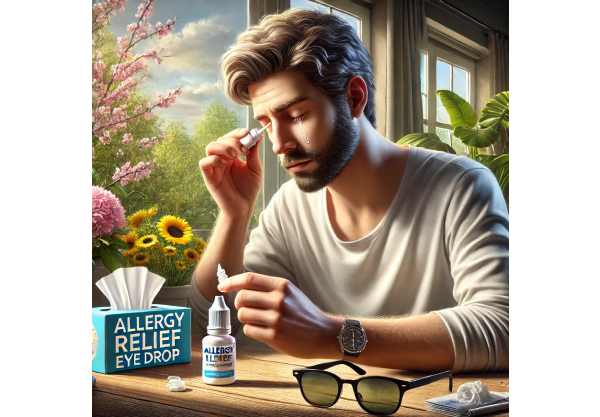
Allergy season can be a challenging time, especially for those who suffer from eye-related symptoms. The itchiness, redness, and watery eyes that accompany allergies can make daily activities uncomfortable and even unbearable. As the seasons change and allergens like pollen, dust, and mold spores fill the air, your eyes become prime targets for irritation. For many, this time of year can turn a beautiful spring day into a struggle to see clearly. But with the right strategies, you can protect your eyes from the worst of allergy season’s effects. In this guide, you’ll find practical, effective ways to care for your eyes and keep them healthy and comfortable during allergy season.
Understanding the Impact of Allergies on Your Eyes
Allergies can wreak havoc on your eyes, transforming a mild irritant into a daily challenge. Understanding how allergens affect your eyes is crucial to managing and preventing the discomfort they cause. Allergic conjunctivitis, commonly referred to as “eye allergies,” is a reaction that occurs when your eyes come into contact with allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or mold. This reaction can lead to inflammation, causing the hallmark symptoms of red, itchy, and watery eyes.
What Happens to Your Eyes During Allergy Season?
During allergy season, the immune system overreacts to harmless substances such as pollen or dust, treating them as threats. This overreaction triggers the release of histamines, which cause blood vessels in the eyes to swell and the eyes themselves to become red, itchy, and watery. This response is meant to flush out the perceived invaders, but it often leads to discomfort and irritation instead.
- Redness and Swelling: The blood vessels in the conjunctiva (the clear tissue covering the white part of your eye) become inflamed, leading to noticeable redness and swelling.
- Itchiness: The release of histamines also triggers intense itching, making it difficult to resist rubbing your eyes, which can worsen symptoms and lead to further irritation.
- Watery Eyes: The eyes may produce excess tears in an attempt to wash out the allergens, leading to constant tearing and blurred vision.
Common Triggers of Eye Allergies
To effectively care for your eyes during allergy season, it’s important to know what triggers your symptoms. Common eye allergy triggers include:
- Pollen: One of the most common triggers, pollen is released by trees, grasses, and weeds during specific times of the year, depending on the plant. It’s particularly prevalent in spring and fall.
- Dust Mites: These tiny creatures thrive in household dust and can be a year-round problem, but they often cause more issues in seasons where indoor air is less ventilated, like winter.
- Pet Dander: Proteins found in the skin flakes, urine, and saliva of pets can trigger eye allergies, especially if you’re in close contact with animals during certain times of the year.
- Mold Spores: Mold grows in damp areas and releases spores into the air, which can be a significant allergen, particularly in fall and during wet weather.
- Smoke and Pollution: Airborne irritants like cigarette smoke, car exhaust, and industrial pollution can exacerbate allergic symptoms, making the eyes more sensitive and inflamed.
The Difference Between Eye Allergies and Other Eye Conditions
It’s important to distinguish between allergic conjunctivitis and other eye conditions that may cause similar symptoms. Eye allergies are typically bilateral (affecting both eyes) and are associated with specific environmental triggers. In contrast, conditions like bacterial or viral conjunctivitis can cause similar symptoms but are usually accompanied by discharge and are often unilateral (affecting one eye more than the other). Understanding the difference ensures that you take the correct steps to manage your symptoms effectively.
Effective Strategies for Protecting Your Eyes During Allergy Season
Caring for your eyes during allergy season requires a combination of preventive measures and symptom management. By adopting specific strategies, you can reduce the severity of your symptoms and protect your eyes from further irritation.
1. Minimize Exposure to Allergens
Reducing your exposure to allergens is the first and most important step in managing eye allergies. While it’s impossible to completely avoid allergens, especially pollen, there are several practical steps you can take to limit your contact with them.
Stay Indoors During Peak Pollen Times
Pollen levels tend to be highest in the early morning and late afternoon. During these times, try to stay indoors as much as possible. Keep windows closed to prevent pollen from entering your home, and use air conditioning instead of fans, as fans can circulate pollen inside.
