Mono (Mononucleosis): Sore Throat, Fatigue, and How It Spreads
Mono can feel deceptively simple at first—just a sore throat, swollen glands, and the kind of tiredness you assume sleep will fix. Then the...
Mucinex vs Robitussin: Which Is Better for Your Type of Cough?
A cough can be protective, irritating, and surprisingly hard to “treat” with one perfect product. That’s partly because cough medicines work on different targets:...
Mullein Tea for Cough: Benefits, Safety, and How to Brew It
A cough can feel simple—until it keeps you up at night or leaves your throat raw and tender. Mullein tea, made from the leaves...
Mycoplasma Pneumoniae (Walking Pneumonia): Symptoms, Testing, and Best Treatment Options
Walking pneumonia is an informal name for a milder form of pneumonia—one that can still leave you wiped out, coughing for weeks, and contagious...
N95 Fit 101: Seal Checks, Common Leaks, and What Facial Hair Changes
An N95 respirator can be an excellent layer of protection for cold, flu, and other respiratory viruses—but only when it actually seals to your...
NAC for Mucus and Chest Congestion: What It Does and Who Should Avoid It
Chest congestion can make even a simple cold feel heavy—thick mucus, a stubborn cough, and that “can’t clear it” sensation that keeps you up...
Nasal Steroid Sprays (Flonase): When They Help Congestion and Postnasal Drip
A blocked nose and a constant “drip” down the back of the throat can feel like the same problem, even when they have different...
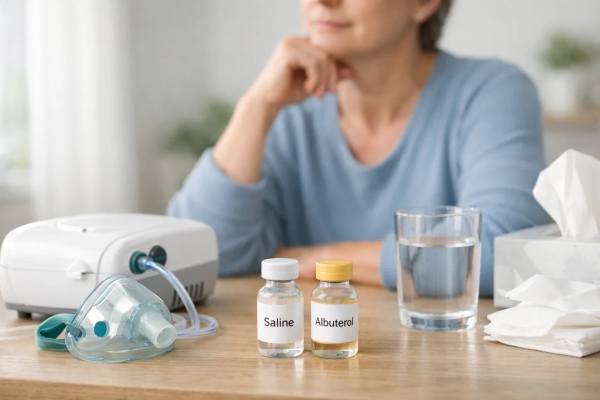
Nebulizers for Viral Wheeze: Saline vs Albuterol vs “Nothing Needed”
Viral wheeze can be frightening: a child who was playing normally at breakfast is suddenly breathing fast, coughing in bursts, and making a whistling...
Nicotine Withdrawal vs Cold Symptoms: How to Tell What’s Causing Your Cough, Anxiety, and Headache
Quitting nicotine is a major change for your nervous system and your airways, so it is common to feel “sick” right as you are...
Nighttime Cough: Common Triggers and What Helps You Sleep
A cough that behaves all day and then flares the moment you lie down can feel unfair—and exhausting. Nighttime cough is common because sleep...
Nirsevimab (Beyfortus) for RSV: Who Should Get It, Timing, and What Parents Should Expect
RSV is a common winter virus, but in young infants it can turn into bronchiolitis or pneumonia quickly—sometimes with little warning beyond fast breathing...
Norovirus vs Flu: Stomach Flu Symptoms, Contagious Period, and What Helps
When people say they have the “stomach flu,” they almost always mean a short, intense bout of vomiting and diarrhea—most commonly caused by norovirus....
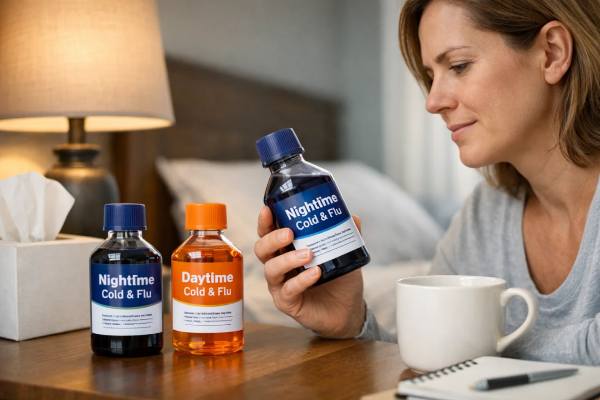
NyQuil vs DayQuil: What’s in Them and When to Use Each
When you feel sick, it’s tempting to reach for a single “do-it-all” bottle and move on with your day. NyQuil and DayQuil are popular...
