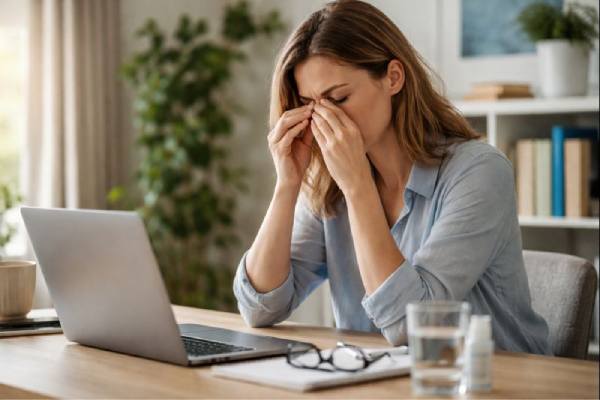
Stress rarely stays “in your head.” It changes breathing, muscle tension, hormones, sleep, and even how often you blink—so it is no surprise that your eyes can feel different when life gets intense. Many people notice blurry focus during a deadline week, eyelid twitching after poor sleep, or dry, gritty eyes when they are anxious and staring at screens for hours. Most of these symptoms are temporary and improve when stress and habits improve. Still, stress can also aggravate underlying issues such as dry eye disease, migraines, and even conditions where vision changes deserve prompt evaluation.
This guide explains what stress can do to your eyes, why it happens, and what helps most in real life. You will also learn the warning signs that should not be brushed off, plus a practical plan to protect your vision when stress is unavoidable.
Key Insights
- Stress can worsen dry eye symptoms, eye strain, and short-term focusing problems, especially with heavy screen use.
- Chronic stress can contribute to behaviors and body changes that may aggravate certain eye conditions in vulnerable people.
- Sudden vision loss, persistent distortion, new flashes or floaters, or eye pain are not “normal stress” symptoms.
- Use a daily eye-protection routine: structured screen breaks, deliberate blinking, and consistent sleep timing.
Table of Contents
- What stress does to your eyes
- Common eye symptoms linked to stress
- Why stress changes vision and comfort
- A practical routine to reduce eye stress
- When eye symptoms need medical attention
- What research says and what it does not
What stress does to your eyes
Stress can affect your eyes in two main ways: directly through body physiology (hormones, blood flow, muscle tension) and indirectly through behavior (screen time, sleep loss, skipped meals, caffeine, reduced time outdoors). The result is often a cluster of symptoms rather than one single “stress eye problem.”
In the short term, stress tends to push your nervous system toward a higher-alert state. Your shoulders rise, your jaw tightens, and the small muscles around the eyes can tense as well. This alone can make your eyes feel tired or “worked,” especially late in the day. Many people respond by squinting without realizing it, which can temporarily improve sharpness but increases muscle fatigue and headaches.
Stress also changes how you use your eyes. Under pressure, people often concentrate harder, stare longer, and blink less—particularly while reading, coding, gaming, or scrolling. A lower blink rate and more incomplete blinks can destabilize the tear film, which is the thin protective layer that keeps the surface of the eye smooth and comfortable. When that layer breaks up too quickly, you may feel burning, grittiness, and fluctuating blur.
Over longer periods, stress can amplify existing issues. If you already have mild dry eye, allergies, uncorrected vision, or migraine tendency, stress may be the “multiplier” that turns manageable symptoms into daily frustration. In a smaller subset of people, prolonged stress is discussed as a risk factor or trigger in certain retinal conditions where distortion or a “smudged” central spot can appear.
The important point is balance: most stress-related eye effects are real, common, and reversible. But you should treat persistent or dramatic changes in vision as a medical question, not a mindset problem.
Common eye symptoms linked to stress
Stress-related eye symptoms usually fall into predictable patterns. Knowing the patterns helps you respond calmly and correctly.
1) Eye strain and heavy, tired eyes
This often feels like sore eye sockets, forehead pressure, or a tired “pulling” sensation. It commonly shows up after hours of near work, especially when you are anxious and pushing through breaks. If you notice that your eyes feel better on weekends or vacations, that is a clue that habits and workload are involved.
2) Dryness, burning, and a gritty feeling
Stress does not “dry the eye” like desert air does, but it increases the behaviors that destabilize tears: reduced blinking, longer screen sessions, and poor sleep. Dry eye symptoms can also rise when you are dehydrated, using heating or air-conditioning, or taking certain medications that may be more common during stressful periods.
3) Fluctuating blur and focusing fatigue
Some people describe it as “my eyes cannot lock in,” especially when switching from near to far. Stress can increase muscle tension and reduce the smooth coordination needed for focusing. You may notice this more at the end of the day, when you are sleep-deprived, or after intense screen sessions.
