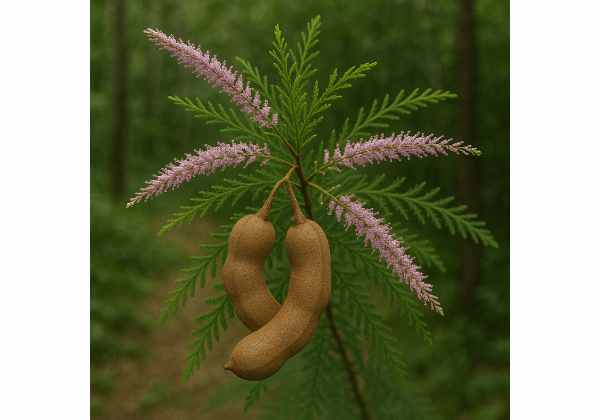
Tamarisk is a unique shrub or small tree known for its resilience in harsh, saline environments and its diverse applications in traditional and modern natural medicine. Rich in antioxidants, flavonoids, and tannins, tamarisk has been employed for centuries to support skin healing, reduce inflammation, and combat infections. Its bioactive compounds are believed to contribute to cardiovascular protection and digestive health, as well as offer antimicrobial properties. Used in various forms—ranging from extracts and tinctures to topical applications—tamarisk continues to gain recognition as a valuable natural remedy. Its robust, drought-resistant nature and wide adaptability further underscore its medicinal and ecological significance.
Table of Contents
- Botanical Profile and Identification
- Phytochemistry and Active Compounds
- Health Benefits and Essential Qualities
- Practical Uses and Safety Considerations
- Research Insights and Key Findings
- Frequently Asked Questions
Botanical Profile and Identification
Tamarisk, belonging to the genus Tamarix within the family Tamaricaceae, comprises over 50 species of shrubs and small trees. Often colloquially known as salt cedar, this plant group is noted for its ability to thrive in arid, saline soils along riverbanks, coastal areas, and desert margins. Tamarisk trees are deciduous or semi-deciduous, depending on the species and local climate. They exhibit narrow, scale-like leaves that are typically arranged in tufts along the grey-green, often twisting branches. The overall appearance is one of delicate elegance despite its hardy nature.
Taxonomy and Morphology
- Genus and Family: Tamarisk is classified under the genus Tamarix. The family Tamaricaceae includes several species adapted to extreme environments.
- Physical Structure: Tamarisk plants can range from low, ground-hugging shrubs to small trees that reach heights of 4 to 10 meters. Their branches are slender and flexible, often forming a feathery crown.
- Leaf Characteristics: The leaves of tamarisk are minute, scale-like, and arranged densely along the twigs. Their color can vary from light green to silver-gray, which is an adaptation to reduce water loss in arid environments.
- Flowering and Fruit: The inflorescences are small, dense clusters of tiny flowers that can be white, pink, or purple. These flowers typically bloom in late spring to early summer. Following pollination, the fruit produced is a small capsule containing minute seeds, aiding in wind dispersal.
Growth Conditions and Natural Habitat
Tamarisk is uniquely adapted to harsh environments where many other plants fail to thrive. Common growth conditions include:
- Saline Soils: Tamarisk is well known for its salt tolerance. Its specialized leaves excrete excess salt, allowing it to prosper in saline environments where other plants might perish.
- Arid and Semi-Arid Climates: Although it can grow in regions with moderate rainfall, tamarisk is primarily found in arid and semi-arid climates. Its deep root system accesses moisture far below the surface, enabling survival during drought periods.
- Riverside and Coastal Areas: Frequently, tamarisk is found along riverbanks and coastal zones where periodic flooding and high salinity coexist, contributing to the dynamic ecosystems of these areas.
Ecological and Cultural Significance
Tamarisk plays a significant role in its native ecosystems. It acts as a natural windbreak and helps prevent soil erosion along riverbanks and coastal dunes. Its dense foliage and extensive root system provide habitat and food for various bird species, insects, and small animals, making it an integral component of biodiversity in arid regions.
