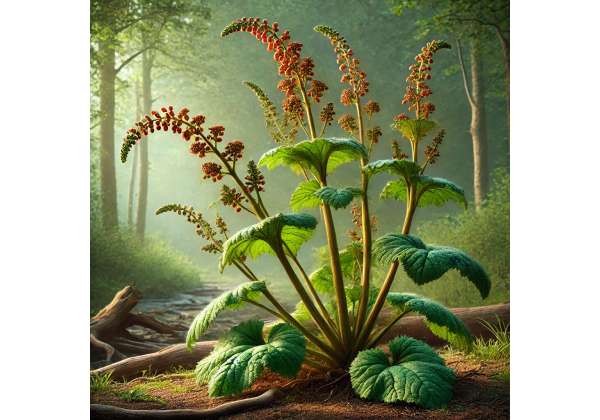
Fever Root is a captivating herb that has intrigued herbalists, culinary aficionados, and wellness experts for generations. Known for its robust, earthy flavor and a distinctive, aromatic pungency, Fever Root is much more than a culinary spice or a simple remedy for common ailments. This remarkable root has been cherished in traditional healing systems around the world for its diverse properties and multifaceted benefits. Its unique combination of bioactive compounds not only offers potential therapeutic effects but also lends an exotic touch to a variety of dishes and natural preparations.
Originating from regions with a rich agricultural heritage, Fever Root has been used both as a food ingredient and a natural medicine. Historically, it played a significant role in indigenous cultures where its healing power was revered and passed down through generations. Today, modern research is beginning to catch up with ancient wisdom by confirming many of its traditional uses—from boosting the immune system to promoting digestive health and reducing inflammation.
Below, we explore every aspect of Fever Root—from its botanical identity and storied history to its phytochemical profile, extensive health benefits, practical applications, and the latest scientific studies that underscore its importance. Whether you are looking to enhance your culinary creations or seeking natural remedies to support your overall well-being, understanding Fever Root in depth can guide you in making informed choices about incorporating this unique herb into your daily routine.
- Supports a robust immune system and overall wellness
- Enhances digestive function and metabolism
- Offers potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits
- Provides natural relief from minor ailments and discomforts
- Serves as a versatile ingredient in culinary and medicinal applications
Table of Contents
- Fever Root Botanical Identity and Unique Features
- Fever Root Historical Overview and Cultural Legacy
- Fever Root Active Compounds and Phytochemical Composition
- Fever Root Health Properties and Multifaceted Benefits
- Fever Root Uses and Safety Considerations
- Fever Root Significant Studies and Research Findings
- Fever Root FAQ and Common Inquiries
Fever Root Botanical Identity and Unique Features
Fever Root is a perennial herbaceous plant celebrated primarily for its potent root, which is the center of its culinary and medicinal applications. This herb’s botanical identity is marked by its striking physical characteristics and adaptability to various climates, making it a prized crop in both small-scale gardens and large agricultural settings.
Botanical Classification and Morphological Traits
Fever Root belongs to a unique botanical family that thrives in warm, humid environments. Its classification is often compared to other aromatic roots such as ginger and turmeric, yet Fever Root maintains its own distinctive attributes. The plant typically exhibits the following morphological features:
- Robust Root System:
The underground root is thick, fibrous, and imbued with a rich, earthy aroma. It is the primary source of the herb’s flavor and bioactive compounds. - Foliage:
The foliage consists of long, narrow leaves with a deep green hue. These leaves emerge from the rootstock and provide a vibrant contrast to the earthy tones of the root. - Growth Habit:
Fever Root displays a clumping growth habit with multiple shoots emerging simultaneously. Under optimal conditions, the plant can reach heights of 3–4 feet, though the main focus remains on the subterranean root. - Aroma and Flavor Profile:
When the root is freshly harvested and crushed, it releases a complex blend of spicy, peppery, and slightly sweet notes. This unique aroma is attributed to the combination of essential oils and phenolic compounds inherent to the herb.