4) Eyelid twitching
A twitching lower eyelid is classic during stressful weeks. It is often associated with fatigue and caffeine. It is usually harmless and self-limited, but it can be annoying and can last days to weeks.
5) Light sensitivity and headaches
Stress can be linked to migraine patterns and tension-type headaches. When headaches rise, light sensitivity and visual discomfort often follow. This can create a loop: discomfort increases stress, and stress increases discomfort.
6) Visual distortion or a new central “smudge”
This is less common, but it matters. If straight lines look wavy, or you have a persistent blurry patch in the center of vision, treat it as a medical symptom—not just “stress eyes.”
Why stress changes vision and comfort
Stress affects vision through a few overlapping mechanisms. You do not need to memorize the science, but understanding the “why” makes the solutions feel more logical.
Stress hormones and nervous system tone
When stress is high, the body releases hormones that influence alertness and circulation. In the short term, this can change muscle tone and how you perceive discomfort. Many people become more aware of sensations they would normally ignore, including dryness and tension around the eyes.
Blink behavior and tear film stability
Blinking is not just a reflex—it is maintenance. A full blink spreads oils from eyelid glands across the tear film, slows evaporation, and smooths the optical surface. Under stress, people often stare. They blink less, and blinks are more likely to be incomplete. The result is faster tear breakup and more surface irritation. This is one reason stress-heavy screen days can cause both dryness and blur: the “lens” of the tear layer becomes uneven.
Focus system overload
Your eyes constantly coordinate focusing (accommodation) and alignment (how both eyes point together). Stress can make you clench and hold tension, which can translate into “tight focus” patterns that feel like fatigue when you try to relax your gaze. Add long near work and poor posture, and the focus system becomes more error-prone by evening.
Sleep disruption and inflammation
Sleep is when the body resets many regulatory systems. During poor sleep, pain sensitivity increases, inflammation can rise, and the eyes may feel more irritable. If stress shortens sleep for weeks, you often see a noticeable increase in dry eye complaints and headache frequency.
Stress-linked conditions
Certain eye problems are frequently discussed in relation to stress. For example, eyelid myokymia is commonly associated with stress and fatigue. Another example is central serous chorioretinopathy, a retinal condition that has been linked in research discussions to stress biology and corticosteroid pathways. In glaucoma care, stress is also discussed as a possible factor that may influence disease course in some people, though it is not a simple cause-and-effect relationship.
The practical takeaway: stress rarely acts alone. It works through habits (screens, sleep, caffeine), surface maintenance (blinking), and body tension (neck, face, and eye muscles). Fixing just one piece helps, but fixing two or three usually changes everything.
A practical routine to reduce eye stress
If you want your eyes to feel better during stressful seasons, you need a routine that is simple enough to repeat. The goal is not perfection—it is lowering the daily “load” on the visual system.
Step 1: Use structured screen breaks
The simplest approach is still effective: every 20 minutes, look at something far away for 20 seconds. If that feels disruptive, scale it: every 30 minutes, take 30 seconds. What matters is giving the focus system a reset. During the break, let your shoulders drop and unclench your jaw.
Step 2: Do a deliberate blink reset
Two or three times per hour during screen work, do this quick sequence:
- Close your eyes gently for 2 seconds.
- Open, then do 5 slow, complete blinks.
- Finish with one “squeeze blink” (firm but not painful), then relax.
This helps restore tear film stability, especially if your blinks have become shallow.
Step 3: Protect your evenings
Eyes often feel worse at night because stress and screens collide with fatigue. Choose one boundary:
- Stop close-up screen work 60 minutes before bed, or
- Switch to larger text and lower brightness after dinner, or
- Use audio for the last hour (calls, podcasts) instead of visually demanding tasks.
Step 4: Reduce eyelid twitch triggers
If your eyelid is twitching, treat it like a recovery signal:
- Prioritize sleep for 3 nights in a row.
- Reduce caffeine for a week (especially after midday).
- Add a short walk outdoors daily to reduce stress load and soften intense near focus.
Step 5: Adjust the environment
Small changes matter:
- Keep the screen slightly below eye level to reduce wide-eye exposure and evaporation.
- Avoid direct airflow from vents or fans aimed at your face.
- Use consistent lighting to reduce glare and squinting.
Step 6: Use eye drops thoughtfully
If you use lubricating drops, preservative-free options are often better for frequent use. Drops can help symptoms, but they work best when you also fix the behavior causing tear instability.
This routine is not “anti-stress.” It is eye-smart behavior that makes stress less visible in your vision.
When eye symptoms need medical attention
It is easy to dismiss symptoms during stressful periods. The problem is that serious eye conditions can also appear during stressful periods—so the timing can mislead you. Use this section as a safety filter.
