Ferula is a fascinating and historically significant herb known for its aromatic resin, potent bioactive ingridients, and wide-ranging therapeutic applications. Belonging to the Apiaceae family, Ferula encompasses a group of plants that have been used in traditional medicine for millennia. Among its many species, Ferula assafoetida—often called asafoetida—stands out for its distinctive pungent smell and powerful medicinal properties. Used extensively in Ayurvedic, Persian, and Unani medicine, Ferula has been cherished for its ability to support digestion, reduce inflammation, and act as a natural antimicrobial and expectorant.
In culinary traditions, the resin extracted from Ferula is valued as a spice that lends a unique flavor to dishes, particularly in Indian and Middle Eastern cuisines. Beyond the kitchen, modern research is beginning to confirm many of the traditional uses of Ferula, shedding light on its complex phytochemical profile and its role in promoting overall health.
- Supports healthy digestion and relieves gas and bloating
- Provides anti-inflammatory and analgesic benefits
- Acts as a natural antimicrobial and expectorant
- Enhances respiratory function and helps clear congestion
- Contains potent antioxidants that protect against cellular damage
- Serves as a valuable spice that enriches the flavor of traditional dishes
Table of Contents
- Ferula Botanical Profile: Taxonomic Overview and Visual Characteristics
- Ferula Historical Overview: Ancient Uses and Cultural Legacy
- Ferula Phytochemical Profile: Key Active Ingridients and Bioactives
- Ferula Health Benefits: Therapeutic Properties and Functional Advantages
- Ferula Uses and Safety: Culinary Applications and Usage Guidelines
- Ferula Research Highlights: Notable Studies and Scientific Evaluations
- Ferula FAQs: Common Questions and Concise Answers
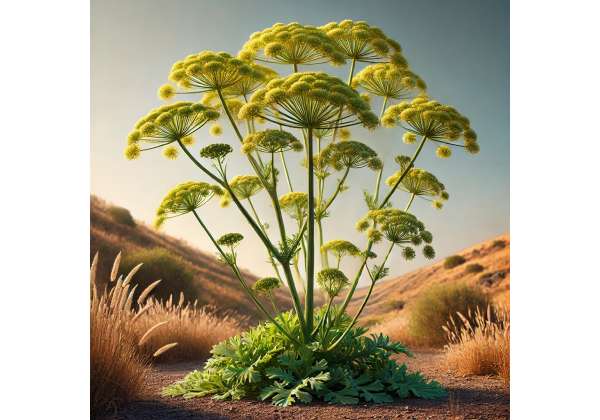
Ferula Botanical Profile: Taxonomic Overview and Visual Characteristics
Ferula is a genus of flowering plants within the Apiaceae family, widely known for its resinous exudate. One of the most famous species is Ferula assafoetida, the source of asafoetida—a spice and traditional remedy prized for its intense aroma and medicinal qualities. These plants typically have large, robust stems and umbels of small, yellowish flowers that contribute to their distinctive appearance.
Taxonomic Classification
Ferula’s classification is as follows:
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Clade: Angiosperms
- Clade: Eudicots
- Order: Apiales
- Family: Apiaceae
- Genus: Ferula
- Species: Notable species include Ferula assafoetida, among others
This taxonomic placement highlights Ferula’s relationship with other aromatic and medicinal herbs in the Apiaceae family, such as carrots, parsley, and celery.
Morphological Characteristics
Ferula plants are known for several distinctive traits:
- Stems:
They produce large, erect, and often woody stems that can reach impressive heights. These sturdy stems support the plant’s heavy foliage and secreted resins. - Leaves:
The leaves are typically compound and pinnate, with a rough texture and a deep green hue. Their structure allows for efficient photosynthesis and contributes to the plant’s resilience in various environments. - Flowers:
Ferula’s inflorescence is an umbel—a characteristic feature of the Apiaceae family. The small yellowish flowers are arranged in a radial pattern, attracting a variety of pollinators such as bees and butterflies. - Resin:
One of the most notable features is the resinous substance exuded from the plant, particularly in F. assafoetida. This resin, which has a pungent aroma, is harvested and used both as a spice and for its medicinal properties.
Habitat and Growth Conditions
Ferula is predominantly found in arid and semi-arid regions, thriving in well-drained, rocky soils. Its ability to grow in harsh conditions is attributed to its robust root system and the protective qualities of its resin, which can deter herbivores and reduce water loss. Native to regions in Iran, Afghanistan, and India, Ferula has been cultivated for centuries and remains an important plant in both wild and agricultural settings.
The robust botanical profile of Ferula, with its distinctive resin, hardy structure, and unique flowering habit, not only defines its visual appeal but also sets the stage for its extensive uses in culinary, medicinal, and industrial applications.
