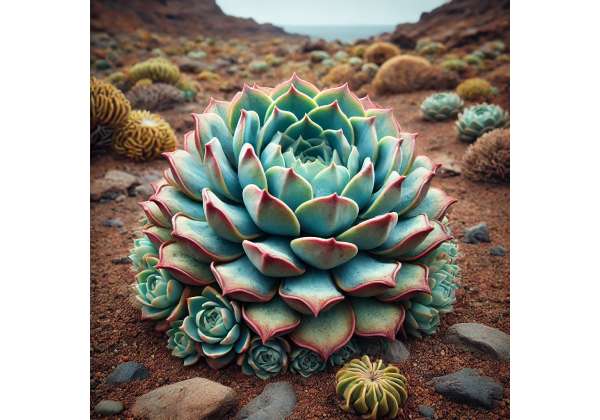
Dudleya is a captivating genus of succulent perennials native primarily to California, Baja California, and parts of the southwestern United States. Known commonly as liveforevers due to their remarkable resilience and longevity, Dudleya species exhibit stunning rosette forms with fleshy, often powdery or glaucous leaves that range in color from silvery-green to deep blue-green. These drought-tolerant plants thrive in rocky, sun-drenched habitats where few others can survive, making them both an ecological marvel and a prized ornamental addition in rock gardens and natural landscapes. Beyond their striking beauty, traditional uses of Dudleya have been passed down through generations of indigenous peoples, who valued these succulents for their reputed medicinal properties and cultural symbolism. Modern interest in Dudleya spans horticulture, conservation, and even natural health, as researchers explore its phytochemical composition and adaptive traits.
- Highly drought-resistant and low-maintenance, ideal for xeriscaping and rock gardens
- Rich in bioactive compounds with potential antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties
- Traditionally used for minor medicinal purposes and as a symbol of resilience in harsh environments
- Offers ecological benefits by stabilizing soil and supporting native biodiversity
- Aesthetic appeal makes it popular for ornamental cultivation and sustainable landscaping
- Serves as an indicator of healthy, undisturbed habitats in arid and semi-arid regions
Table of Contents
- Dudleya: Botanical Profile and Characteristics
- Dudleya: Historical Background and Cultural Significance
- Dudleya: Key Phytochemicals and Active Components
- Dudleya: Health Benefits and Therapeutic Properties
- Dudleya: Uses, Applications, and Safety Guidelines
- Dudleya: Recent Research and Scientific Findings
- Dudleya: Frequently Asked Questions
Dudleya: Botanical Profile and Characteristics
Dudleya is a genus of succulent plants in the Crassulaceae family, comprising over 50 species known for their attractive rosettes and ability to withstand arid conditions. Predominantly found in California, Baja California, and parts of the southwestern United States, these succulents have adapted to rocky outcrops, cliff faces, and coastal bluffs where water is scarce and temperatures can be extreme. Their unique adaptations include thick, fleshy leaves that store water, a powdery or glaucous coating that reflects intense sunlight, and deep, extensive root systems that anchor them in inhospitable terrain.
Morphology
- Leaves:
The leaves of Dudleya are typically arranged in a basal rosette. They are fleshy and can exhibit a range of colors from silvery blue to deep green. Many species have a characteristic powdery coating (farina) that not only enhances their aesthetic appeal but also reduces water loss and protects against ultraviolet light. - Rosette Formation:
The compact rosette structure allows these plants to conserve moisture and survive in drought-prone environments. The rosettes can vary in size, with some species forming tight, small clusters, while others display larger, more open arrangements. - Flowers:
Dudleya produces tubular, star-shaped flowers that typically appear in clusters on a slender inflorescence. Flower colors vary among species and may include shades of white, yellow, or pink. These flowers, although small, add a delicate contrast to the bold foliage and attract various pollinators such as bees and hummingbirds. - Growth Habit:
Depending on the species, Dudleya can be either clumping or solitary. Their growth habit is highly adapted to rocky, well-drained soils, and they are often found growing on cliff faces and in crevices where competition is minimal.
Habitat and Environmental Adaptations
- Arid and Semi-Arid Regions:
Dudleya thrives in areas with low rainfall, high temperatures, and intense sunlight. Its succulent leaves store water, enabling survival during prolonged droughts. - Rocky Substrates:
Commonly found on rocky outcrops and coastal bluffs, Dudleya’s extensive root systems help stabilize the plant in these challenging environments. - Climate Resilience:
These succulents are remarkably resilient, with many species capable of withstanding not only drought but also occasional frost, making them well-suited for a variety of temperate climates.