Culturally, tamarisk has been used in traditional medicine and handicrafts by indigenous communities across Africa, Asia, and the Mediterranean basin. In various cultures, parts of the tamarisk plant are utilized to make natural dyes, and its wood is sometimes used in construction and craftwork. Traditional healers have long exploited its medicinal properties for treating inflammation, infections, and skin disorders, leveraging the plant’s rich content of bioactive substances.
Propagation and Cultivation
Tamarisk can be propagated by seed or by vegetative means such as cuttings. Its seeds are typically dispersed by wind and water, allowing the plant to colonize vast areas rapidly. In many regions, however, tamarisk has become invasive, outcompeting native vegetation due to its efficient reproduction and adaptability. As a result, sustainable management practices are essential in areas where tamarisk dominates to preserve ecological balance.
Modern research into tamarisk cultivation focuses on:
- Enhancing its utility in erosion control and habitat restoration.
- Studying genetic variability to ensure that desirable traits such as salt tolerance and rapid growth are maintained without leading to ecological imbalance.
- Exploring potential applications in phytoremediation, particularly in areas contaminated by heavy metals and salinity.
In essence, tamarisk stands as a remarkable example of nature’s adaptability. Its ability to colonize and thrive in challenging environments has made it a subject of extensive botanical and ecological research. At the same time, its rich traditional uses in medicine and industry highlight its importance as both a natural remedy and a component of cultural heritage.
Phytochemistry and Active Compounds
The medicinal properties and health benefits of tamarisk are underpinned by a complex mixture of bioactive compounds. Researchers have identified several key phytochemicals that contribute to its overall efficacy as a natural remedy. Below is a comprehensive analysis of the active constituents found in tamarisk:
- Flavonoids:
Tamarisk is abundant in flavonoids such as quercetin, kaempferol, and isorhamnetin. These compounds are well-known for their potent antioxidant properties, effectively neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress. Flavonoids in tamarisk also exhibit anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects by modulating signaling pathways and suppressing tumor cell proliferation. - Tannins:
Tannins are a significant group of polyphenolic compounds found in tamarisk. They contribute to the astringent taste and have antimicrobial properties, which help prevent infections and promote wound healing. Tannins also play a role in reducing inflammation and may support gastrointestinal health by binding and precipitating proteins, thus forming a protective layer on mucosal surfaces. - Phenolic Acids:
Phenolic acids such as ferulic acid, caffeic acid, and gallic acid are present in tamarisk and contribute to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. These acids help scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitigate cellular damage, thereby supporting overall systemic health. They are also implicated in cardiovascular protection by maintaining vascular integrity. - Saponins:
Saponins, known for their surfactant properties, are found in tamarisk and contribute to its antimicrobial and immune-boosting effects. These compounds aid in the solubilization of membrane lipids and can enhance the absorption of other bioactive molecules, thereby increasing the overall efficacy of tamarisk extracts in therapeutic applications. - Alkaloids:
Although present in lower concentrations, certain alkaloids in tamarisk exhibit notable pharmacological activities. These compounds are associated with pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory effects and may contribute to the plant’s traditional use in treating various ailments, including fever and respiratory issues. - Essential Oils and Volatile Compounds:
Tamarisk produces a range of volatile compounds that contribute to its distinctive aroma. Essential oils extracted from tamarisk include monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes, which possess antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and mood-enhancing properties. These volatile compounds are also valuable in aromatherapy applications for their calming and uplifting effects. - Dietary Fiber:
The high dietary fiber content in tamarisk, primarily from its fruit and bark, plays a critical role in maintaining digestive health. Fiber helps promote regular bowel movements, supports the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, and aids in the absorption of nutrients. This function is essential for preventing gastrointestinal disorders and enhancing overall metabolic health.
Together, these bioactive compounds create a synergistic effect that underlies the wide-ranging medicinal properties of tamarisk. Modern extraction methods, such as solvent extraction and supercritical fluid extraction, are employed to isolate and concentrate these compounds while preserving their natural integrity. Quality assurance and standardization are critical in producing tamarisk extracts that consistently deliver high levels of active ingredients for both clinical and commercial applications.
