDL cholesterol levels, increased HDL cholesterol, and improved arterial function, supporting its role in heart health. - Anti-Inflammatory and Immune-Modulating Effects (2016):
A controlled trial published in Phytotherapy Research examined the anti-inflammatory properties of sesame extracts. The study found that the polyphenols and lignans in sesame effectively reduced markers of inflammation, suggesting potential benefits for individuals with inflammatory conditions such as arthritis and gastrointestinal disorders. - Digestive Health and Gut Microbiota (2018):
A study in Food & Function highlighted that the dietary fiber and bioactive compounds in sesame positively influence gut microbiota composition. Improved gut health was linked to better digestion, enhanced nutrient absorption, and reduced gastrointestinal inflammation, underscoring the importance of sesame in maintaining a healthy digestive system. - Skin Health and Anti-Aging Benefits (2019):
An investigation published in Cosmetic Science and Technology explored the dermatological benefits of sesame oil. The findings revealed that sesame oil’s high tocopherol (vitamin E) content and antioxidants help protect the skin from UV damage, reduce signs of aging, and improve hydration, affirming its utility in cosmetic formulations. - Synergistic Effects in Nutraceutical Formulations (2021):
A multi-center study in the Journal of Functional Foods examined the synergistic action of sesame with other natural ingredients in nutraceutical products. The research demonstrated that when combined, these ingredients produced enhanced health benefits—improving antioxidant status, cardiovascular health, and metabolic markers more effectively than when used individually.
Collectively, these studies validate the traditional knowledge surrounding sesame by providing scientific evidence for its myriad health benefits. The ongoing research continues to reveal new insights into its mechanisms of action and potential applications, paving the way for innovative dietary supplements and therapeutic formulations.
Frequently Asked Questions about Sesame
What are the primary health benefits of sesame?
Sesame is well-known for its potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cardioprotective properties. Its lignans, such as sesamin and sesamolin, help lower cholesterol and protect cells from oxidative damage, while its high fiber content supports healthy digestion.
How can sesame be incorporated into the diet?
Sesame can be consumed in various forms: whole seeds sprinkled on dishes, as cold-pressed oil for cooking or dressings, or in the form of tahini, a paste used in sauces and spreads. It is also available as dietary supplements.
What active compounds in sesame contribute to its health effects?
Key compounds include sesamin, sesamolin, and sesamol—powerful lignans responsible for antioxidant and lipid-regulating benefits. Additionally, sesame contains polyunsaturated fatty acids, tocopherols (vitamin E), and phenolic acids that enhance its overall therapeutic profile.
Are there any side effects of consuming sesame?
For most people, sesame is safe when consumed in moderate amounts. However, sesame is a known allergen for some individuals, and excessive intake may lead to digestive discomfort. People with allergies or specific health conditions should consult their healthcare provider.
How does sesame contribute to heart health?
Sesame’s lignans and phytosterols help lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL levels, while its antioxidants protect blood vessels from oxidative stress. These combined effects support improved cardiovascular function and reduced risk of heart disease.
Can sesame improve skin and hair health?
Yes, sesame oil is highly valued in skincare for its moisturizing and anti-aging properties due to high levels of vitamin E and antioxidants. It nourishes the skin and hair, protecting them from environmental damage and promoting a healthy appearance.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider before beginning any new herbal regimen.
Please feel free to share this article on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or your preferred social network, and follow us on social media for more insights into natural health remedies.