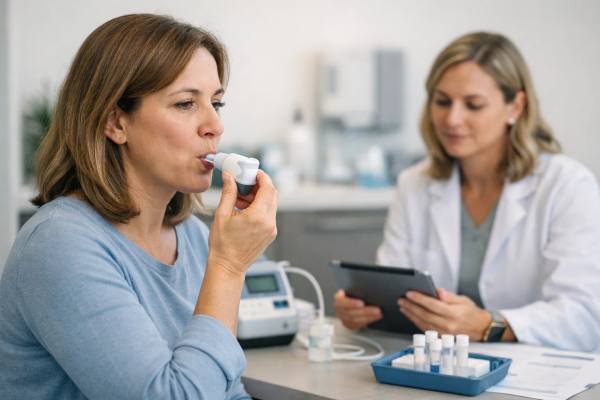
SIBO Breath Test: How It Works, Prep, and Interpreting Results
A SIBO breath test is one of the most common noninvasive ways clinicians look for excess microbial fermentation in the small intestine. When bacteria...
SIBO Relapse: Why It Comes Back and How to Reduce Recurrence
If you have dealt with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) once, a relapse can feel especially discouraging. The hard part is not always the...
SIBO Symptoms: Bloating, Gas, and Food Intolerance Explained
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) is often talked about as a single diagnosis, yet the day-to-day experience is usually a set of repeating patterns:...
SIBO Treatment: Antibiotics, Diet, and What to Expect
Treating small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) works best when you think beyond a single pill or diet and focus on the full process: lowering...
Silent Reflux (LPR): Throat Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Silent reflux—also called laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR)—can be confusing because it often shows up without classic heartburn. Instead, it can feel like a throat problem:...
Slippery Elm for Heartburn: Evidence, Best Forms, and Medication Timing
Heartburn can feel deceptively simple—just a burning sensation—but the reasons it shows up (and the best way to calm it) can vary widely. Slippery...
Small Intestinal Fungal Overgrowth (SIFO): Symptoms, Testing, and How It Differs from SIBO
Small intestinal fungal overgrowth (SIFO) is one of those diagnoses people often encounter after months of bloating, unpredictable bowel habits, and a growing list...
Sourdough Bread and Digestion: Why Some People Tolerate It Better (and When They Don’t)
Sourdough bread has a reputation for being “easier on the stomach,” and for some people that is genuinely true. The reason is not magic—it...
Spore-Based Probiotics: Bacillus Strains, IBS Claims, and Safety
Spore-based probiotics are often marketed as the “hardy” option: they can survive stomach acid, tolerate heat and shelf storage, and arrive in the gut...
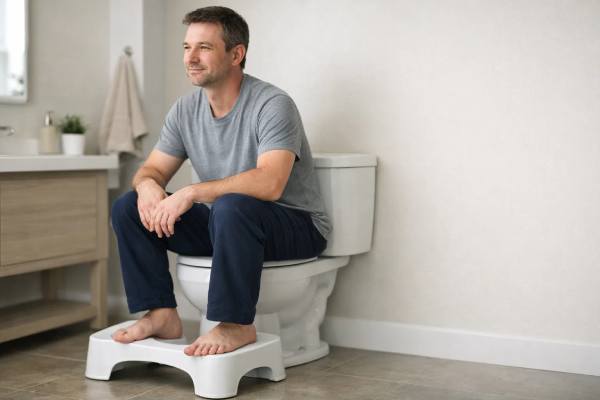
Squatty Potty Benefits: Does It Help Constipation and Hemorrhoids?
A toilet stool (often called a “Squatty Potty,” after the popular brand) is a simple tool: it lifts your feet while you sit, bringing...
Stomach Burning: Causes, Home Relief, and When It’s Serious
A burning feeling in the upper abdomen can be unsettling because it sits at the crossroads of many digestive conditions—from simple irritation after a...
Stomach Cramps and Diarrhea: Causes and When to Seek Care
Stomach cramps with diarrhea can feel dramatic—even when the cause is short-lived—because the gut reacts quickly to irritation, infection, or a food trigger. Most...
Stomach Noises (Borborygmi): Why Your Gut Gurgles and What It Means
Most people notice stomach noises at the worst possible moment: a quiet meeting, a first date, or right after a meal when you expected...
Stomach Ulcer Symptoms: Pain Patterns, Causes, and When to Seek Care
A stomach ulcer is a sore in the stomach lining that can cause discomfort, nausea, and sometimes surprisingly subtle symptoms. Many people imagine “classic”...
Stool Changes You Shouldn’t Ignore: A Practical Guide to Red Flags
Most stool changes are harmless and temporary, but a few patterns deserve prompt attention because they can signal bleeding, infection, inflammation, or problems with...
Stool DNA Tests (Cologuard) vs Colonoscopy: Accuracy, Pros and Cons, and Who Should Choose Which
Choosing a colorectal cancer screening test is less about finding a “perfect” option and more about matching the test to your risk, comfort level,...
Stool Softeners vs Laxatives: Which to Choose and When
Constipation is common, but “treating it” is not one-size-fits-all. Some people struggle with hard, dry stools that are painful to pass, while others feel...
Stress and Digestion: Why Anxiety Triggers Gut Symptoms
Most people learn about the “nervous stomach” the hard way: an important meeting, an intense argument, a stretch of sleepless nights—and suddenly your gut...
Sucralfate for Gastritis and Ulcers: Uses, Timing Rules, and Side Effects
When your stomach lining is irritated or ulcerated, the pain is often less about “too much acid” and more about exposed tissue being rubbed...
Sugar Alcohols (Sorbitol, Xylitol): Why They Cause Gas and Diarrhea
Sugar alcohols are a quiet workhorse of modern food and medicine: they sweeten without acting exactly like sugar, help keep “sugar-free” products palatable, and—especially...
Sulfur Burps: Causes, Stomach Bugs, and When to Worry
Sulfur burps—often described as “rotten egg burps”—are unpleasant, but they are also surprisingly informative. That distinctive smell usually comes from hydrogen sulfide gas, which...
Synbiotics vs Probiotics: What’s the Difference and Who Benefits?
Probiotics have become a familiar tool for digestive comfort, but synbiotics are now appearing on more labels and supplement shelves—often with the promise of...
TikTok “Oatzempic” and Gut Health: Fiber, Fullness, and Why It’s Not a Real Ozempic Substitute
“Oatzempic” is a catchy name for a simple idea: use oats and water (often blended into a thick drink) to feel fuller and eat...
Tirzepatide Side Effects on Digestion: Nausea, Diarrhea, Constipation, and What Helps
Tirzepatide has reshaped treatment for type 2 diabetes and obesity because it can meaningfully reduce appetite, improve blood sugar control, and support weight loss....