What is Pinguecula?
Pinguecula is a common, harmless ocular condition characterized by a yellowish, slightly raised thickening of the conjunctiva, the clear tissue that covers the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelid. This lesion usually appears on the part of the conjunctiva that is exposed when the eyelids are open, which is often the side closest to the nose. Pingueculae are most common in people who spend a lot of time outside without proper eye protection, as chronic exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, wind, and dust are the primary causes.
While pinguecula is usually harmless and asymptomatic, it can occasionally cause irritation, dryness, or the sensation of a foreign body in the eye. In more severe cases, it can cause pingueculitis, a type of inflammation that causes redness, swelling, and discomfort. Although the exact cause of pinguecula is unknown, environmental factors and age-related changes in the conjunctiva are thought to play important roles. Preventive measures, such as wearing UV-protective sunglasses and hats, can help lower the likelihood of developing this condition. Early detection and treatment are critical for alleviating symptoms and avoiding complications.
Pinguecula Care and Treatment
The primary goals of pinguecula management and treatment are to relieve symptoms and prevent further irritation. Conservative approaches, medical therapies, and surgical interventions are all standard treatment options, depending on the severity of the condition and the patient’s specific symptoms.
Conservative Approaches: In many cases, conservative management is enough to control pinguecula. Patients should wear UV-protected sunglasses and wide-brimmed hats to shield their eyes from UV radiation and environmental irritants. Lubricating eye drops, such as artificial tears, can alleviate the dryness and discomfort associated with pinguecula. These measures are usually effective in mild cases where the pinguecula does not cause any noticeable symptoms.
Medical Therapies: When conservative approaches fail, medical therapies may be used to alleviate symptoms. Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids can be used to alleviate inflammation and discomfort. NSAIDs, such as ketorolac, work by inhibiting inflammatory pathways, which reduces redness and swelling. Topical corticosteroids, such as prednisolone, are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that can provide immediate relief from symptoms. However, long-term corticosteroid use is not recommended due to the risk of side effects such as increased intraocular pressure and cataract formation.
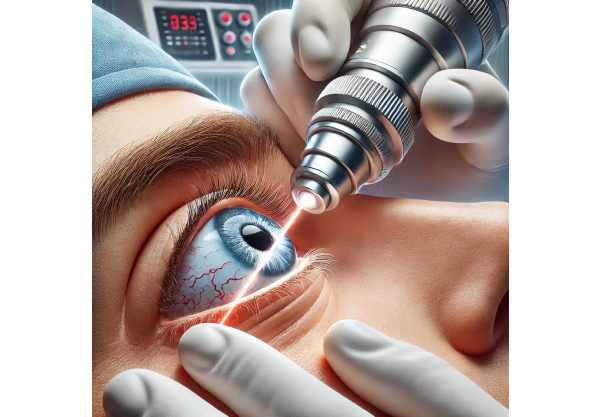
Surgical Interventions: If pinguecula causes significant discomfort, cosmetic concerns, or complications such as recurring inflammation, surgical removal may be an option. Surgical excision involves removing the pinguecula and suturing the conjunctiva. This procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia and is fairly simple. To promote healing and prevent infection, postoperative care includes the use of topical antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications. While surgery can effectively remove the lesion, there is a risk of recurrence, especially if the patient remains exposed to environmental risk factors.
Innovative Pinguecula Treatment Options
The treatment landscape for pinguecula has changed with the introduction of novel therapies and advanced technologies, giving patients new hope for effective and minimally invasive solutions. These cutting-edge treatments are intended to improve patient outcomes, lower recurrence rates, and alleviate the discomfort associated with traditional methods.
Amniotic Membrane Transplantation: Amniotic membrane transplantation (AMT) is a new treatment option for pinguecula that involves grafting amniotic membrane tissue into the affected area. The amniotic membrane, which comes from the placenta’s innermost layer, has anti-inflammatory, scarring, and healing properties. It promotes epithelialization and reduces inflammation, making it a good treatment for recurring or severe pinguecula. AMT is an outpatient procedure with promising results in terms of recurrence rates and cosmetic outcomes.