Seek urgent evaluation (same day if possible) if you have:
- Sudden vision loss in one or both eyes
- New flashes of light, a shower of floaters, or a curtain-like shadow in vision
- Eye pain with redness, nausea, or halos around lights
- New double vision that persists
- A new blind spot, persistent central smudge, or lines that look wavy
These are not typical “stress symptoms,” even if you are under pressure.
Schedule a prompt eye visit (days to weeks) if you have:
- Blurry vision that lasts more than 1–2 weeks despite better sleep and fewer screens
- Dry eye symptoms that require drops multiple times daily for relief
- Eyelid twitching that continues beyond a few weeks, spreads to other facial muscles, or interferes with opening the eye
- Frequent headaches with visual symptoms (sparkles, zigzags, temporary blind areas), especially if new for you
If you have glaucoma risk or known glaucoma
Stress management can be part of a broader plan, but it should not replace glaucoma monitoring and treatment. If you have glaucoma or a strong family history, keep routine follow-ups and report any meaningful symptom changes.
If you have diabetes or blood pressure issues
Stress can destabilize routines and may affect blood sugar and blood pressure. Vision blur in these settings deserves extra caution because it may reflect systemic changes that also affect the retina.
A practical rule
If a symptom changes quickly with rest, breaks, and hydration, it is more likely to be functional strain. If a symptom persists, distorts, or progresses—treat it as a medical problem until proven otherwise.
You do not need to panic. You just need to give your eyes the same respect you give chest pain or persistent neurological symptoms: timing matters, and evaluation is protective.
What research says and what it does not
The science around stress and eye health is active, and it is nuanced. Stress is not usually a single “cause” of eye disease. More often, it is a contributing factor that interacts with sleep, inflammation, hormones, and behaviors such as screen exposure.
Dry eye and mental health links
Research increasingly discusses relationships between dry eye symptoms and anxiety or depression measures. The relationship can run both ways: discomfort can increase anxiety, and anxiety can increase discomfort, attention to symptoms, and behaviors that worsen tear stability. Some studies also explore stress biomarkers (such as cortisol) and their relationship to ocular surface measures.
Stress and eyelid twitching
Clinical resources consistently describe eyelid myokymia as commonly associated with stress, fatigue, and stimulants like caffeine. Importantly, typical eyelid myokymia is benign. The research emphasis is less about “damage” and more about triggers, reassurance, and when to evaluate for other disorders.
Central serous chorioretinopathy and stress biology
Central serous chorioretinopathy has long been discussed in the context of stress and corticosteroid pathways. This does not mean everyday stress guarantees a retinal problem. It means that if someone develops characteristic symptoms (distortion, central blur), clinicians consider stress physiology and steroid exposure among the relevant risk factors.
Glaucoma and stress
A growing body of discussion explores whether psychological or physiological stress might influence glaucoma development or progression in some people, possibly via vascular regulation, autonomic nervous system shifts, or pressure dynamics. Still, glaucoma is complex. Eye pressure, optic nerve susceptibility, blood flow factors, genetics, and age remain central. Stress management is best viewed as supportive—valuable for general health and potentially helpful for symptom burden and adherence—rather than a substitute for medical care.
What research does not support
- The idea that stress alone “ruins your eyesight” in a direct, inevitable way
- The idea that you can treat serious eye disease with relaxation techniques alone
- The idea that all stress-related vision changes are harmless
A fair summary is this: stress commonly worsens comfort and short-term visual performance, and it may interact with certain conditions in vulnerable people. The smartest approach is practical—reduce visual load, protect sleep, address dry eye habits, and get evaluated when symptoms are persistent or unusual.
References
- Impact of Physiological and Psychological Stress on Glaucoma Development and Progression: A Narrative Review 2025 (Review)
- Treatment of central serous chorioretinopathy: new options for an old disease 2025 (Review)
- Dry eye disease and psychosomatics—benefits of mind-body therapy for dry eye disease 2025 (Review)
- Association Between Dry Eye Disease with Anxiety and Depression Among Medical Sciences Students in Qassim Region: Cortisol Levels in Tears as a Stress Biomarker 2024
- Eyelid Myokymia – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf 2023
Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Vision changes can have many causes, some of which require urgent care. If you have sudden vision loss, new flashes or floaters, eye pain, marked redness, or persistent distortion (such as wavy lines), seek prompt evaluation by an eye care professional or emergency service. If you have chronic conditions such as glaucoma, diabetes, or autoimmune disease, follow your clinician’s guidance and keep scheduled eye exams.
If you found this helpful, please consider sharing it on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or any platform you prefer, and follow us on social media. Your support through sharing helps our team continue producing high-quality health content.