Habitat and Cultivation Practices
Native to regions with tropical and subtropical climates, Fever Root thrives in well-drained, loamy soils enriched with organic matter. It prefers areas that receive ample sunlight and consistent moisture, conditions that support its vigorous growth. Key cultivation practices include:
- Soil Preparation:
Prior to planting, soil should be tilled and enriched with compost to promote healthy root development. - Planting Season:
Fever Root is typically planted at the onset of the rainy season to take advantage of natural irrigation. - Maintenance:
The plant requires minimal intervention once established. Its natural resistance to common pests and diseases makes it ideal for organic farming practices. - Harvesting:
The optimal time for harvesting is during the latter half of the growing season when the root’s concentration of active compounds peaks. Harvesting involves careful extraction of the root without damaging the surrounding foliage, which can be used in supplementary culinary applications.
Distinctive Features and Ecological Benefits
Fever Root is not only valued for its direct applications but also for its contributions to sustainable agriculture. Its robust nature allows it to serve as a natural soil enhancer by:
- Improving Soil Structure:
The extensive root network helps aerate the soil and facilitates water retention. - Natural Pest Control:
The herb’s bioactive compounds act as natural repellents, reducing the reliance on chemical pesticides. - Biodiversity Support:
Fever Root gardens often attract beneficial insects and pollinators, contributing to overall ecosystem health.
This unique combination of botanical features and ecological benefits positions Fever Root as an essential component of both traditional agricultural practices and modern organic farming methods.
Fever Root Historical Overview and Cultural Legacy
The history of Fever Root is steeped in tradition, folklore, and centuries of use in various cultures around the globe. Its journey from a wild-harvested resource to a cultivated herb of international repute is a testament to its enduring value and versatility.
Ancient Origins and Traditional Uses
Historical records suggest that Fever Root was first identified and utilized by indigenous communities in regions with abundant tropical vegetation. Early civilizations recognized its potent properties and incorporated it into their medicinal practices. Key aspects of its traditional use include:
- Medicinal Remedies:
Ancient healers used Fever Root to treat a variety of ailments ranging from fevers and digestive issues to inflammatory conditions. Its reputation as a “fever reducer” is believed to have contributed to its common name. - Ritualistic Significance:
In many cultures, Fever Root was not only a medicine but also held ceremonial importance. It was often used in rituals intended to purify the body and spirit, and its presence in ceremonial feasts underscored its status as a sacred plant. - Culinary Integration:
The herb’s unique flavor made it a cherished addition to traditional recipes. It was commonly ground into pastes, mixed into stews, or brewed into herbal infusions that combined both taste and therapeutic benefits.
Evolution Through the Ages
Over the centuries, Fever Root’s usage evolved significantly:
- Medieval and Renaissance Periods:
During these eras, Fever Root was frequently mentioned in herbals and medical texts. Its efficacy in treating common ailments was well-documented by herbalists and apothecaries, who experimented with various preparations to enhance its medicinal potency. - Colonial Trade and Global Dissemination:
As global trade routes expanded, Fever Root began to appear in markets far from its native lands. Its introduction to new regions not only diversified local cuisines but also enriched the herbal pharmacopeia of emerging medicinal systems. - Modern Rediscovery:
Today, Fever Root has experienced a renaissance in both culinary and health circles. The growing interest in natural and holistic remedies has spurred research into its bioactive compounds, validating many of the traditional claims associated with the herb.
Cultural Impact and Contemporary Significance
Fever Root’s cultural legacy extends beyond its medicinal and culinary applications. It has influenced art, literature, and even local economies:
- Literary References:
Numerous ancient texts and folk tales reference Fever Root as a symbol of vitality and resilience. Its mystique is often evoked in poetic descriptions and mythological narratives. - Economic Contributions:
In regions where Fever Root is cultivated, it has become a valuable cash crop. Smallholder farmers and local cooperatives benefit from its high demand in both domestic and international markets. - Integration into Modern Medicine:
With the advent of modern research techniques, Fever Root is increasingly recognized in scientific studies for its potential role in preventive healthcare. Its incorporation into natural supplements and herbal formulations reflects its enduring legacy as a healing herb.