Femtosecond Laser-Assisted Surgery: The application of femtosecond laser technology to ocular surgery has transformed the treatment of a variety of eye conditions, including pinguecula. When compared to traditional surgical methods, femtosecond laser-assisted surgery allows for more precise and minimally invasive pinguecula removal with less tissue damage and faster healing. The laser generates ultra-short light pulses to precisely dissect the pinguecula while minimizing trauma to the surrounding tissues. This advanced technique improves surgical precision, reduces post-operative discomfort, and lowers the risk of recurrence.
Autologous Serum Eye Drops: Autologous serum eye drops are a new therapeutic approach that uses the patient’s own blood serum to create personalized eye drops. These drops contain important growth factors and nutrients that promote healing and reduce inflammation. Autologous serum eye drops have been shown to be effective in treating dry eye symptoms and ocular surface disorders, such as pinguecula. These drops can relieve discomfort and improve the overall health of the ocular surface by stimulating the conjunctiva’s natural healing process.
Topical Immunomodulatory Agents: Recent advances in immunomodulatory therapies have opened up new options for treating pinguecula. Topical cyclosporine A and lifitegrast are immunomodulatory drugs that can reduce inflammation and improve symptoms in pinguecula patients. Cyclosporine A, a common treatment for dry eye disease, inhibits T-cell activation and reduces inflammatory cytokine production. Lifitegrast, another immunomodulatory agent, works by targeting lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) to reduce inflammation. These agents are an alternative to traditional corticosteroids, providing effective symptom relief while lowering the risk of side effects.
Collagen Cross-Linking (CXL): Collagen cross-linking is a novel technique that has potential applications for pinguecula. CXL entails the use of riboflavin (vitamin B2) eye drops followed by exposure to UVA light. This procedure strengthens the collagen fibers in the cornea and conjunctiva, increasing structural integrity. In the case of pinguecula, CXL can help stabilize the conjunctival tissue, slow the progression of the lesion, and prevent relapse. The efficacy of CXL for pinguecula is still being studied, but preliminary findings are encouraging.
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) is a non-invasive treatment that targets abnormal tissues with photosensitizing agents and light. PDT has been tested on a variety of ocular surface conditions, including pinguecula. The treatment consists of applying a photosensitizing agent to the pinguecula and then exposing it to a specific wavelength of light. This activates the photosensitizer, causing selective destruction of the abnormal tissue while leaving healthy surrounding tissues unharmed. PDT provides a targeted and precise approach to pinguecula treatment while minimizing discomfort and downtime.
Gene Therapy: Gene therapy is a growing field with potential applications in pinguecula treatment. Gene therapy, which targets specific genetic pathways involved in pinguecula development and progression, aims to correct underlying abnormalities and prevent lesion formation. Although still in the experimental stage, gene therapy has the potential to provide long-term and possibly curative treatments for pinguecula. Ongoing research aims to identify relevant genetic targets and develop safe and effective delivery methods for therapeutic genes.
Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery: Nanotechnology has transformed drug delivery systems, creating new opportunities for the targeted and sustained release of therapeutic agents. Nanoparticles can be designed to deliver anti-inflammatory, anti-scarring, and healing agents directly to the pinguecula. This targeted approach increases treatment efficacy while reducing systemic side effects. Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems are being investigated for a variety of ocular conditions, including pinguecula, with the hope of improving patient outcomes and reducing the need for frequent medication administration.