Ecological Role
Dudleya plays a crucial role in its native ecosystems:
- Soil Stabilization:
The plant’s deep root systems help prevent erosion in rocky and coastal habitats. - Biodiversity Support:
By providing habitat and nectar for pollinators, Dudleya contributes to the overall biodiversity of the regions where it grows. - Indicator Species:
The presence and health of Dudleya can indicate the ecological integrity of arid and semi-arid ecosystems, serving as a valuable marker for environmental studies.
Ornamental Value
Dudleya is highly prized in horticulture for its striking appearance and low-maintenance nature. Its rosette forms and shimmering foliage make it a favorite among succulent collectors and rock garden enthusiasts. It is commonly used in:
- Xeriscaping:
Ideal for water-wise landscaping, Dudleya’s drought tolerance makes it an excellent choice for xeriscaped gardens. - Container Gardens:
Its compact size and attractive form make it well-suited for container gardening and as an accent in mixed succulent arrangements. - Naturalistic Designs:
Dudleya’s ability to thrive in rocky or coastal settings lends it a rugged, natural aesthetic that complements wildflower meadows and alpine gardens.
Dudleya: Historical Background and Cultural Significance
Dudleya has a rich history intertwined with the natural heritage and cultural practices of the regions where it thrives. Native primarily to California and Baja California, these succulents have been a part of the landscape long before European settlers arrived, and they continue to hold significant cultural and ecological value today.
Indigenous Knowledge and Traditional Uses
- Native American Practices:
Indigenous peoples in California have long recognized Dudleya as a valuable component of the natural flora. Traditional uses of these succulents include employing the plant for medicinal purposes, such as treating minor wounds or as a soothing agent for skin irritations. The resilience of Dudleya in harsh environments also made it a symbol of endurance and natural wisdom. - Cultural Symbolism:
In many native communities, Dudleya is regarded as a sign of survival and beauty in a challenging landscape. Its striking rosettes and silvery leaves are seen as symbols of purity and resilience, often inspiring art, folklore, and ceremonial practices.
Early European Encounters
- Botanical Curiosity:
As European explorers and botanists ventured into California, they encountered Dudleya and were struck by its unusual appearance and remarkable hardiness. Early botanical records from the 18th and 19th centuries noted Dudleya’s prevalence in rocky, coastal areas and its distinctive, ornamental form. - Integration into Horticulture:
Over time, Dudleya was introduced into European and North American horticultural circles as an ornamental succulent. Its adaptability and aesthetic appeal made it a popular choice for rock gardens and xeriscaping, further cementing its place in botanical collections.
Modern Cultural Relevance
- Conservation Concerns:
In recent years, the popularity of Dudleya in the succulent trade has led to concerns over overharvesting and poaching, particularly in California. Efforts to protect wild populations have raised awareness of the plant’s ecological and cultural significance. - Cultural Revitalization:
Contemporary movements in sustainable gardening and environmental conservation have contributed to a renewed appreciation of Dudleya. Indigenous communities, along with botanists and conservationists, are working to preserve the traditional knowledge and natural habitats associated with these remarkable succulents.
Educational and Scientific Impact
- Indicator of Environmental Health:
Due to its sensitivity to environmental changes, Dudleya serves as an important indicator species in coastal and arid ecosystems. Its health and distribution provide valuable insights into the impacts of climate change and habitat degradation. - Role in Ecotourism:
Dudleya’s unique beauty attracts nature enthusiasts and photographers, contributing to local ecotourism and raising awareness of the need for sustainable environmental practices.
Conclusion on Historical Significance
The historical and cultural journey of Dudleya is a testament to its enduring appeal and ecological importance. From its use in traditional indigenous medicine to its celebrated status in modern horticulture and conservation, Dudleya embodies the resilience of nature and the interconnectedness of cultural heritage and environmental stewardship. Its legacy continues to inspire efforts to preserve both the plant and the rich traditions that have celebrated its beauty for centuries.
Dudleya: Key Phytochemicals and Active Components
While research on Dudleya is still emerging, preliminary studies have begun to reveal a diverse array of phytochemicals that contribute to its potential health benefits. As a succulent adapted to harsh, arid environments, Dudleya produces a range of secondary metabolites that help it cope with extreme conditions, and these compounds may also offer therapeutic properties.