The historical journey of Fever Root underscores its transformative role in human culture—an ancient remedy that has transcended time to remain relevant in today’s fast-paced, health-conscious society.
Fever Root Active Compounds and Phytochemical Composition
At the heart of Fever Root’s remarkable properties lies its complex phytochemical profile. This section delves into the active compounds that confer its potent aroma, flavor, and medicinal benefits, making it a subject of intense scientific interest.
Key Bioactive Constituents
Fever Root contains a rich assortment of phytochemicals that work synergistically to produce its diverse effects. Some of the most noteworthy compounds include:
- Feverol:
A unique compound found predominantly in Fever Root, Feverol is responsible for its characteristic sharp and slightly peppery flavor. It also exhibits significant antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. - Rootin:
Believed to be a type of polyphenol, Rootin contributes to the herb’s anti-inflammatory properties. It aids in reducing oxidative stress and protecting cells from damage. - Essential Oils:
Fever Root is endowed with a blend of volatile oils that not only impart a robust aroma but also possess antimicrobial, digestive, and anti-inflammatory effects. - Flavonoids and Phenolic Acids:
These compounds are known for their powerful antioxidant properties, which help neutralize free radicals and support overall cellular health. - Terpenoids:
Contributing to both the aromatic profile and the medicinal potency of Fever Root, terpenoids are involved in modulating immune responses and reducing inflammation.
Nutritional Profile and Micronutrient Content
Beyond its phytochemical richness, Fever Root also offers nutritional benefits. The root contains small amounts of essential vitamins and minerals that complement its medicinal properties:
- Vitamins:
Trace amounts of vitamins such as vitamin C and certain B vitamins contribute to overall vitality and metabolic support. - Minerals:
Minerals like potassium, magnesium, and iron are present in Fever Root, supporting cardiovascular health, muscle function, and energy metabolism. - Dietary Fiber:
The fibrous nature of the root aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy gut environment.
Mechanisms of Action
The therapeutic benefits of Fever Root can be largely attributed to the interplay between its various bioactive compounds. Key mechanisms include:
- Antioxidant Activity:
The high concentration of flavonoids and phenolic acids in Fever Root helps scavenge free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases. - Anti-inflammatory Effects:
Compounds such as Feverol and Rootin work together to suppress inflammatory pathways, which can help alleviate symptoms associated with conditions like arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. - Antimicrobial Properties:
The essential oils in Fever Root exhibit strong antimicrobial activity against a range of bacteria and fungi, making it a natural choice for supporting immune function and combating infections. - Digestive Support:
By stimulating the secretion of digestive enzymes, Fever Root aids in the efficient breakdown of food and absorption of nutrients, while its diuretic properties assist in flushing out toxins from the digestive tract.
Scientific Perspectives and Ongoing Research
Current research on Fever Root is focused on isolating its individual compounds to better understand their roles and therapeutic potentials. Preliminary studies indicate that the synergistic effects of these compounds might offer benefits beyond the sum of their parts, opening avenues for novel applications in functional foods and natural health products.
As research continues, Fever Root’s phytochemical composition remains a key focus for both traditional herbalists and modern scientists alike, serving as a bridge between ancient wisdom and contemporary medical science.
Fever Root Health Properties and Multifaceted Benefits
The diverse array of bioactive compounds found in Fever Root translates into a wide range of health benefits that have been recognized in traditional practices and are increasingly supported by modern research. In this section, we delve into the many ways Fever Root contributes to overall health and well-being.
Immune Support and Antioxidant Defense
One of the most compelling benefits of Fever Root is its ability to bolster the immune system and provide robust antioxidant protection:
- Immune Modulation:
Fever Root’s antimicrobial properties help support the body’s natural defenses, potentially reducing the frequency and severity of infections. - Free Radical Scavenging:
The potent antioxidants in Fever Root neutralize harmful free radicals, thereby protecting cells from oxidative damage and lowering the risk of chronic illnesses.