Biodegradable Implants: Biodegradable implants represent a novel approach to delivering long-acting medications for pinguecula treatment. These implants are intended to gradually release therapeutic agents over time, providing long-term relief from symptoms while reducing the frequency of medication administration. Biodegradable implants can be placed in the conjunctival tissue, where they gradually degrade and release the medication. This approach ensures consistent drug delivery, increases patient compliance, and reduces the need for frequent eye drops or injections.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Diagnosis and Monitoring: The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in ophthalmology has transformed the diagnosis and management of a variety of ocular conditions, including pinguecula. AI algorithms can analyze large datasets from imaging studies, such as anterior segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT) and slit-lamp photographs, to detect subtle changes and predict pinguecula progression. AI-powered tools enable earlier diagnosis, more accurate monitoring, and personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s specific needs. Healthcare providers can use AI to provide more precise and effective pinguecula management.
Alternative Treatment Options for Pinguecula
In addition to traditional and cutting-edge medical treatments for pinguecula, several alternative treatment methods have received attention for their potential efficacy. These methods frequently emphasize natural and holistic approaches, with a focus on lifestyle changes, dietary interventions, and alternative therapies. While the scientific evidence for some alternative treatments is limited, many patients report symptomatic relief and improved eye health from these practices.
*1. Nutritional Interventions
Diet is essential for maintaining ocular health, and certain nutrients have been identified as beneficial in the prevention and treatment of pinguecula. Incorporating specific foods and supplements into one’s diet can improve conjunctival health and reduce inflammation.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, flaxseeds, and chia seeds, have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce the irritation and inflammation caused by pinguecula. Regular consumption of these fatty acids may help to reduce dryness and improve overall eye comfort.
- Antioxidants: Vitamins C and E, as well as beta-carotene and zinc, are potent antioxidants that help protect ocular tissues from oxidative stress. Fruits and vegetables, nuts, and seeds all contain these nutrients. According to research, antioxidants can slow the progression of a variety of eye conditions, including pinguecula, by neutralizing free radicals and promoting cellular health.
- Lutein and Zeaxanthin: Leafy green vegetables such as spinach, kale, and collard greens contain high levels of these carotenoids. They accumulate in the retina and are thought to protect the eyes from harmful blue light and UV rays. Increased intake of lutein and zeaxanthin has been linked to a lower risk of developing pinguecula and other ocular surface disorders.
*2. Herbal Remedies
Herbal remedies have been used for centuries to treat various eye conditions, and some have shown promise in treating pinguecula. While more research is needed to confirm their efficacy, these treatments are generally considered safe when used correctly.
- Bilberry Extract: High in anthocyanins, bilberry extract is known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits. It is thought to improve microcirculation in the eyes, reducing irritation and dryness. Bilberry supplements are available in capsule form and can be added to a daily regimen to promote eye health.
- Eyebright (Euphrasia officinalis): Eyebright is a traditional herbal remedy that relieves eye inflammation and irritation. It’s available as an eye drop, tincture, and tea. To relieve the discomfort and redness caused by pinguecula, apply eyebright drops directly to the eyes.
- Turmeric: Curcumin, the active ingredient in turmeric, has strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Turmeric supplements or incorporating turmeric into one’s diet may help reduce conjunctival inflammation and relieve pinguecula symptoms.
**3. *Homeopathic treatments*
Homeopathy provides a variety of remedies designed to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes. While homeopathic treatments for pinguecula are based on individual symptoms and constitutional types, a number of remedies are commonly used to improve eye health.
- Natrum Muriaticum: This remedy is frequently recommended for dry, irritated eyes that feel gritty. It is especially useful for people who have eye discomfort as a result of environmental factors like wind and sunlight.
- Pulsatilla: Pulsatilla is recommended for people who have dry eyes that worsen in warm, stuffy environments but improve with fresh air. It can help to reduce inflammation and the appearance of pinguecula.
- Sulphur: Sulphur, which is known for its efficacy in treating a variety of inflammatory conditions, is used to treat red, itchy eyes that burn. It is beneficial for people whose symptoms are exacerbated by heat but relieved by cool compresses.
4. Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine practice that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to promote balance and healing. Acupuncture has been studied as a complementary therapy for a number of eye conditions, including pinguecula.