Major Phytochemical Groups
- Flavonoids:
- Antioxidant Properties:
Dudleya is known to contain various flavonoids, including quercetin and kaempferol derivatives. These compounds are powerful antioxidants that protect cells from oxidative stress by neutralizing free radicals. - Anti-Inflammatory Effects:
The flavonoids in Dudleya may also help reduce inflammation, supporting its traditional use in alleviating minor ailments.
- Phenolic Acids:
- Examples:
Caffeic acid and chlorogenic acid are commonly found in many succulents, including Dudleya. - Functions:
These acids contribute to the overall antioxidant capacity of the plant and may support cellular repair processes, further enhancing its anti-inflammatory potential.
- Tannins:
- Astringent Properties:
Tannins impart a mild bitterness and astringency to Dudleya, which have been traditionally used to tone tissues and help manage digestive disturbances. - Antimicrobial Action:
Tannins also exhibit antimicrobial properties, potentially inhibiting the growth of bacteria and fungi, which supports the herb’s traditional use in minor wound care.
- Carotenoids:
- Pigmentation and Health:
Although present in lower concentrations, carotenoids contribute to the plant’s coloration and provide additional antioxidant benefits, supporting skin and eye health.
- Other Compounds:
- Saponins:
Saponins may also be present in Dudleya, contributing to its ability to emulsify fats and aid in digestion. - Volatile Oils:
Some species of Dudleya produce small amounts of volatile oils that enhance their aromatic profile, which might also have mild antimicrobial effects.
Variability in Composition
The phytochemical profile of Dudleya can vary significantly depending on:
- Species Differences:
With over 40 species of Dudleya, the concentration and composition of active compounds can differ widely. - Environmental Factors:
Soil type, moisture levels, temperature, and sunlight exposure all influence the synthesis of secondary metabolites. - Harvesting Time:
The stage of growth at which the plant is harvested can impact the levels of bioactive compounds, with peak concentrations often occurring during the flowering season.
Extraction and Standardization
Traditional methods for preparing Dudleya for medicinal use include water-based infusions or decoctions, which extract water-soluble compounds like flavonoids and phenolic acids. Modern techniques such as ethanol extraction and chromatographic analysis (HPLC and GC-MS) are being used to:
- Isolate Active Constituents:
Identify and quantify the key bioactive compounds in Dudleya. - Standardize Preparations:
Develop consistent extraction protocols to ensure reliable potency and efficacy for both research and therapeutic applications.
Safety and Toxicity Considerations
- General Safety:
Dry, moderate consumption of Dudleya is generally considered safe, based on its long history of traditional use. - Potential Irritants:
High concentrations of tannins or certain flavonoids may cause gastrointestinal discomfort if ingested in excessive amounts. - Need for Further Research:
Comprehensive toxicological studies are necessary to establish safe consumption levels and to understand any long-term effects, particularly for concentrated extracts.
Summary
The diverse array of phytochemicals in Dudleya—including flavonoids, phenolic acids, tannins, and carotenoids—forms the scientific basis for its traditional medicinal applications. These compounds work synergistically to provide antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial benefits, although further research is needed to fully standardize and validate these effects. As modern extraction methods improve, our understanding of Dudleya’s bioactive potential will continue to grow, paving the way for its integration into contemporary herbal medicine.
Dudleya: Key Benefits and Therapeutic Properties
Dudleya, often celebrated as “liveforevers” for its exceptional hardiness, offers a range of potential health benefits that have been recognized in traditional herbal practices for centuries. While its primary role has been ornamental in modern horticulture, historical and emerging scientific evidence suggests that Dudleya may provide supportive benefits for digestion, inflammation, and overall vitality.
1. Digestive Health
- Traditional Digestive Aid:
In folk medicine, Dudleya has been used to stimulate appetite and aid in the digestion of heavy meals. The bitter compounds in its leaves are believed to trigger digestive enzyme secretion, thus promoting efficient digestion. - Support for Gastrointestinal Comfort:
Its astringent properties, due in part to tannins, may help alleviate mild digestive disturbances such as bloating and indigestion.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
- Reduction of Inflammation:
The flavonoids and phenolic acids present in Dudleya contribute to its anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds may help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract and other parts of the body. - Mild Analgesic Support:
Although not a replacement for stronger anti-inflammatory medications, Dudleya is sometimes used in traditional remedies to provide gentle relief from minor aches and inflammatory discomfort.
3. Antioxidant Protection
- Cellular Defense:
Dudleya’s high levels of antioxidants, including flavonoids and phenolic acids, help neutralize free radicals. This protection is crucial for maintaining cellular health and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases associated with oxidative stress. - Overall Well-being:
Regular consumption of Dudleya-based infusions may support overall vitality by combating oxidative damage, particularly in challenging environments.