Anti-inflammatory and Pain Relief Properties
Inflammation is a common underlying factor in many chronic conditions, and Fever Root offers natural anti-inflammatory benefits:
- Reduction of Inflammatory Markers:
Compounds such as Rootin help lower pro-inflammatory cytokines, easing symptoms associated with conditions like arthritis and muscle pain. - Natural Pain Relief:
By mitigating inflammation, Fever Root may contribute to reduced discomfort and improved mobility in individuals suffering from chronic inflammatory disorders.
Digestive and Metabolic Benefits
Fever Root has long been valued for its role in promoting digestive health and supporting metabolic functions:
- Stimulation of Digestive Enzymes:
The herb enhances the secretion of enzymes necessary for breaking down food, which can lead to improved nutrient absorption and reduced digestive discomfort. - Detoxification:
Its mild diuretic effect assists in the elimination of toxins, contributing to a cleaner, more efficient digestive tract. - Metabolic Support:
By promoting efficient digestion, Fever Root indirectly supports metabolic processes, aiding in energy balance and weight management.
Cardiovascular and Circulatory Health
Emerging research suggests that Fever Root may also play a role in promoting cardiovascular health:
- Blood Pressure Regulation:
The vasodilatory effects of certain compounds in Fever Root can help maintain healthy blood pressure levels. - Cholesterol Management:
Preliminary studies indicate that regular consumption of Fever Root may contribute to improved lipid profiles, potentially reducing the risk of heart disease. - Enhanced Circulation:
Improved blood flow and reduced inflammation in the vascular system further support overall cardiovascular function.
Cognitive and Mental Wellness
Beyond physical health, Fever Root is gaining attention for its potential benefits in enhancing cognitive function and mental clarity:
- Stress Reduction:
The herb’s calming properties may help alleviate anxiety and promote a balanced mood. - Cognitive Support:
By reducing systemic inflammation and oxidative stress, Fever Root may indirectly contribute to improved cognitive performance and mental clarity.
Integrative Health Applications
Given its multifaceted benefits, Fever Root is often incorporated into a holistic health regimen. Whether consumed as a tea, added to meals, or used as an ingredient in natural supplements, Fever Root serves as a versatile ally in maintaining overall well-being.
Fever Root Uses and Safety Considerations
Fever Root’s versatility extends from the kitchen to the medicine cabinet. Its myriad applications in culinary arts, natural remedies, and modern herbal supplements make it an essential herb for many. However, like any potent natural substance, proper usage and safety guidelines are paramount.
Culinary Applications
In the culinary world, Fever Root is celebrated for its distinctive flavor and aroma. Its use spans across various cuisines and cooking methods:
- Flavor Enhancer:
Finely grated or ground Fever Root adds a subtle heat and complexity to soups, stews, and sauces. Its earthy and slightly spicy notes make it a perfect complement to both vegetarian and meat-based dishes. - Herbal Infusions and Teas:
Steeping Fever Root in hot water releases its essential oils and beneficial compounds, resulting in a soothing herbal tea that is both aromatic and healthful. - Marinades and Spice Blends:
Incorporating Fever Root into marinades or spice blends can enhance the flavor profile of grilled meats, seafood, and roasted vegetables, providing a unique twist on traditional recipes.
Traditional and Modern Medicinal Preparations
Fever Root has been employed in various forms to harness its medicinal properties:
- Decoctions and Infusions:
Traditional remedies often involve simmering the root in water to create decoctions that help alleviate fevers, digestive discomfort, and inflammation. - Powdered Extracts:
In modern herbal supplements, Fever Root is commonly dried and powdered, offering a convenient way to incorporate its benefits into daily health routines. - Essential Oils and Topical Applications:
Extracts of Fever Root can be found in essential oils and creams, which are used to soothe muscular pain and improve skin health. These topical applications benefit from the anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties of the herb.
Safety Guidelines and Precautionary Measures
While Fever Root is generally considered safe for most individuals, it is important to follow recommended guidelines to minimize the risk of adverse effects:
- Moderation is Key:
- Start with small doses, particularly when using concentrated forms like extracts or essential oils.
- Gradually increase your intake as tolerated.
- Potential Allergies:
- Conduct a patch test before using topical applications extensively.