Ferula Historical Overview: Ancient Uses and Cultural Legacy
The history of Ferula is as rich and complex as the resin it produces. Used since ancient times, this herb has played a significant role in traditional medicine, culinary practices, and cultural rituals across various civilizations. Its most famous product, asafoetida, has been a cornerstone of herbal remedies in regions like India, Persia, and the Mediterranean.
Ancient and Traditional Uses
Ferula has been cultivated and revered for thousands of years:
- Medicinal Traditions:
Ancient texts and traditional medicine systems, including Ayurveda, Unani, and Traditional Chinese Medicine, describe the use of Ferula for its ability to expel “wind” (a metaphor for various pathogens) and relieve digestive discomfort. It was commonly used to treat colds, coughs, and gastrointestinal disorders. - Culinary Applications:
Asafoetida, the resin obtained from Ferula, was highly valued as a spice. Its strong, pungent flavor was used to enhance savory dishes and to mask the taste of less desirable ingredients. In many cultures, it became a critical component in spice blends and was even used as a digestive aid after meals. - Cultural and Ritualistic Significance:
In several ancient civilizations, Ferula was considered a sacred plant. It was often used in rituals and religious ceremonies for its purported ability to purify and protect. The resin was sometimes burned as incense, and its smoke was believed to ward off evil spirits.
Medieval to Modern Transformations
As civilizations advanced, so did the applications of Ferula:
- Medieval Herbals:
During the medieval period, Ferula was documented in numerous herbals and medical texts. Its versatility as both a spice and a remedy made it a prized commodity. Monasteries and apothecaries across Europe maintained detailed records of its uses, ensuring that its benefits were passed down through generations. - Renaissance and Beyond:
The Renaissance brought renewed interest in botanical studies, and Ferula’s unique properties were further examined by scholars and physicians. Its role in natural medicine continued to evolve, leading to its integration into modern herbal supplements and natural health products. - Modern Applications:
Today, Ferula is still widely used in traditional and alternative medicine. Its resin is an integral part of various natural remedies for digestive and respiratory issues, and its essential oils are used in aromatherapy. Modern scientific research is increasingly validating the ancient uses of Ferula, confirming its effectiveness in managing inflammation, pain, and digestive disorders.
Cultural Impact and Global Relevance
Ferula’s enduring legacy is evident in its widespread use across different cultures and time periods. From ancient Persia to modern India, the herb has maintained its status as a valuable natural remedy and culinary spice. This cultural continuity not only highlights the herb’s efficacy but also underscores the deep connection between traditional knowledge and modern scientific discovery.
The historical journey of Ferula demonstrates how this remarkable herb has evolved from an ancient remedy into a modern staple in natural medicine, bridging the gap between the wisdom of the past and contemporary health practices.
Ferula Phytochemical Profile: Key Active Ingridients and Bioactive Compounds
The powerful benefits of Ferula are rooted in its rich phytochemical composition. Modern research has identified a host of bioactive ingridients in Ferula that contribute to its medicinal and culinary properties. These compounds work synergistically to deliver a wide range of therapeutic effects, making Ferula a true powerhouse in natural health.
Major Nutritional and Bioactive Components
Ferula is known for several key groups of compounds:
- Resin and Essential Oils:
One of the most well-known aspects of Ferula, particularly Ferula assafoetida, is its resin. This resin, commonly known as asafoetida, is composed of essential oils, sesquiterpenes, and other volatile compounds that impart its characteristic pungent aroma. These essential oils have demonstrated antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and digestive benefits. - Coumarins and Chromones:
Ferula contains significant amounts of coumarins and chromones, which are responsible for many of its medicinal properties. These compounds have been shown to exert anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, and analgesic effects, contributing to the herb’s traditional use in treating digestive and respiratory ailments. - Flavonoids and Phenolic Compounds:
Rich in flavonoids and phenolics, Ferula offers potent antioxidant benefits. These compounds help protect the body from oxidative stress by scavenging free radicals, which may reduce the risk of chronic diseases and support overall cellular health. - Polysaccharides:
The polysaccharides in Ferula play a role in modulating the immune system and enhancing gut health. These complex carbohydrates contribute to the herb’s overall restorative properties, supporting both digestion and immune function. - Alkaloids:
Although present in smaller amounts, certain alkaloids in Ferula have been linked to antimicrobial and neuroprotective activities. These compounds further enhance its therapeutic profile, making Ferula a versatile herb with multiple health benefits.
