Stopping Minoxidil: Shedding, Timeline, and How to Transition Safely
There is a particular kind of worry that comes with a half-used bottle of minoxidil on the bathroom shelf. Sometimes the concern is irritation....
Sudden Hair Shedding: Common Triggers and When to See a Doctor
A sudden increase in hair shedding can feel alarming because it often shows up all at once: more strands on the pillow, a fuller...
Sulfate-Free Shampoo: Who Needs It and Who Doesn’t
Sulfate-free shampoo has become one of the most repeated labels in hair care, often treated as a shortcut for “better,” “cleaner,” or “safer.” In...
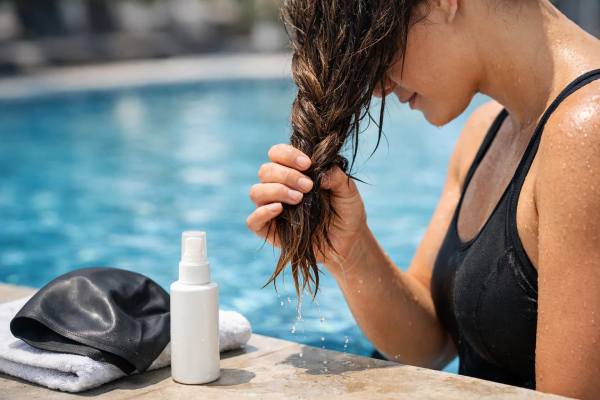
Swimming and Hair Damage: Chlorine Effects and How to Protect Hair
Pool hair damage usually begins quietly. Hair that felt smooth in early summer starts drying faster, tangling more easily, losing shine, and looking lighter...
Syphilis Hair Loss: “Moth-Eaten” Thinning Pattern and When to Test
A patchy scalp that suddenly looks as though small pieces have been taken out of it can be alarming, especially when the hair loss...
Tea Tree Oil for Scalp: Dandruff Relief, Irritation Risks, and Dilution Tips
A flaky, itchy scalp can make even a simple wash day feel frustrating. Tea tree oil often comes up as a natural fix, and...
Telogen Effluvium: Stress-Related Hair Shedding Explained
Hair shedding often feels sudden, even when the biology behind it started months earlier. One week the drain looks normal; the next, there is...
Testosterone Therapy and Hair Loss: DHT Risk, Monitoring, and Prevention
Testosterone therapy sits at an awkward crossroads for hair. For many people, it can improve energy, sexual symptoms, body composition, or gender-affirming goals. At...
Thinning at the Temples: Causes, Hormone Links, and What Helps
Temple thinning is one of the most unsettling forms of hair loss because it changes the shape of the face so quickly. A slightly...
Thinning Hair After 40: Hormones, Nutrition, and Treatment Options
Hair often changes gradually after 40, but the shift can still feel sudden when it finally becomes visible. A part looks wider in bright...
Thinning Hair in Your 20s: Common Causes and Early Prevention
Hair thinning in your 20s can feel especially unsettling because it seems to arrive ahead of schedule. For many people, this is the decade...
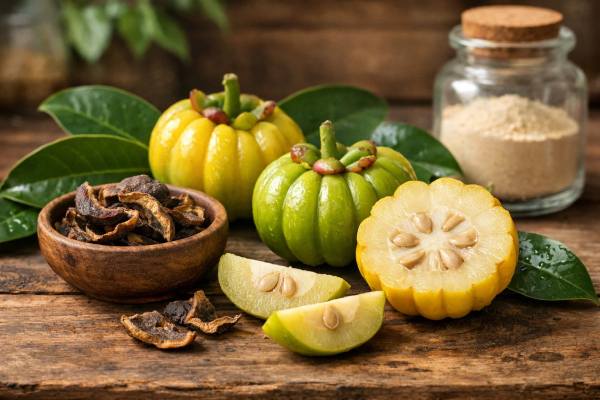
Garcinia Cambogia (Garcinia gummi-gutta) Weight Loss Benefits, Side Effects, and Dosage
Garcinia cambogia, now more properly identified as Garcinia gummi-gutta, is a small tropical fruit whose dried rind has long been used in South Indian...
Giloy medicinal benefits, dosage range, and who should avoid it
Giloy, botanically known as Tinospora cordifolia, is one of the most recognized herbs in Ayurveda, where it is also called guduchi and often described...
Gou Teng (Uncaria rhynchophylla) Medicinal Properties, Traditional Uses, and Safety Guide
Gou Teng, the hooked stem of Uncaria rhynchophylla, is a classic East Asian medicinal herb best known in traditional Chinese medicine for calming “internal...
Griffonia Uses for mood support, sleep quality, and safe dosage
Griffonia, botanically known as Griffonia simplicifolia, is a West African climbing shrub that has become globally known for one reason above all others: its...
Gumweed Benefits, Uses, Respiratory Support, Dosage, and Safety Guide
Gumweed, Grindelia camporum, is a resinous yellow-flowered herb traditionally used for stubborn coughs, irritated airways, and certain itchy or inflamed skin conditions. Native to...
Thyroid Hair Loss: Symptoms, Lab Tests, and Regrowth Timeline
Hair shedding linked to thyroid disease is often subtle at first. A brush fills faster. The ponytail feels smaller. Hair looks drier, rougher, or...
Tight Hairstyles and Hairline Thinning: Prevention Tips That Work
Hairline thinning rarely starts as a dramatic event. More often, it begins quietly: a ponytail that feels sore by evening, tiny broken hairs at...
Too Much Zinc and Hair Loss: Copper Deficiency, Symptoms, and How to Fix It
Zinc has a healthy reputation, so people rarely suspect it when hair starts shedding. It appears in immune formulas, cold lozenges, acne supplements, multivitamins,...
Topical Finasteride vs Oral Finasteride: Effectiveness, Side Effects, and Absorption
Few hair-loss decisions feel as loaded as this one. Oral finasteride has the longest track record in male pattern hair loss, but many people...
Topical JAK Inhibitors for Alopecia Areata: Do Creams Work and Who Benefits?
Topical JAK inhibitors are one of the most intriguing ideas in alopecia areata care because they promise something many patients want: a targeted treatment...
Topical Melatonin for Hair Loss: Evidence, Best Strengths, and How to Use
Topical melatonin sits in an unusual place in hair care. It is familiar as a sleep hormone, yet on the scalp it is discussed...
Topical Tretinoin With Minoxidil: Does It Boost Results and Who Should Skip It?
Minoxidil has a frustrating reputation: it helps many people, but not equally, and not always as quickly as they hope. That is why topical...
Topical vs Oral Minoxidil: Which Is Better and Who Should Avoid Each
Minoxidil has become one of the few hair-loss treatments that people across very different situations end up considering: early temple thinning, diffuse shedding after...