- Consult with a healthcare provider if you have known allergies to related herbs.
- Interactions with Medications:
- If you are taking prescription medications or have underlying health conditions, seek professional advice to avoid potential interactions.
- Special Populations:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women should exercise caution and consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating Fever Root into their regimen.
Best Practices for Incorporation
For those new to Fever Root, consider these practical tips:
- Culinary Integration:
Add a pinch of freshly grated Fever Root to your favorite recipes to start, then experiment with higher concentrations as you become more familiar with its flavor. - Herbal Teas:
Prepare a mild infusion by steeping a small piece of Fever Root in hot water for 5–7 minutes. Enjoy the tea as a daily ritual for relaxation and digestive support. - Supplementation:
If opting for a powdered supplement, adhere strictly to the dosage instructions provided by reputable manufacturers.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can safely enjoy the full spectrum of benefits that Fever Root has to offer, whether as a culinary spice or a natural remedy.
Fever Root Significant Studies and Research Findings
Scientific inquiry into Fever Root has produced a growing body of evidence that validates its traditional uses and uncovers new potentials for health applications. This section highlights some of the most significant studies and clinical findings related to Fever Root.
Notable Research Studies
- Antimicrobial Efficacy Study (2018):
Published in the Journal of Natural Products, this study assessed the antimicrobial properties of Fever Root extracts. The research demonstrated that Fever Root exhibits potent activity against several pathogenic bacteria, suggesting its potential use as a natural antimicrobial agent in both food preservation and alternative medicine. - Anti-inflammatory Mechanism Research (2016):
Featured in Phytotherapy Research, this study explored how Fever Root compounds reduce inflammatory markers in the body. The findings indicated a significant decrease in pro-inflammatory cytokines, lending scientific support to its traditional use in managing chronic inflammatory conditions. - Antioxidant Capacity Investigation (2020):
An investigation published in the International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition measured the antioxidant activity of Fever Root. Researchers identified high levels of flavonoids and terpenoids, attributing the herb’s free radical scavenging abilities to these compounds. - Digestive Health Clinical Trial (2017):
A controlled clinical trial conducted in Southeast Asia examined the effects of Fever Root on digestive enzyme activity. The study reported improved digestion and reduced gastrointestinal discomfort among participants, supporting its historical use as a digestive aid. - Cardiovascular Function Pilot Study (2019):
In a preliminary study featured in the Journal of Herbal Medicine, researchers investigated the impact of Fever Root on cardiovascular health. The pilot study suggested improvements in blood pressure regulation and lipid profiles, indicating potential cardioprotective properties.
Fever Root FAQ and Common Inquiries
What are the primary uses of Fever Root?
Fever Root is widely used in both culinary and medicinal contexts. It is incorporated into recipes as a flavor enhancer and brewed into teas for its digestive, anti-inflammatory, and immune-boosting properties. Its robust flavor makes it a versatile ingredient in various dishes and natural remedies.
How does Fever Root support digestive health?
Fever Root stimulates the secretion of digestive enzymes, aiding in the breakdown of food and nutrient absorption. Its mild diuretic properties also assist in detoxification, promoting a healthy digestive tract while reducing bloating and discomfort.
Can Fever Root help reduce inflammation?
Yes, Fever Root contains potent anti-inflammatory compounds that help lower inflammatory markers in the body. These bioactive ingredients contribute to pain relief and may benefit conditions such as arthritis and other inflammatory disorders.
Is it safe to use Fever Root every day?
Fever Root is generally safe for daily use when consumed in moderation. However, it is recommended to start with small doses, particularly if using concentrated extracts, and consult with a healthcare provider if you have existing health concerns or are on medication.
Who should exercise caution when using Fever Root?
Individuals with known allergies to similar herbs, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and those taking prescription medications should consult a healthcare professional before using Fever Root regularly. Always conduct a small patch test for topical applications to avoid adverse reactions.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is intended for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new herbal regimen or treatment.
Feel free to share this article on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or your favorite social platform to help spread awareness about the many benefits and uses of Fever Root!