Use Air Purifiers
Investing in a high-quality air purifier with a HEPA filter can significantly reduce the concentration of allergens in your home. Place air purifiers in the rooms where you spend the most time, particularly the bedroom, to create a safe space where you can breathe more easily.
Clean Regularly to Reduce Dust and Mold
Regular cleaning is essential to minimize dust mites and mold spores in your home. Vacuum carpets, rugs, and upholstered furniture frequently using a vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter. Wash bedding in hot water at least once a week to kill dust mites. In damp areas like bathrooms, kitchens, and basements, use a dehumidifier to keep moisture levels low, and clean mold-prone areas with a bleach solution to prevent mold growth.
Limit Outdoor Activities
During peak allergy season, it’s wise to limit your outdoor activities, especially on windy days when pollen and other allergens are more likely to be in the air. If you need to be outside, consider wearing wraparound sunglasses to protect your eyes from airborne particles, and shower immediately after returning indoors to wash away any allergens clinging to your skin and hair.
2. Implement Proper Eye Hygiene
Maintaining good eye hygiene can significantly reduce the risk of irritation and infection during allergy season. Simple daily practices can go a long way in keeping your eyes clean and comfortable.
Avoid Rubbing Your Eyes
One of the most challenging but important habits to break is rubbing your eyes when they itch. Rubbing can worsen inflammation, spread allergens further into your eyes, and even cause damage to the cornea. Instead of rubbing, use a cool, damp cloth over your eyes to soothe itching.
Use Artificial Tears
Artificial tears are a great way to flush out allergens and provide moisture to irritated eyes. Use preservative-free artificial tears, which can be applied multiple times throughout the day. These eye drops not only help to wash out allergens but also create a protective barrier on the surface of your eyes, reducing discomfort.
Wash Your Face and Hands Regularly
Washing your face and hands frequently helps remove pollen, dust, and other allergens that can accumulate throughout the day. Pay special attention to your eyelids and eyelashes, where allergens can easily collect. Washing your face before bed is particularly important to remove any allergens that could irritate your eyes while you sleep.
Cold Compresses for Relief
If your eyes are particularly swollen and irritated, applying a cold compress can provide immediate relief. Simply soak a clean cloth in cold water, wring it out, and place it over your closed eyes for several minutes. The cold temperature constricts blood vessels, reducing swelling and providing soothing relief.
3. Medications and Treatments to Manage Symptoms
When preventive measures and hygiene practices aren’t enough to keep symptoms at bay, medications can be a helpful addition to your allergy management plan. There are various over-the-counter and prescription options available that can alleviate eye allergy symptoms effectively.
Over-the-Counter Antihistamine Eye Drops
Antihistamine eye drops are designed to reduce itching and redness by blocking the action of histamines, the chemicals in your body that cause allergic reactions. These drops can provide quick relief, but they should be used according to the instructions, as overuse can sometimes lead to rebound redness.
Prescription Eye Drops
For more severe symptoms, your doctor may prescribe stronger eye drops, such as corticosteroids or mast cell stabilizers. Corticosteroids are highly effective at reducing inflammation, but they are typically used for short periods due to potential side effects. Mast cell stabilizers prevent the release of histamines and other chemicals that contribute to allergic reactions and are often used as a preventive treatment throughout allergy season.
Oral Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines can be helpful in managing both eye symptoms and other allergy symptoms, such as sneezing and nasal congestion. However, some oral antihistamines can cause dry eyes as a side effect, so it’s important to balance their use with other moisturizing treatments like artificial tears.
Allergy Shots (Immunotherapy)
For those who suffer from severe and persistent allergies, allergy shots (immunotherapy) may be an option. This treatment involves receiving regular injections of small amounts of allergens to gradually build up your tolerance. Over time, immunotherapy can reduce the severity of allergic reactions, including eye symptoms.
4. Long-Term Strategies for Eye Health During Allergy Season
While managing symptoms during allergy season is important, adopting long-term strategies can help improve your overall eye health and reduce the impact of future allergy seasons.
Regular Eye Checkups
Seeing an eye doctor regularly can help you stay on top of your eye health, especially if you suffer from seasonal allergies. Your doctor can provide tailored advice and prescribe treatments to keep your eyes healthy year-round.
Maintain a Healthy Diet
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can support overall eye health and reduce inflammation. Foods like spinach, kale, and salmon are particularly beneficial for maintaining healthy eyes. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water helps keep your eyes moist and less susceptible to irritation.
Practice Good Overall Health Habits
Healthy lifestyle choices such as regular exercise, not smoking, and managing stress can have a positive impact on your immune system and overall well-being. A strong immune system is better equipped to handle allergic reactions and reduce the severity of symptoms.