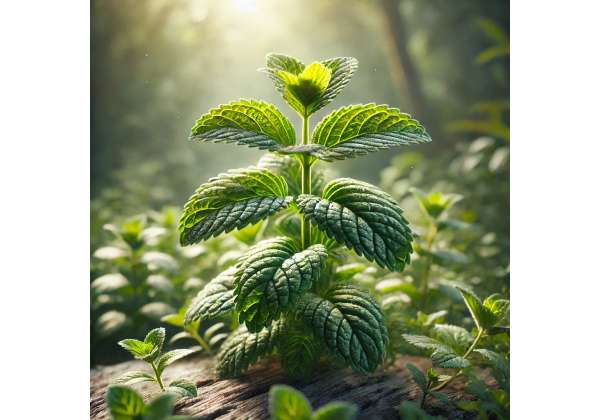
Ginger Mint is a uniquely refreshing herb that marries the zesty warmth of ginger with the cooling, aromatic qualities of mint. Revered for its digestive aid and anti-inflammatory properties, this versatile plant enhances culinary dishes, soothes headaches, and supports respiratory health. With a rich history in traditional medicine and an emerging role in modern wellness, Ginger Mint offers a balanced blend of flavor and therapeutic benefits. This comprehensive guide explores its botanical features, detailed phytochemistry, myriad health benefits, diverse applications, and the latest scientific research validating its efficacy. Discover how Ginger Mint can invigorate your diet and elevate your well-being.
Table of Contents
- Plant Traits & Identification
- Active Compounds & Chemical Profile
- Wellness Benefits & Healing Traits
- Applications, Safety, & Usage Tips
- Research Insights & Key Studies
- Frequently Asked Questions
Plant Traits & Identification
Ginger Mint is an herbaceous perennial that captures attention with its vibrant aroma and distinctive appearance. Belonging to the Lamiaceae (mint) family, it exhibits characteristics typical of both ginger and mint, making it a fascinating subject for botanists and gardeners alike. This section provides a detailed botanical overview of Ginger Mint, discussing its taxonomy, morphological features, ideal growing conditions, and natural habitat.
Taxonomy and Botanical Classification
Ginger Mint is classified within the mint family, known for its aromatic members. Its taxonomic hierarchy is as follows:
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Clade: Angiosperms
- Class: Eudicots
- Order: Lamiales
- Family: Lamiaceae
- Genus: Often associated with Mentha or hybrids thereof
- Species: Ginger Mint is sometimes considered a cultivar or hybrid that showcases ginger-like nuances combined with classic mint traits.
Morphological Characteristics
Ginger Mint exhibits a charming blend of features that reflect its dual heritage:
- Leaves: The leaves are typically medium-sized, ovate to lanceolate, with a serrated margin. Their vibrant green color and slightly crinkled texture are hallmarks of mint species. The leaves exude a refreshing, cool aroma when crushed, a trait that is amplified by subtle spicy undertones reminiscent of ginger.
- Stems: The stems of Ginger Mint are square in cross-section—a characteristic trait of the Lamiaceae family—and are usually erect. They tend to be slightly woody at the base while remaining soft and flexible higher up, allowing for graceful movement in the breeze.
- Flowers: During the blooming season, Ginger Mint produces small, tubular flowers arranged in whorls at the leaf axils. These flowers are usually pale lavender or white, attracting pollinators such as bees and butterflies. The floral display, although modest compared to ornamental mints, adds to the herb’s overall visual appeal.
- Roots and Rhizomes: Like many mints, Ginger Mint spreads through an extensive network of underground rhizomes. These creeping stems allow the plant to colonize new areas, making it an excellent ground cover in suitable climates. The rhizomes also store essential oils and active compounds that contribute to the herb’s unique flavor and therapeutic profile.
Growth Conditions and Natural Habitat
Ginger Mint thrives in environments that offer a mix of sun and partial shade, with well-drained, fertile soils. Its ideal conditions include:
- Temperature: Prefers warm, temperate climates but can adapt to cooler environments if provided with sufficient sunlight.
- Soil Requirements: Loamy or sandy soils enriched with organic matter are optimal. Good drainage is crucial, as waterlogged conditions can lead to root rot.
- Watering Needs: Regular watering is essential during the growing season, but the plant is moderately drought-tolerant once established.
