Undigested Food in Stool: Common Causes and When to Worry
Seeing pieces of food in the toilet can be unsettling, especially when it happens more than once. In many cases, it is simply a...
Upper Abdominal Bloating: Reflux, Gas, or Gallbladder?
Upper abdominal bloating can feel deceptively simple—“My stomach is swollen”—yet the causes span everything from swallowed air to reflux, delayed stomach emptying, and gallbladder...
Upper Left Abdominal Pain: Common Causes and When to Worry
Upper left abdominal pain can be unsettling because it sits near organs people associate with “serious” problems: the stomach, spleen, pancreas, and even the...
Upper Right Abdominal Pain: Gallbladder, Liver, or Reflux?
Upper right abdominal pain can feel deceptively simple—“something under my ribs hurts”—yet the right upper quadrant sits at a crossroads of digestion, breathing, and...
Vomiting After Eating: Causes, Red Flags, and When to Seek Care
Vomiting after eating can be frightening, inconvenient, and surprisingly hard to interpret. Sometimes it is the body’s short-lived response to irritation—an oversized meal, a...
Walking After Meals for Digestion: Benefits for Bloating and Blood Sugar
A short walk after eating is one of the simplest digestion-friendly habits that can deliver outsized benefits. It gently nudges the stomach and intestines...
Watery Diarrhea: Causes, Dehydration Risks, and What to Do
Watery diarrhea is common, unpleasant, and often short-lived—but it can become risky faster than many people expect. When stool turns liquid, the body can...
Wheat Allergy vs Gluten Intolerance: Key Differences and Next Steps
When wheat-based foods cause symptoms, it is easy to assume “gluten” is the problem. In reality, wheat reactions fall into different categories that behave...
When to See a Gastroenterologist: Symptoms That Need Evaluation
Digestive symptoms are common, and many are harmless or short-lived. The hard part is knowing when discomfort crosses the line into something that deserves...
Why Am I Always Bloated? Daily Triggers and When to Get Checked
Daily bloating can feel like a mystery: you wake up fine, then by afternoon your abdomen feels tight, full, or visibly larger—sometimes after foods...
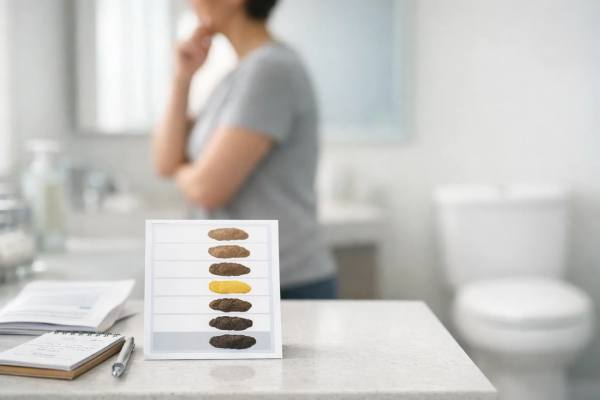
Yellow Poop: Fat Digestion, Diet Causes, and When It’s a Red Flag
Seeing yellow stool can be unsettling, especially when it happens more than once. The good news is that stool color is naturally variable, and...
Zinc L-Carnosine for Gastritis: Benefits, Dosing, and Safety
Gastritis can feel deceptively simple—burning, nausea, early fullness—yet it often has several overlapping drivers, from irritation after an NSAID to chronic inflammation linked to...
“Can’t Take a Deep Breath” with a Cold: Congestion vs Anxiety vs Asthma vs Something Urgent
A cold can make breathing feel strangely “off” even when your lungs are working well. Swollen nasal passages force you to mouth-breathe, thick mucus...
2025–2026 COVID Vaccine Guidance: Who Should Get It Under Shared Decision-Making
When COVID-19 vaccine guidance is framed as shared decision-making, the goal is not to make vaccination “uncertain.” The goal is to make it intentional—matching...
2025–2026 Flu Vaccine: Why It’s Trivalent Now and What That Means for Protection
If you have noticed that the 2025–2026 flu shot is described as trivalent, you are not imagining a shift. For years, many seasonal flu...
Acetaminophen and Alcohol: Liver Risk When You’re Sick and How to Dose Safely
When you are sick, acetaminophen (also called paracetamol) can feel like the most reliable tool you have: it lowers fever, eases aches, and is...
Acetaminophen vs Ibuprofen for Fever and Body Aches: Which to Choose?
When you feel sick, fever and body aches can turn even simple tasks into work. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) are the two...
Acute Bronchitis: How Long It Lasts and Best Home Treatments
Acute bronchitis can feel dramatic: a relentless cough, a heavy chest, and the sense that your lungs are “irritated” with every breath. The good...
Adenovirus: Sore Throat, Pink Eye, and How Long You’re Contagious
Adenovirus is one of those infections that can feel like two illnesses at once: a harsh sore throat and a stubborn “pink eye” that...
Air Purifiers for Allergies and Colds: What Helps and What Doesn’t
If you are sneezing through spring pollen or dragging yourself through a cold, an air purifier can feel like a simple, practical upgrade: plug...
Air Quality and Cough: When Pollution Triggers Respiratory Symptoms
A cough is often blamed on a cold, but air quality can be the hidden driver—especially during wildfire smoke, high-traffic smog, dusty winds, or...
Albuterol for Cough: Who Benefits and When to Avoid It
A stubborn cough can make people reach for whatever might “open the lungs,” and albuterol is often the first medication that comes to mind....
Alcohol and the Immune System: Does Drinking Increase Your Risk of Catching Colds or Flu?
Most people think about alcohol in terms of mood, sleep, or the next-day headache. Fewer think about what it does to the immune system—especially...
Allergies vs Cold: Runny Nose, Sneezing, and What’s Different
A runny nose can feel deceptively simple—until you have to decide whether you are contagious, whether you should cancel plans, and which medicine actually...