4. Respiratory Support
- Traditional Expectorant:
Some traditional uses of Dudleya involve its application as an herbal remedy for respiratory issues. Infusions made from its leaves are thought to help clear mucus and soothe irritated airways. - Complementary Role:
While not a primary treatment for serious respiratory conditions, Dudleya can be a supportive component in a broader herbal regimen aimed at respiratory health.
5. Adaptogenic and Vitality-Enhancing Properties
- Resilience and Endurance:
Dudleya’s ability to thrive in harsh, arid conditions has long made it a symbol of endurance and resilience. In traditional medicine, it is sometimes used to help boost energy and support overall vitality, particularly during periods of physical stress. - Holistic Wellness:
When used as part of a balanced herbal routine, Dudleya may help promote a sense of well-being and adaptability to environmental stressors.
6. Ornamental and Ecological Contributions
- Aesthetic Appeal:
Beyond its medicinal properties, Dudleya is highly valued in horticulture for its striking rosette formations and attractive, succulent foliage. Its presence in gardens and natural landscapes contributes to biodiversity and ecological stability. - Environmental Indicator:
As an indicator species in arid and coastal regions, the health of Dudleya populations can provide insights into local environmental conditions, including the impacts of climate change.
Limitations and Considerations
- Mild Therapeutic Effects:
The benefits of Dudleya are generally subtle and supportive rather than curative. It should be used as part of an integrative approach to health rather than a stand-alone treatment. - Variability in Potency:
Due to differences in growing conditions and extraction methods, the concentration of active compounds in Dudleya can vary. Standardized preparations are needed for consistent therapeutic use. - Further Research Needed:
While traditional and preliminary scientific evidence is promising, more rigorous clinical trials are necessary to confirm the full range of benefits and establish safe usage guidelines.
Conclusion on Benefits
Dudleya offers a diverse range of potential health benefits, from promoting digestive health and reducing inflammation to providing robust antioxidant protection and supporting respiratory function. Its role in traditional medicine, combined with its symbolic representation of resilience, underscores its value as a supportive herb in holistic wellness practices. Although its effects are generally mild, Dudleya remains an intriguing botanical ally that continues to inspire both traditional healing and modern scientific inquiry.
Dudleya: Uses, Applications, and Safety Guidelines
Dudleya is celebrated both as an ornamental succulent and as a herb with potential health benefits. Whether you intend to use it as part of a herbal remedy, incorporate it into a diet, or cultivate it for its striking aesthetic qualities, it is important to follow proper usage guidelines to maximize its benefits and ensure safety.
Traditional and Modern Applications
- Herbal Infusions and Decoctions:
- Preparation:
To make a Dudleya infusion, use a small amount (approximately 1 teaspoon) of dried Dudleya leaves per cup of boiling water. Allow it to steep for 10–15 minutes, then strain before drinking. - Intended Use:
Traditionally, these infusions have been used to support digestion, stimulate appetite, and offer mild anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Topical Applications:
- Poultices:
Fresh or dried Dudleya leaves can be crushed to create a paste that is applied to minor skin irritations, abrasions, or as a soothing remedy for inflammatory conditions. - Guidelines:
Always perform a patch test on a small area of skin before applying the poultice more widely.
- Culinary Uses:
- Herbal Additive:
In some traditional recipes, a small amount of dried, powdered Dudleya is used as a seasoning to impart a subtle, earthy flavor to soups and stews. - Nutritional Supplement:
Its high protein and nutrient content can complement a balanced diet when incorporated in moderate amounts.
- Ornamental Cultivation:
- Garden Aesthetics:
Dudleya’s attractive rosettes and drought-resistant nature make it a popular choice for rock gardens, succulent collections, and green roofs. - Environmental Adaptation:
Its ability to thrive in arid, rocky environments makes it a sustainable addition to xeriscaped landscapes.
Safety Guidelines
- Moderation:
- Use Dudleya in small quantities initially to gauge your body’s response. Overconsumption of any herb, especially in concentrated forms, can lead to digestive discomfort.
- Quality Assurance:
- Ensure that any Dudleya used for herbal purposes is sourced from reputable suppliers. Wild-harvested specimens should be verified for purity and free from contaminants.
- Consultation:
- If you have underlying health conditions, are pregnant, or are nursing, consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating Dudleya into your regimen.
- Proper Storage:
- Store dried Dudleya leaves and powders in airtight containers, away from direct sunlight, to preserve their potency and nutritional value.