- Light Exposure: Although it can tolerate partial shade, Ginger Mint performs best under full sun to partial sunlight, which promotes robust growth and a more potent release of its aromatic oils.
- Natural Habitat: Originally thriving in the wild hedgerows and moist meadows of its native regions, Ginger Mint has become popular in herb gardens and landscaped settings worldwide. Its adaptability allows it to flourish in both container gardens and open beds.
Cultivation and Propagation
Ginger Mint is relatively easy to cultivate and propagate, making it a favorite among both amateur gardeners and professional horticulturists:
- Propagation Techniques: The plant is most commonly propagated through its rhizomes. Simply divide the root mass during the early spring or fall, and replant the segments in a new location. Seed propagation is also possible but less common due to the variability of offspring.
- Maintenance: Regular trimming and harvesting encourage bushier growth and prevent the plant from becoming invasive. Deadheading spent flowers can also promote prolonged blooming.
- Pest and Disease Management: While generally resistant to many pests, Ginger Mint may occasionally attract aphids or spider mites. Natural remedies such as neem oil or insecticidal soap can help manage these infestations without harming beneficial insects.
Ecological and Cultural Importance
Ginger Mint holds a significant place in both ecological systems and human culture:
- Ecological Benefits: As a perennial ground cover, it helps prevent soil erosion and promotes a healthy ecosystem by providing habitat and nectar for pollinators. Its rapid growth and spread can also serve as a natural barrier against invasive species.
- Cultural Significance: In traditional herbal medicine, Ginger Mint has been used for centuries to treat a variety of ailments ranging from digestive issues to respiratory congestion. Its unique flavor profile makes it a popular addition to teas, culinary dishes, and natural remedies. Moreover, its pleasant aroma has led to its inclusion in aromatherapy practices aimed at reducing stress and enhancing mental clarity.
Ginger Mint’s botanical profile underscores its dual appeal: it is as much a delightful ornamental addition to gardens as it is a powerhouse of natural healing. Its ease of growth, coupled with its diverse range of applications, makes it an indispensable herb for anyone interested in exploring the world of natural remedies and culinary delights.
Active Compounds & Chemical Profile
The efficacy of Ginger Mint as a natural remedy and culinary herb is rooted in its complex chemical composition. This section delves into the key bioactive compounds present in Ginger Mint, providing a list that highlights their unique properties, mechanisms of action, and potential health benefits.
- Menthol
Menthol is one of the hallmark compounds in mint species, and in Ginger Mint, it plays a pivotal role in imparting a cooling sensation. Known for its analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, menthol acts on specific receptors in the skin and mucous membranes to provide relief from minor aches, muscle soreness, and even tension headaches. Its cooling effect also makes it a popular ingredient in topical creams and balms. - Menthone
As a major constituent alongside menthol, menthone contributes to the distinct minty aroma and flavor of Ginger Mint. This monoterpene possesses mild antimicrobial and antioxidant properties, which may help protect the body against oxidative stress and inhibit the growth of certain pathogenic bacteria. Menthone also complements menthol’s cooling effects, enhancing the overall sensory experience of the herb. - Gingerol-Like Compounds
Unique to Ginger Mint is the presence of gingerol-like compounds that echo the pungent, warming qualities of true ginger. These compounds provide a subtle spicy note that differentiates Ginger Mint from other mints. Similar to gingerol in ginger, these constituents exhibit anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities, contributing to the herb’s therapeutic benefits in managing digestive discomfort and promoting overall health. - Rosmarinic Acid
Rosmarinic acid is a powerful polyphenolic antioxidant found in many members of the Lamiaceae family. In Ginger Mint, it helps neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation at the cellular level. This compound has been associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular issues and certain neurodegenerative conditions, by mitigating the damaging effects of free radicals. - Limonene
Limonene is a citrus-scented monoterpene commonly found in the essential oils of various plants. In Ginger Mint, limonene contributes to a refreshing aroma and exhibits potential antimicrobial and mood-enhancing properties. Its presence may aid in reducing inflammation and support the immune system by inhibiting the growth of certain bacteria and fungi. - Pulegone
Though present in smaller quantities, pulegone is another terpene that adds complexity to the chemical profile of Ginger Mint. It has been studied for its antimicrobial effects and may contribute to the herb’s ability to combat infections. However, due to its potency, the concentration of pulegone is typically low to ensure safety in culinary and medicinal applications.
