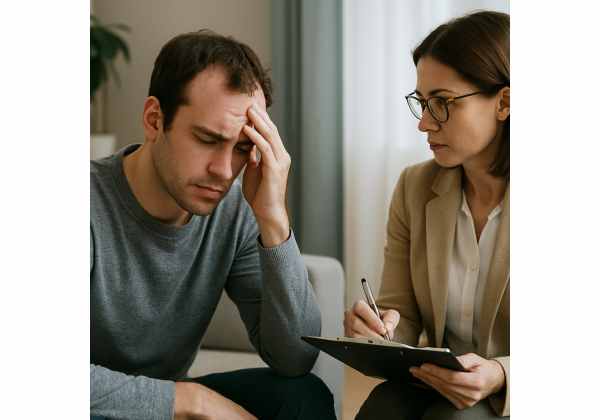
Psychasthenia is a psychological condition characterized by chronic, excessive worry, obsessions, and compulsions that interfere with daily functioning. Individuals often experience persistent, intrusive thoughts—such as fear of contamination or harm—and engage in repetitive behaviors or mental rituals to alleviate anxiety. First described by Pierre Janet in the late 19th century, psychasthenia overlaps with modern concepts of obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), yet retains distinct features of mental fatigue and indecisiveness. Early recognition and a nuanced understanding of underlying cognitive, neurobiological, and psychosocial factors are essential for effective intervention. This comprehensive guide explores the origins, presentation, risk contributors, diagnostic pathways, and evidence-based treatments for psychasthenia.
Table of Contents
- Exploring the Depths of Mental Fatigue
- Spotting Core Anxious and Compulsive Patterns
- Uncovering Vulnerabilities and Preventive Steps
- Navigating Diagnostic Assessments
- Crafting Management and Therapy Approaches
- Frequently Asked Questions
Exploring the Depths of Mental Fatigue
Psychasthenia derives from the Greek for “weakness of the psyche,” reflecting the overwhelming mental exhaustion patients feel when intrusive thoughts dominate their cognition. Unlike general anxiety, these individuals often report a relentless battle against their own minds—continuously checking, doubting, and analyzing even mundane decisions. Neuroimaging studies implicate hyperactivity in the cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical circuitry, mirroring findings in OCD, while HPA-axis dysregulation underscores chronic stress’s role. Janet’s original framework emphasized abnormal dissociation and impaired attention, elements still relevant today: many with psychasthenia struggle to sustain focus, feel indecisive, and endure persistent mental fatigue, even when overt compulsions are minimal.
Spotting Core Anxious and Compulsive Patterns
Key manifestations include:
- Intrusive Worries: Persistent doubts (e.g., “Did I lock the door?”) that recur despite reassurance.
- Ritualistic Behaviors: Checking, counting, or mental reviewing to neutralize anxiety.
- Indecisiveness: Difficulty making simple choices, leading to repeated rumination.
- Somatic Tension: Muscle aches, headaches, and fatigue stemming from prolonged arousal.
- Avoidance: Steering clear of situations that trigger obsessions, reinforcing anxiety cycles.
Uncovering Vulnerabilities and Preventive Steps
Risk contributors:
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history of OCD or anxiety disorders raises susceptibility.
- Neurochemical Imbalance: Serotonergic and dopaminergic dysregulation correlates with obsessional thinking.
- Traumatic Stress: Early-life stress sensitizes the HPA axis, amplifying later worry-proneness.
- Personality Traits: High harm-avoidance and perfectionism fuel psychasthenic patterns.
- Environmental Triggers: Chronic stressors—workplace, relationship pressures—can precipitate onset.
Preventive measures:
- Stress Management: Mindfulness, relaxation training, and regular exercise buffer HPA-axis activation.
- Early Intervention: Psychoeducation for at-risk individuals fosters adaptive coping before rituals solidify.
- Healthy Decision-Making Habits: Structured choice frameworks (pros/cons lists) minimize rumination.
Navigating Diagnostic Assessments
Accurate diagnosis blends clinical interview with standardized tools:
- Yale–Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (Y-BOCS): Measures obsession and compulsion severity.
- Obsessive–Compulsive Inventory–Revised (OCI-R): Self-report on specific symptom dimensions.
- Structured Clinical Interview (SCID): Rules out other anxiety or mood disorders.
- Neuropsychological Testing: Assesses attention, executive function, and processing speed to gauge mental fatigue’s impact.
Crafting Management and Therapy Approaches
Evidence-based interventions:
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Emphasizes exposure and response prevention (ERP) to break ritual cycles, combined with cognitive restructuring to challenge maladaptive beliefs.
- Pharmacotherapy: SSRIs (e.g., fluoxetine, sertraline) at OCD-level dosing; augmentation with atypical antipsychotics in resistant cases.
- Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT): Enhances decentering from intrusive thoughts, reducing reactivity.
- Stress-Reduction Techniques: Progressive muscle relaxation, biofeedback, and yoga support long-term resilience.
- Psychoeducation and Family Involvement: Equips support networks to reinforce adaptive behaviors and reduce family accommodation of rituals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What differentiates psychasthenia from general anxiety?
Psychasthenia centers on persistent, intrusive thoughts and compulsive mental rituals—beyond the broad worry spectrum of generalized anxiety—and often involves marked indecisiveness and mental exhaustion.
Can medication alone resolve psychasthenia?
Medication (SSRIs) can reduce obsessional thinking, but combining pharmacotherapy with CBT—especially ERP—is essential for sustained improvement and relapse prevention.
How long does therapy typically take?
Most patients see meaningful symptom reduction after 12–20 CBT sessions; ERP intensity and adherence predict speed of progress.
Are there lifestyle changes that help?
Regular physical exercise, structured daily routines, adequate sleep, and mindfulness practices bolster stress resilience and decrease obsessional urges.
Is psychasthenia curable?
While some individuals achieve full remission, many benefit from ongoing maintenance strategies—therapy booster sessions and stress management—to sustain gains and prevent relapse.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified mental health provider for personalized diagnosis and treatment.
If you found this guide helpful, please share it on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or your favorite platform—and follow us on social media for more mental health insights. Your support helps us continue producing quality content!