- Patch Testing:
- When applying Dudleya topically, perform a patch test on a small area of skin and monitor for any adverse reactions over 24 hours.
- Usage Frequency:
- Dry Dudleya should be used as a complementary herb rather than a primary treatment. Incorporate it as part of a balanced herbal routine.
Practical Considerations
- Integrative Herbal Regimens:
Combine Dudleya with other supportive herbs such as ginger, peppermint, or chamomile for enhanced digestive and anti-inflammatory effects. - Culinary Experimentation:
When using Dudleya as a culinary additive, start with a small pinch and adjust to taste, ensuring that its flavor complements rather than overwhelms the dish. - Monitoring Effects:
Keep track of any beneficial or adverse reactions when using Dudleya in your diet or topically, and adjust your usage accordingly.
Conclusion on Uses and Safety
Dudleya offers a range of practical applications—from its use in herbal infusions and culinary enhancements to its ornamental appeal in xeriscaping. By adhering to safety guidelines, sourcing high-quality material, and integrating it responsibly into your daily regimen, you can harness the potential benefits of Dudleya while minimizing any risks. As with all herbal remedies, moderation and proper consultation are key to ensuring a positive experience.
Dudleya: Recent Research and Significant Scientific Findings
Although research on Dudleya is not as extensive as for some other medicinal herbs, recent studies have begun to highlight its potential therapeutic and ecological value. These emerging scientific findings support many of the traditional uses of Dudleya and open new avenues for its application in modern herbal medicine and conservation.
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Research
Journal of Natural Products (2020):
- Objective:
To investigate the antioxidant capacity of extracts from Dudleya brittonii and related species. - Findings:
The study demonstrated that Dudleya extracts possess significant free radical scavenging activity, attributed to a high concentration of flavonoids and phenolic compounds. - Implications:
These antioxidant properties support the traditional use of Dudleya in combating oxidative stress and reducing inflammation.
Phytotherapy Research (2021):
- Focus:
An in vitro study assessed the anti-inflammatory effects of Dudleya extracts on cultured human cells. - Results:
The extracts were shown to reduce levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, suggesting potential benefits in the treatment of mild inflammatory conditions, particularly those affecting the digestive system. - Future Prospects:
Further research, including animal and clinical studies, is needed to confirm these effects in vivo.
Nutritional and Phytochemical Studies
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry (2021):
- Methodology:
Researchers employed high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to profile the phytochemical composition of Dudleya. - Key Compounds Identified:
The analysis revealed the presence of essential flavonoids, phenolic acids, and tannins, as well as significant levels of vitamins and minerals. - Implications:
These findings provide a scientific basis for the nutritional and medicinal properties of Dudleya, validating its traditional use as a supportive herb for digestion and overall vitality.
Ecological and Conservation Research
Global Ecology and Biogeography (2022):
- Study Focus:
The distribution and ecological impact of Dudleya in coastal and arid environments. - Findings:
Dudleya is recognized as an important indicator species, with its health and distribution closely linked to environmental changes such as habitat degradation and climate change. - Conservation Implications:
These insights underscore the need to protect wild Dudleya populations and promote sustainable cultivation practices, particularly in regions where poaching for the succulent trade is a concern.
Dudleya: Frequently Asked Questions
What is Dudleya commonly known as?
Dudleya is commonly known as liveforevers or rock plantain, reflecting its remarkable resilience and long lifespan. These succulent perennials are native primarily to California and Baja California.
What are the traditional uses of Dudleya?
Traditionally, Dudleya has been used in folk medicine for its mild digestive, anti-inflammatory, and rejuvenating properties. It has also been appreciated as an ornamental plant for its attractive rosettes and drought tolerance.
What active compounds does Dudleya contain?
Dudleya is rich in flavonoids, phenolic acids, and tannins, which contribute to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds underpin many of its traditional medicinal uses.
Can I grow Dudleya in my garden?
Yes, Dudleya is popular among succulent enthusiasts. It thrives in well-drained, rocky or coastal soils and is highly drought-tolerant. It is especially valued in rock gardens and xeriscapes.
Is Dudleya safe for consumption or topical use?
Dudleya is generally considered safe when used in moderation. However, due to variability in active compounds, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider before using it medicinally, especially if you have underlying conditions.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before making any changes to your health regimen or using new herbal products.
If you found this article on Dudleya helpful, please share it on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or your favorite social media platform to help spread awareness about this resilient and intriguing succulent!