Decongestants Explained: Pseudoephedrine vs Phenylephrine vs Nasal Sprays
A blocked nose can make everything harder—sleep, exercise, work, even tasting food. What surprises many people is that “congestion” is usually less about extra...
Decongestants That Actually Work: Pseudoephedrine, Oxymetazoline, and Safer Alternatives by Condition
Nasal congestion is more than “too much mucus.” The blocked, pressurized feeling usually comes from swollen nasal lining and engorged blood vessels that narrow...
Dehydration with Flu: Signs, Risks, and Rehydration Tips
When you have the flu, dehydration can sneak up quickly—sometimes before you realize you’re even behind on fluids. Fever raises fluid needs, rapid breathing...
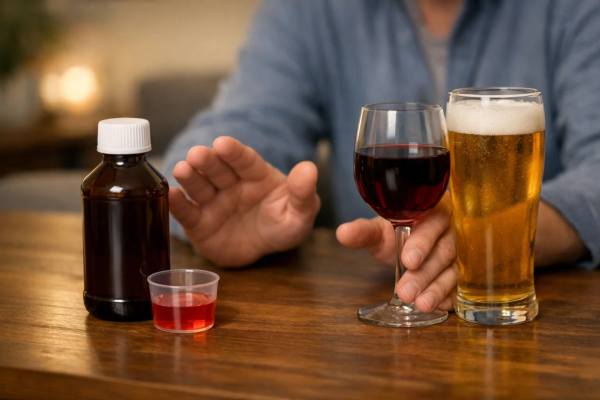
Dextromethorphan (Cough Syrup) and Alcohol: Why the Combo Can Be Dangerous
Dextromethorphan is one of the most widely used over-the-counter cough suppressants. When you have a dry, irritating cough from a cold or flu, it...
Disinfecting vs Ventilating: What Reduces Spread of Respiratory Viruses Most?
If you’ve ever tried to keep a household, classroom, or workplace healthy during respiratory virus season, you’ve probably faced the same question: should you...
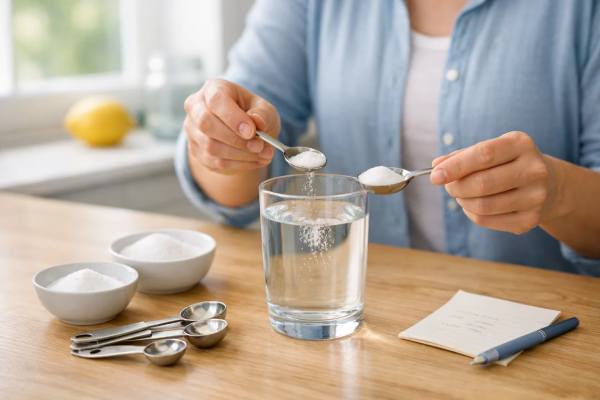
DIY ORS Recipe: The Safe Home Mix for Flu, Fever, and Diarrhea
When flu, fever, vomiting, or diarrhea hits, dehydration can become the problem behind the problem. You may not feel dramatically “thirsty,” yet your body...
Dry Air Cough: Winter Heating, Humidity, and Simple Fixes
A cough that shows up every winter can feel mysterious—especially when you are not “sick.” Often, the culprit is not an infection at all,...
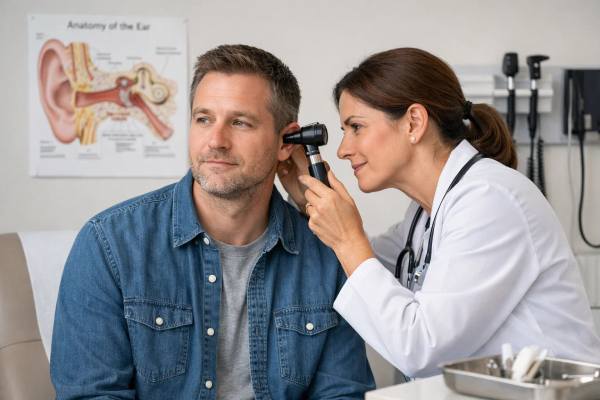
Ear Infection in Adults: Symptoms, Treatment, and When Antibiotics Help
Ear infections are often thought of as a childhood problem, yet adults can absolutely get them—sometimes with sharper pain, more pressure, and more disruption...
Ear Infection in Kids: Signs, Pain Relief, and When to See a Doctor
Ear infections are one of the most common reasons children end up in the pediatrician’s office—often after a cold, and often right when sleep...
Ear Pain After Flying with a Cold: Eustachian Tube Problems and How to Prevent Them Next Trip
Ear pain after a flight can feel unfairly intense when you already have a cold. The discomfort is not “just pressure” in a vague...
Ear Pain During a Cold: Causes, Home Care, and When to Treat
Ear pain during a cold can be alarming—especially when it shows up suddenly, wakes you at night, or makes hearing feel “foggy.” Most of...
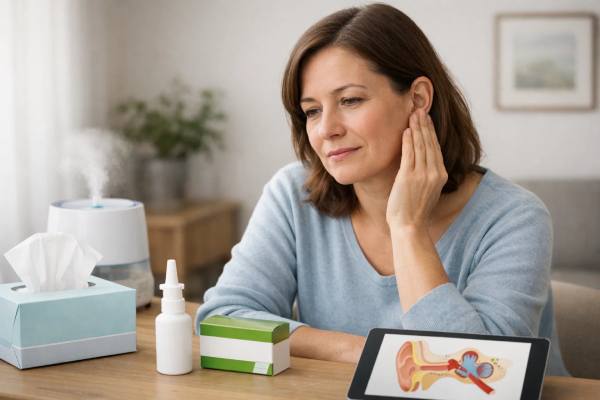
Ear Pressure and Popping: Congestion, Eustachian Tube Dysfunction, and Relief
Ear pressure and popping can be annoying, distracting, and sometimes painful—especially when you are congested from a cold, allergies, or a sinus flare. The...
Echinacea for Colds: Does It Work and Who Should Avoid It?
Echinacea sits in a unique space between folk remedy and modern supplement: it is widely used, heavily marketed, and genuinely studied—yet the answer to...
Elderberry for Cold and Flu: Benefits, Risks, and Drug Interactions
Elderberry is one of the most common “immune season” supplements, and it earns that attention for a few practical reasons: it is widely available,...
Electrolyte Drinks When Sick: What to Look For and What to Avoid
When you are sick, “hydration” is not always as simple as drinking more water. Fever, sweating, fast breathing, poor appetite, and especially vomiting or...
EVALI (Vaping-Associated Lung Injury): Symptoms, Warning Signs, and When to Go to the ER
EVALI is a serious lung injury linked to vaping that can escalate from “feeling a bit off” to dangerous breathing problems in a short...