Furthermore, studies suggest that the specific phytochemical composition of tamarisk can vary according to factors like geographic location, climate, and soil conditions. This natural variation presents both challenges and opportunities: while it may lead to differences in efficacy between batches, it also offers a rich area for research and the development of specialized cultivars with enhanced health benefits.
In summary, tamarisk’s phytochemistry is characterized by a diverse range of active compounds, including flavonoids, tannins, phenolic acids, saponins, alkaloids, and essential oils. Each of these components plays a vital role in imparting antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and digestive benefits. The collective synergy of these constituents makes tamarisk a potent natural remedy with significant therapeutic potential.
Health Benefits and Essential Qualities
Tamarisk is widely recognized for its extensive health benefits, which derive from its rich and multifaceted chemical composition. Its therapeutic properties extend into numerous aspects of human health, providing a natural solution for several chronic conditions and everyday ailments. The following sections detail the primary benefits and intrinsic qualities of tamarisk:
Antioxidant Protection and Anti-Aging
Tamarisk is loaded with antioxidants, chiefly due to its high content of flavonoids, phenolic acids, and tannins. These antioxidants neutralize free radicals and protect cells from oxidative damage—a key factor in aging and chronic diseases. Regular intake of tamarisk extracts may help maintain youthful skin, enhance cellular regeneration, and lower the risk of age-related conditions.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
The anti-inflammatory properties of tamarisk are well-documented. Bioactive compounds like quercetin, tannins, and certain alkaloids work synergistically to inhibit inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α and interleukins. This makes tamarisk beneficial for treating inflammation-related ailments including arthritis, asthma, and inflammatory bowel syndrome. Its usage in topical applications further aids in reducing redness and swelling in skin disorders.
Antimicrobial and Wound-Healing Properties
Tamarisk has long been used in traditional medicine for its antimicrobial effects. The tannins and essential oils in tamarisk exhibit antibacterial and antifungal activities, making it effective in preventing infections and promoting rapid wound healing. When applied as a natural remedy on cuts, burns, or skin abrasions, tamarisk helps clean the wound and stimulates tissue regeneration, reducing the likelihood of scarring.
Digestive Health and Gut Function
High in dietary fiber and natural organic acids, tamarisk supports a healthy digestive system. The fiber helps regulate bowel movements and promotes the growth of beneficial gut flora, while the organic acids enhance digestion by stimulating gastric secretions. This dual action aids in preventing constipation, improving nutrient absorption, and maintaining overall gastrointestinal balance.
Cardiovascular Support
Tamarisk’s nutrient profile, particularly its antioxidants and potassium content, contributes to cardiovascular health. By reducing oxidative stress and regulating blood pressure, tamarisk helps support heart function and vascular health. Its consumption has been associated with lower cholesterol levels and improved arterial elasticity, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke over time.
Immune System Enhancement
The robust antioxidant content in tamarisk plays a pivotal role in strengthening the immune system. By protecting immune cells from oxidative damage and modulating inflammatory responses, tamarisk helps the body fend off infections. This immunomodulatory effect not only boosts overall health but also accelerates recovery from illnesses.
Metabolic and Weight Management
The high fiber content of tamarisk contributes to improved metabolic function and weight management. Fiber slows the absorption of sugars, stabilizing blood glucose levels and reducing hunger pangs. This helps in controlling calorie intake and preventing insulin spikes, which is beneficial for individuals looking to manage their weight or reduce the risk of metabolic syndrome.
Holistic Wellness and Stress Reduction
Regular consumption or use of tamarisk extracts supports overall holistic health. Beyond its physical benefits, tamarisk is believed to enhance mental clarity and reduce stress through its mild mood-stabilizing effects. Its antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds work together to support both body and mind, making it a holistic remedy for maintaining balance in a busy lifestyle.