- Mechanism of Action: Acupuncture is thought to increase blood flow to the eyes, reduce inflammation, and regulate the immune system. Acupuncture can help alleviate symptoms of dryness, redness, and irritation by focusing on specific acupoints associated with eye health.
- Efficacy: Although research into the effectiveness of acupuncture for pinguecula is limited, some patients report symptomatic relief and improved eye comfort. Regular acupuncture sessions, combined with lifestyle and dietary changes, may improve overall eye health.
**5. *Eye exercises and palming*
Eye exercises and palming techniques are natural ways to relieve eye strain and improve circulation to the ocular tissues. Individuals with pinguecula may benefit from these practices, particularly those who spend long periods of time in front of screens or in UV-rich environments.
- Eye Exercises: Simple exercises like eye rotations, focusing on distant and nearby objects, and blinking can help relax the eye muscles and increase blood flow. To maintain eye health and reduce the risk of developing pinguecula, perform these exercises on a regular basis.
- Palming: Palming is the process of covering closed eyes with the palms of one’s hands to create a warm, dark environment. This technique relaxes the eye muscles, reduces strain, and promotes a state of calm. Palming can be done several times per day, particularly during breaks from activities that strain the eyes.
6. Hydration and humidity
Maintaining adequate hydration and creating a humid environment are critical for preventing and treating pinguecula. Dry air can aggravate symptoms and promote the development of ocular surface disorders.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day will keep your body and eyes hydrated. Proper hydration promotes tear production and helps to keep conjunctival tissues healthy.
- Humidification: Using a humidifier in dry indoor environments can help maintain moisture levels in the air, preventing dry and irritated eyes. This is especially important in areas with low humidity or during the winter, when indoor heating can reduce air moisture.
**7. *Protective eyewear*
Wearing protective eyewear is a simple but effective way to prevent the spread of pinguecula. Sunglasses that block 100% of UV rays and wrap around the sides of the eyes offer the most protection from harmful UV radiation and environmental irritants.
- UV Protection: High-quality sunglasses with full UV protection are essential for protecting the eyes from the harmful effects of UV rays. Polarized lenses can also reduce glare and provide better visual comfort.
- Wraparound Design: Sunglasses with a wraparound design offer additional protection by keeping dust, wind, and other irritants out of the eyes. This design is especially useful for people who spend a lot of time outdoors or participate in activities that expose them to environmental elements.
**8. *Lifestyle modifications*
Certain lifestyle changes can have a significant impact on the prevention and treatment of pinguecula. These changes aim to reduce risk factors while also promoting overall ocular health.
- Avoiding Smoking: Smoking is a known risk factor for a variety of eye diseases, including pinguecula. Quitting smoking can reduce inflammation, increase blood flow to the eyes, and improve the overall health of the ocular surface.
- Managing Screen Time: Excessive screen time can cause digital eye strain and worsen symptoms of dryness and irritation. Implementing the 20-20-20 rule (taking a 20-second break every 20 minutes to look at something 20 feet away) can help reduce eye strain and keep your eyes comfortable.
- Wearing Protective Gear: Individuals working in environments with high levels of dust, chemicals, or other irritants should wear protective eyewear, such as safety goggles, to avoid exposure and reduce the risk of developing pinguecula.
9. Complimentary Therapies
Several complementary therapies can be incorporated into the pinguecula treatment plan to improve overall eye health and well-being.
- Yoga and Meditation: These practices can help reduce stress, improve circulation, and promote relaxation. These practices may help people with pinguecula by relieving eye strain and improving overall ocular health.
- Aromatherapy: Using essential oils like lavender, chamomile, and frankincense can help to relax and reduce inflammation. These essential oils can be diffused or applied (diluted) around the eyes, but direct contact should be avoided.
- Massage Therapy: A gentle massage around the eyes and temples can increase blood flow, reduce tension, and relieve symptoms of dryness and discomfort. This therapy can be performed with clean fingers or a soft cloth, and it should be done with caution to avoid putting pressure on the eyes.