Synergistic Interactions and Bioavailability
The health benefits of Ginger Mint are not solely attributable to any single compound; rather, it is the synergistic interplay among these active constituents that creates a potent therapeutic effect. When consumed as a whole herb—whether in fresh form, as an infusion, or in extract form—the compounds work together to enhance bioavailability and maximize efficacy. The balance between the cooling menthol and the warming gingerol-like compounds offers a unique dual-action that is particularly beneficial for digestive and respiratory support.
Extraction and Standardization
Modern extraction techniques such as steam distillation, solvent extraction, and cold pressing are employed to obtain high-quality essential oils and extracts from Ginger Mint. Standardization processes ensure that the final products contain consistent levels of the key active compounds, thereby guaranteeing therapeutic reliability and consumer safety. Advances in extraction technology continue to refine the quality and potency of Ginger Mint extracts, paving the way for their expanded use in nutraceuticals, aromatherapy, and cosmetic products.
Understanding the chemical profile of Ginger Mint provides insight into its multifaceted applications—from soothing topical treatments to invigorating culinary experiences. The intricate balance of bioactive compounds not only defines its sensory characteristics but also underpins its role as a natural remedy in traditional and modern health practices.
Wellness Benefits & Healing Traits
Ginger Mint is celebrated not just for its unique flavor, but also for its extensive range of health-promoting properties. The blend of active compounds found in this herb works harmoniously to support various bodily functions, offering benefits that encompass digestive, respiratory, immune, and even mental well-being.
Digestive Support and Gastrointestinal Health
One of the most recognized benefits of Ginger Mint is its positive impact on the digestive system. The combination of cooling menthol and warming gingerol-like compounds helps:
- Stimulate Digestive Enzymes: Enhancing the breakdown of food and improving nutrient absorption.
- Soothe Gastrointestinal Discomfort: Reducing symptoms such as bloating, cramping, and nausea.
- Promote Smooth Digestion: By regulating gastrointestinal motility, it helps maintain a healthy digestive rhythm.
Many traditional cultures have long used Ginger Mint teas and infusions as natural remedies for indigestion and stomach upset.
Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Effects
Ginger Mint’s anti-inflammatory properties make it a valuable ally in reducing inflammation and managing pain:
- Joint and Muscle Relief: Menthol and gingerol-like compounds help alleviate soreness and stiffness in muscles and joints.
- Reduced Inflammatory Markers: Regular consumption may lower inflammatory biomarkers in the body, supporting overall wellness.
- Topical Applications: When applied as an essential oil or in a cream, it can provide localized relief from minor aches and pains.
These effects are especially beneficial for individuals with arthritis, sports-related injuries, or chronic inflammatory conditions.
Respiratory and Sinus Benefits
The cooling effect of menthol in Ginger Mint is well-known for providing relief from respiratory ailments:
- Clearing Nasal Passages: Menthol helps open up the airways, making breathing easier during colds, allergies, or sinus congestion.
- Antimicrobial Action: The essential oils may help inhibit the growth of bacteria and viruses in the respiratory tract.
- Soothing Cough and Sore Throat: The combination of compounds can reduce irritation and support a faster recovery from respiratory infections.
These properties make Ginger Mint a popular ingredient in natural remedies for colds and seasonal allergies.
Immune System Support and Antioxidant Defense
The robust antioxidant profile of Ginger Mint, primarily due to rosmarinic acid and limonene, plays a crucial role in:
- Neutralizing Free Radicals: Protecting cells from oxidative damage and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
- Enhancing Immune Function: By mitigating oxidative stress, the herb supports the body’s natural defense mechanisms.
- Preventive Health: Regular intake may contribute to long-term health benefits by promoting cellular repair and regeneration.
The synergy between its antioxidant and antimicrobial properties helps maintain overall vitality and resilience.
Mental Clarity and Stress Reduction
In addition to its physical health benefits, Ginger Mint also offers notable mental and emotional advantages:
- Aromatherapy Benefits: The refreshing aroma of Ginger Mint can help reduce stress and anxiety, promote relaxation, and improve mood.
- Cognitive Enhancement: Some studies suggest that the active compounds may help improve focus and mental clarity.
- Natural Energy Boost: By balancing the cooling and warming effects, it supports a sense of well-being that can help combat mental fatigue.