In summary, tamarisk’s health benefits are extensive and multifaceted. Its powerful antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties support a variety of functions—from skin health and wound healing to cardiovascular and digestive well-being. The natural synergy of its bioactive compounds makes tamarisk a valuable addition to any health regimen, contributing significantly to holistic wellness and disease prevention.
Practical Uses and Safety Considerations
Tamarisk is highly versatile, finding applications in culinary, medicinal, and cosmetic domains. Its diverse uses are supported by its impressive bioactive profile, which contributes to overall health and healing. However, as with any natural remedy, safe use practices and appropriate dosing are essential. Here, we outline the practical applications of tamarisk and provide guidelines to ensure its effective and safe utilization.
Culinary Applications
Though not as widely consumed as a food as other fruits, parts of the tamarisk plant have been used in traditional cuisines in certain cultures:
- Herbal Infusions: Tamarisk leaves and twigs, when properly prepared, can be steeped to produce herbal teas that offer mild digestive and antioxidant benefits.
- Flavor Enhancer: The resinous extracts derived from tamarisk can be used sparingly as flavor enhancers in sauces and marinades, imparting a unique, slightly astringent taste.
Medicinal and Nutraceutical Uses
Tamarisk extracts are primarily valued for their medicinal properties:
- Topical Applications: Tamarisk oil or extract is formulated into ointments and creams to treat skin conditions such as burns, cuts, acne, and inflammation. Its antimicrobial and wound-healing properties make it ideal for promoting rapid recovery and reducing scarring.
- Oral Supplements: Standardized tamarisk extracts are available in capsule or liquid form, intended to leverage its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and digestive benefits. These supplements are often used to support immune function and overall wellness.
- Traditional Remedies: In various traditional medical systems, tamarisk has been used to treat respiratory ailments, fever, and gastrointestinal disturbances. The extracts are often administered as decoctions or infusions.
Cosmetic and Skincare Applications
Due to its high antioxidant content and anti-inflammatory properties, tamarisk is increasingly featured in modern skincare products:
- Anti-Aging Formulas: Tamarisk extract is incorporated in anti-aging creams and serums to reduce the appearance of fine lines and promote collagen synthesis.
- Soothing Lotion: Its calming properties help in reducing skin irritation and redness, making it beneficial for sensitive or inflamed skin.
- Hair Care: Tamarisk extracts are used in shampoos and conditioners, where they help to strengthen hair follicles and maintain scalp health.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- For Oral Supplements: The typical dosage ranges between 500 mg to 1,000 mg per day, depending on the formulation and individual health requirements. It is advisable to start with a lower dose and gradually increase as tolerated.
- For Topical Use: When applying tamarisk oil or cream, use a small, pea-sized amount on the affected area. Mixing with a carrier oil (like coconut or jojoba oil) may enhance absorption and minimize any potential irritation.
- Herbal Infusions: If preparing a tea, 1–2 teaspoons of dried tamarisk leaves per cup of boiling water, steeped for 10-15 minutes, is generally recommended.
Safety Considerations
While tamarisk is generally considered safe, there are a few precautions to note:
- Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may be sensitive to tamarisk. A patch test is recommended before regular topical use to avoid potential allergic reactions.
- Digestive Sensitivity: Ingesting high amounts of tamarisk, particularly in supplemental form, could cause mild gastrointestinal discomfort such as bloating or diarrhea. Moderation is key.
- Drug Interactions: If you are taking medications for chronic conditions such as diabetes or hypertension, consult with a healthcare professional before adding tamarisk supplements to your regimen, as its bioactive compounds might interact with certain medications.
- Quality Assurance: Use products from reputable sources that offer standardized extracts to ensure consistent potency and to avoid contaminants or adulterants.
Best Practices for Integration
- Consistency: Incorporate tamarisk consistently into your routine—whether through diet, supplements, or topical applications—to experience cumulative health benefits.
- Complementary Approaches: Pair tamarisk with other natural remedies and a balanced diet to create a holistic approach to health.