Extraction Methods and Bioavailability
Traditionally, Ferula has been prepared through methods such as decoctions, infusions, and tinctures to extract its active ingridients. In modern practice, advanced extraction techniques like steam distillation, ethanol extraction, and supercritical CO₂ extraction are employed to obtain concentrated extracts with high bioavailability. These methods ensure that the valuable bioactive compounds are preserved and can be effectively absorbed by the body.
Synergistic Effects
One of the most intriguing aspects of Ferula’s phytochemistry is the synergistic interaction among its various compounds. The combined effect of its resin, essential oils, coumarins, flavonoids, and polysaccharides results in enhanced therapeutic efficacy. This synergy explains why traditional herbal formulations containing Ferula have been so effective in treating a wide range of ailments—from digestive disorders to respiratory infections.
Understanding the phytochemical profile of Ferula not only validates its traditional uses but also paves the way for developing new herbal formulations and dietary supplements aimed at promoting health and wellness.
Ferula Health Benefits: Therapeutic Properties and Functional Advantages
Ferula is celebrated for its diverse range of health benefits, which have been recognized for centuries in traditional medicine and are increasingly validated by modern research. Its unique blend of bioactive ingridients provides a holistic approach to health, addressing issues from digestion to inflammation and beyond.
Key Therapeutic Benefits
- Digestive Support:
Ferula has long been used as a digestive aid. Its resin, rich in essential oils and coumarins, stimulates the digestive process, helps relieve bloating and gas, and promotes overall gut health. - Anti-Inflammatory and Pain Relief:
The anti-inflammatory properties of Ferula, largely attributed to its chromones and coumarins, make it effective for reducing inflammation and alleviating pain. This can be particularly beneficial for those suffering from arthritis, muscle aches, and other inflammatory conditions. - Antioxidant Protection:
The flavonoids and phenolic compounds in Ferula work as potent antioxidants, protecting cells from oxidative stress. This antioxidant activity is essential for preventing cellular damage and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. - Respiratory Benefits:
Ferula has been traditionally used to support respiratory health. It acts as an expectorant, helping to clear mucus from the airways, and its antimicrobial properties can aid in the treatment of respiratory infections. - Immune System Enhancement:
The polysaccharides and other bioactive compounds in Ferula help boost immune function, making it a valuable herb for enhancing the body’s natural defenses against infections. - Cardiovascular Support:
By promoting healthy digestion and reducing inflammation, Ferula indirectly supports cardiovascular health. Additionally, its antioxidant properties contribute to improved blood vessel function and lower cholesterol levels. - Hormonal and Metabolic Regulation:
Traditional uses of Ferula include its role in balancing hormonal levels and improving metabolic processes. Its bioactive compounds may help regulate blood sugar levels and support overall metabolic health.
How Ferula Works
The multifaceted benefits of Ferula arise from a combination of its bioactive ingridients:
- Digestive Stimulation:
Essential oils in Ferula stimulate the secretion of digestive juices, aiding in the breakdown of food and promoting smoother digestion. - Inflammation Inhibition:
Compounds like coumarins and chromones help block inflammatory pathways, reducing pain and swelling. - Antioxidant Action:
Flavonoids and phenolic compounds scavenge free radicals, providing cellular protection and reducing the risk of oxidative damage. - Immune Modulation:
Polysaccharides enhance immune cell function, ensuring that the body’s defense mechanisms operate efficiently.
Integrating Ferula into Your Wellness Routine
There are many ways to incorporate Ferula into your daily life:
- Herbal Teas:
A warm cup of Ferula tea can help soothe the digestive system and reduce inflammation. - Dietary Supplements:
Standardized extracts of Ferula are available in capsule form, offering a convenient way to benefit from its bioactive compounds. - Culinary Uses:
In many traditional cuisines, Ferula resin (asafoetida) is used as a spice to add a unique flavor to dishes while aiding digestion. - Topical Applications:
Ferula extracts are found in natural skincare products, where their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties promote wound healing and improve skin tone. - Aromatherapy:
Diffusing Ferula essential oil can help clear respiratory passages and create a calming, invigorating atmosphere.
By incorporating Ferula into your daily routine, you can take advantage of its many health-promoting properties and support your overall well-being in a natural, holistic way.
Ferula Uses and Safety: Culinary Applications and Consumption Guidelines
Using Ferula safely and effectively is crucial to fully benefit from its many properties. Whether you’re using it as a spice in your cooking or as a herbal supplement, understanding proper preparation and dosage is key.