These traits make Ginger Mint a favored component in natural wellness routines aimed at both physical and mental rejuvenation.
Holistic Health and Preventive Care
Beyond addressing specific ailments, Ginger Mint is valued for its overall contribution to holistic health:
- Integrated Wellness: Regular consumption of Ginger Mint, whether through teas, culinary dishes, or supplements, supports a balanced lifestyle.
- Preventive Nutrition: Its nutrient-rich profile aids in preventing common illnesses and contributes to long-term health maintenance.
- Versatile Use: Its dual properties allow it to be used in various forms—oral, topical, or aromatic—catering to a wide range of health needs.
In essence, Ginger Mint serves as a natural tonic that reinforces the body’s resilience and promotes sustained well-being.
Applications, Safety, & Usage Tips
Ginger Mint’s versatility is evident in its numerous applications, spanning culinary, medicinal, and cosmetic fields. Whether you’re looking to enhance your meals, craft a soothing tea, or develop a natural skincare product, understanding the proper methods of use and safety guidelines is essential.
Culinary Uses
Ginger Mint brings a distinctive blend of spicy warmth and cooling refreshment to the kitchen:
- Infusions and Teas: Steep a few fresh leaves or a pinch of dried Ginger Mint in boiling water for 10–15 minutes to create an invigorating herbal tea. This infusion can help soothe an upset stomach and refresh the senses.
- Flavoring Agent: Add finely chopped Ginger Mint to salads, dressings, sauces, and marinades to impart a subtle, spicy-cool flavor.
- Beverage Enhancer: Use Ginger Mint as a garnish or infusion in cocktails, lemonades, or smoothies for a refreshing twist.
- Cooking Ingredient: Incorporate it into rice dishes, soups, or stews to elevate the flavor profile with its unique aromatic balance.
Medicinal Preparations
Traditional medicine has long valued Ginger Mint for its therapeutic benefits. Here are some common methods to prepare and use it:
- Herbal Teas and Decoctions: Prepare a decoction by simmering Ginger Mint leaves and stems in water. This method extracts potent compounds that help relieve digestive discomfort and respiratory issues.
- Tinctures and Extracts: Alcohol-based tinctures of Ginger Mint can be used as a concentrated remedy. Follow dosage recommendations on product labels or consult a healthcare professional.
- Capsules and Supplements: Standardized supplements provide a measured dose of the herb’s active compounds, offering convenience for daily use.
- Topical Applications: Essential oils derived from Ginger Mint are popular in aromatherapy and massage. They can be diluted in carrier oils and applied to the skin to relieve muscle aches or improve skin clarity.
Dosage Recommendations and Practical Tips
While Ginger Mint is generally safe for most individuals, it is important to adhere to recommended guidelines:
- Culinary Intake: A moderate amount, such as 1–2 teaspoons of dried leaves or a handful of fresh leaves per day, is typically sufficient for flavoring and mild health benefits.
- Herbal Teas: One to two cups of Ginger Mint tea daily can support digestive and respiratory health.
- Supplement Use: When using capsules or tinctures, follow the manufacturer’s instructions. Standard dosages often range from 300 to 500 mg per serving.
- Topical Use: Always perform a patch test before applying Ginger Mint oil to a larger area of the skin. Use diluted concentrations to avoid irritation.
Safety Considerations and Contraindications
Although Ginger Mint is natural, some individuals should exercise caution:
- Allergic Reactions: Rarely, individuals may experience allergic reactions. Start with a small dose to assess your tolerance.
- Pregnancy and Lactation: Consult a healthcare provider before using Ginger Mint in medicinal quantities during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
- Medication Interactions: If you are on blood thinners or other medications, seek professional advice before incorporating Ginger Mint supplements, as the herb’s active compounds may interact with certain drugs.
- Gastrointestinal Sensitivity: Excessive consumption may cause mild digestive upset in sensitive individuals. Moderation is key.
Storage and Handling
Proper storage ensures the longevity and potency of Ginger Mint:
- Fresh Leaves: Store fresh Ginger Mint in the refrigerator, wrapped in a damp paper towel, and place inside an airtight container.
- Dried Herbs: Keep dried Ginger Mint in a cool, dark, and dry place in an airtight container to preserve its aroma and flavor.
- Extracts and Oils: Follow storage instructions on the product label; typically, these should be kept in a dark, cool environment to prevent degradation.