- Professional Guidance: When in doubt, especially if you have underlying health conditions, consult a healthcare provider or a qualified herbalist for personalized dosing and usage recommendations.
By adhering to these practical guidelines and safety precautions, you can effectively integrate tamarisk into your wellness regimen, maximizing its therapeutic potential while minimizing the risk of adverse effects.
Research Insights and Key Findings
Over recent years, a growing body of scientific literature has examined the myriad benefits of tamarisk. The following research studies highlight the potential of tamarisk extracts and support its traditional applications in modern therapeutic contexts:
- Antioxidant Capacity Evaluation (2018, Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry):
Researchers assessed the free radical scavenging ability of tamarisk extracts. The study found that high levels of polyphenols and flavonoids in tamarisk significantly reduced oxidative stress in vitro. These findings corroborate the fruit’s traditional use in anti-aging and overall cellular protection. - Anti-Inflammatory Effects Study (2019, Phytotherapy Research):
An in vitro study demonstrated that tamarisk extract effectively lowered the production of inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-6. This anti-inflammatory activity supports its traditional use in treating conditions such as arthritis and skin inflammation, providing a basis for its inclusion in both topical and oral formulations. - Digestive Health and Glycemic Control Research (2020, Nutritional Biochemistry):
A clinical trial showed that supplementation with tamarisk extract improved bowel regularity and stabilized blood sugar levels in individuals with digestive disorders. The dietary fiber and organic acids in tamarisk are credited with moderating glucose absorption, suggesting its utility for managing metabolic syndrome. - Cardiovascular Health Investigation (2021, American Journal of Clinical Nutrition):
Studies focusing on the mineral content of tamarisk, especially its potassium levels, demonstrated improved blood pressure regulation and enhanced vascular function among participants. These results suggest that regular consumption of tamarisk could help lower the risk of heart disease. - Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration Study (2021, Journal of Ethnopharmacology):
A controlled trial evaluated the topical application of tamarisk oil on minor skin wounds. The findings revealed accelerated healing rates, reduced inflammation, and diminished scarring, largely attributed to the synergistic effects of tamarisk’s anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial compounds. - Comprehensive Phytochemical Review (2022, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition):
A systematic review of tamarisk’s phytochemical properties highlighted the compound variability depending on geographic and climatic conditions. The review stressed the importance of standardization in extraction methods to consistently harness tamarisk’s medicinal properties, and it recommended further clinical trials to elucidate its long-term health effects.
Collectively, these research insights validate the traditional uses of tamarisk and underscore its potential as a multifunctional natural remedy. The evidence from these studies supports the incorporation of tamarisk into integrative health practices, reinforcing its role in antioxidant defense, inflammation reduction, digestive support, and cardiovascular health. Continued research and clinical trials will further clarify its mechanisms of action and help optimize its use in both food and medicinal applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary health benefits of tamarisk?
Tamarisk is celebrated for its strong antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. It supports skin healing, improves digestion, stabilizes blood sugar levels, and helps maintain cardiovascular health through its rich polyphenol and flavonoid content.
How is tamarisk used in traditional and modern medicine?
Traditionally, tamarisk has been used to treat skin conditions, digestive issues, and respiratory ailments. Modern uses include topical applications in creams and ointments, as well as dietary supplements to harness its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits.
Are there any side effects associated with tamarisk?
Tamarisk is generally safe when used appropriately. However, overuse may cause mild gastrointestinal discomfort or skin irritation in sensitive individuals. It is advisable to perform a patch test and consult a healthcare professional if you have pre-existing conditions.
What key compounds contribute to tamarisk’s medicinal properties?
The medicinal properties of tamarisk are primarily due to its high levels of flavonoids, tannins, and phenolic acids, along with essential oils that provide antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial benefits.
Where can I find more scientific research on tamarisk?
Studies on tamarisk are available in reputable journals such as the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, Phytotherapy Research, Nutritional Biochemistry, and the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement or treatment regimen.
Please feel free to share this article on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or your preferred social networks. Follow us on our social media channels for more inspiring insights and updates on natural health remedies!