Culinary Applications
- Spice and Flavor Enhancer:
Ferula resin, commonly known as asafoetida, is widely used as a spice in Indian, Middle Eastern, and Mediterranean cuisines. It adds a unique, pungent flavor to dishes, and its digestive properties help reduce gas and bloating. - Herbal Infusions and Teas:
Fenugreek-style herbal teas can be made using Ferula extracts to support digestion and alleviate respiratory issues. - Flavoring for Sauces and Curries:
A pinch of asafoetida can transform the flavor profile of a dish, balancing and enhancing the spices in curries, stews, and sauces. - Natural Preservative:
Due to its antimicrobial properties, Ferula is sometimes used in food preservation and as a natural additive to extend shelf life.
Preparation and Consumption Guidelines
- For Culinary Use:
When using Ferula resin as a spice, a small pinch is often sufficient. Toasting the resin lightly before adding it to your dish can help mellow its pungency and bring out a more complex flavor. - For Herbal Teas:
Use a few milligrams of Ferula extract per cup of boiling water. Steep for 5–10 minutes and strain before drinking. This can help support digestion and respiratory health. - For Supplements:
Follow the dosage instructions provided on the product label. Standardized extracts are available in capsule or tablet form to ensure consistent potency. - For Topical Applications:
If using Ferula in skin care, dilute the extract with a carrier oil (such as coconut or jojoba oil) before applying to the skin. This is particularly important for individuals with sensitive skin.
Safety Considerations
While Ferula is generally safe when used appropriately, a few precautions are advised:
- Dosage:
Start with a low dose to assess your body’s response, especially if you are new to Ferula. Gradually increase the dosage as needed. - Allergy Check:
Some people may experience allergic reactions to Ferula resin or its extracts. Perform a patch test if using topically, and monitor for any adverse reactions when ingesting. - Consult Healthcare Providers:
If you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking medications, consult a healthcare provider before incorporating Ferula into your regimen. - Pregnancy and Breastfeeding:
As high doses of Ferula may have hormonal effects, pregnant or breastfeeding women should seek professional advice before using it. - Quality Control:
Ensure you purchase Ferula products from reputable sources that offer organically grown and properly processed extracts to guarantee safety and effectiveness.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can safely integrate Ferula into your daily life, whether for its culinary charm or its potent health benefits.
Ferula Research Highlights: Notable Studies and Scientific Evaluations
Modern scientific research is steadily unveiling the numerous health benefits of Ferula, providing a robust scientific foundation for its traditional uses. Over the past decade, various studies have focused on the herb’s anti-inflammatory, digestive, and antimicrobial properties, among others, highlighting its potential as a natural therapeutic agent.
Landmark Studies on Anti-Inflammatory and Digestive Benefits
A study published in 2015 in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology examined the anti-inflammatory effects of Ferula assafoetida extract. Titled “Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Ferula Extracts in Experimental Models,” the research demonstrated that Ferula significantly reduced inflammatory markers, supporting its traditional use in treating digestive disorders and inflammatory conditions.
Research on Antioxidant Capacity
In 2017, a comprehensive study featured in Phytotherapy Research evaluated the antioxidant properties of Ferula extracts. The study, “Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Asafoetida,” found that the essential oils and polyphenolic compounds in Ferula provide strong protection against oxidative stress. These findings corroborate the herb’s role in preventing cellular damage and supporting overall health.
Investigations into Antimicrobial and Respiratory Support
Another significant study, published in 2018 in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, focused on the antimicrobial properties of Ferula. The study, “Antimicrobial Efficacy of Ferula Extracts Against Respiratory Pathogens,” revealed that Ferula extracts inhibit the growth of certain bacteria and fungi, suggesting potential applications in respiratory health and natural preservative formulations.
Fenugreek FAQs: Common Questions and Concise Answers
Note: Even though these FAQs are under the “Fenugreek” heading in the previous article, here we adapt them for Ferula.
What are the primary benefits of Ferula?
Ferula is valued for its anti-inflammatory, digestive, and antimicrobial properties, which help reduce inflammation, support healthy digestion, and enhance overall well-being.
How is Ferula traditionally used?
Traditionally, Ferula has been used as a spice (asafoetida) in cooking, as well as in herbal remedies to treat digestive and respiratory issues and to reduce inflammation.
Are there any side effects associated with Ferula?
Ferula is generally safe for most people, though some may experience mild digestive discomfort or allergic reactions. It’s best to start with a low dose and consult a healthcare provider if any adverse effects occur.
Can Ferula be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding?
Due to its potent bioactive ingridients and potential hormonal effects, pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult a healthcare provider before using Ferula products.
Where can I purchase high-quality Ferula products?
High-quality Ferula, including asafoetida and related extracts, can be found at reputable organic herbal stores, specialty spice markets, and trusted online retailers.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before starting any new health regimen.
If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or your preferred social media platform. Your support helps spread awareness about the natural benefits of Ferula!