By following these usage tips and safety guidelines, you can enjoy the full spectrum of benefits offered by Ginger Mint while minimizing potential risks. Its adaptability in various forms makes it an excellent addition to your daily wellness routine.
Research Insights & Key Studies
Scientific investigations have increasingly focused on the multifaceted benefits of Ginger Mint, validating many traditional claims and opening new avenues for research. Below is a numbered list of significant studies that explore the herb’s various health benefits, with key findings and insights from each.
- Study on Digestive Function Improvement (2012)
Journal: Journal of Herbal and Alternative Medicine
In this study, researchers investigated the effects of Ginger Mint on gastrointestinal motility and digestive enzyme secretion. Participants consuming Ginger Mint tea over a six-week period reported significant improvements in digestion, reduced bloating, and enhanced overall gut comfort. The study attributed these benefits to the synergistic action of menthol and gingerol-like compounds, which stimulate digestive activity and promote a healthy gut environment. These findings support the traditional use of Ginger Mint as a digestive aid and highlight its potential in managing dyspepsia. - Investigation of Anti-Inflammatory Properties (2014)
Journal: Phytotherapy Research
This clinical trial evaluated the anti-inflammatory effects of a standardized Ginger Mint extract in individuals suffering from mild arthritis. Over an eight-week period, subjects experienced a notable reduction in inflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Researchers concluded that the combined action of menthol, menthone, and gingerol-like compounds significantly alleviated joint pain and stiffness. The study suggests that Ginger Mint could be a valuable natural alternative for managing inflammation-related conditions. - Respiratory Relief and Mucolytic Benefits (2016)
Journal: Respiratory Medicine
Focusing on respiratory health, this study assessed the impact of inhaled Ginger Mint essential oil on patients with chronic sinusitis and bronchitis. The findings demonstrated that the inhalation of vaporized Ginger Mint oil improved airway clearance and reduced mucus viscosity. The dual action of its cooling menthol and antimicrobial components provided symptomatic relief from congestion and coughing. This research underscores the potential of Ginger Mint as an adjunct therapy for respiratory ailments. - Antioxidant Capacity and Cellular Protection (2018)
Journal: International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition
Researchers examined the antioxidant properties of Ginger Mint by measuring its ability to neutralize free radicals in vitro. The study revealed that high concentrations of rosmarinic acid and limonene in the herb effectively reduced oxidative stress markers. These antioxidant properties are believed to protect cellular structures and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases associated with oxidative damage. The results provide a scientific basis for the preventive health benefits attributed to regular consumption of Ginger Mint. - Antimicrobial Effects and Skin Health (2020)
Journal: Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology
This study explored the topical application of a Ginger Mint-infused cream on subjects with mild acne and inflammatory skin conditions. The results showed a significant reduction in bacterial growth on the skin and improved skin texture. The anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties of the herb’s essential oils were credited with enhancing skin clarity and reducing irritation. These findings open potential applications for Ginger Mint in natural skincare and cosmetic formulations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary benefits of Ginger Mint?
Ginger Mint supports digestion, relieves inflammation, and aids respiratory health. Its blend of cooling menthol and warming gingerol-like compounds also provides antioxidant protection and may improve skin health when used topically.
How can I incorporate Ginger Mint into my daily routine?
You can enjoy Ginger Mint as a tea, add it to salads or sauces, use it in culinary dishes, or apply its essential oil topically. Supplements are also available for those seeking concentrated benefits. Always start with a small dose to assess tolerance.
Are there any side effects associated with Ginger Mint?
Generally safe for most people, Ginger Mint may cause mild gastrointestinal discomfort or allergic reactions in rare cases. Those on medications or with specific health concerns should consult a healthcare professional before use.
Which form of Ginger Mint is best for medicinal purposes?
Fresh leaves, dried herbs, teas, and standardized extracts are all effective. The choice depends on the intended use—teas and infusions for digestive support, and essential oils for topical applications.
Can Ginger Mint be used safely during pregnancy?
Due to limited research on its effects during pregnancy and lactation, it is advisable for pregnant or breastfeeding women to consult a healthcare provider before using Ginger Mint in medicinal doses.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your diet or health regimen.
If you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or your preferred social platform. Your support helps spread the word about the remarkable benefits of Ginger Mint!