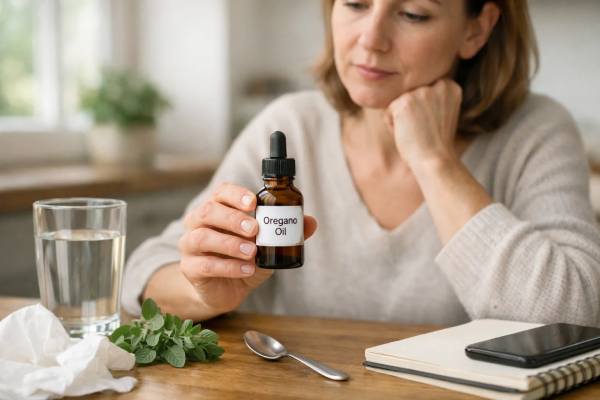
Oil of Oregano for Colds: Hype vs Helpful and How to Use It Safely
Oil of oregano sits in that crowded space between kitchen herb and “natural antibiotic” hype. The reality is more nuanced—and more useful—than either extreme....
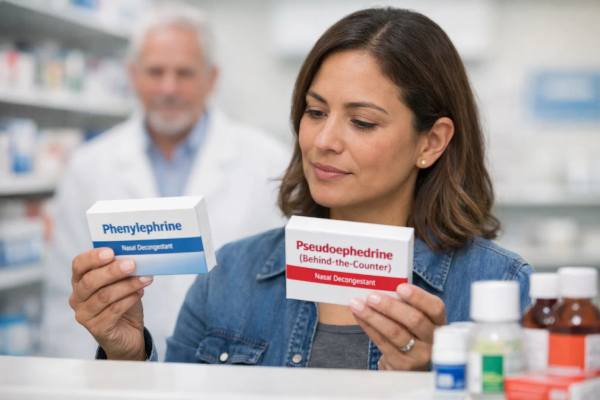
Oral Phenylephrine (Sudafed PE) Doesn’t Work: What FDA’s Move Means and What to Use Instead
If you have ever taken an oral “PE” decongestant and still felt sealed shut, you are not imagining it. Oral phenylephrine (the “PE” in...
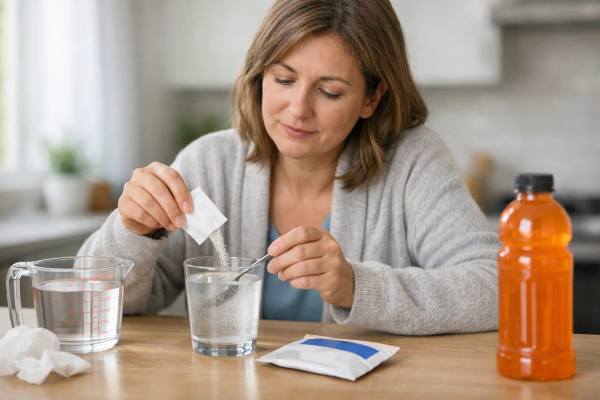
Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS): When It’s Better Than Sports Drinks and How to Use It
When you are sick with a respiratory infection, dehydration can sneak up fast—especially if fever, rapid breathing, and poor appetite stack up over a...
Over-the-Counter Cold Medicine: What Works and What’s Not Worth It
Cold medicine can feel like a maze: dozens of boxes promise “fast relief,” yet your symptoms still seem to run their course. That is...
Parainfluenza in Kids: Croup-Like Symptoms and When to Worry
When a child suddenly develops a harsh “barky” cough and noisy breathing at night, it can be startling—even if the day started with nothing...
Paxlovid Drug Interactions: What to Avoid and When to Ask Your Pharmacist
Paxlovid can be a powerful tool for lowering the risk of severe COVID-19 in people at higher risk—but it comes with an unusually important...
Paxlovid for COVID: Who It’s For, When It Helps, and Common Side Effects
Paxlovid is one of the few at-home treatments that can meaningfully change the course of COVID for people who are more likely to get...
PCR vs Rapid Antigen COVID Tests: Which to Choose and When
COVID testing is no longer just a yes-or-no question—it is a timing and purpose question. PCR (a type of molecular test) is built to...
PCR, NAAT, and Rapid Antigen: A Plain-English Guide to What Each Test Detects and When
When you feel sick or learn you were exposed, the hardest part is often not taking a test—it’s choosing the right one and trusting...
PEMGARDA (Pemivibart) for COVID Prevention: Who Qualifies, How It Works, and Key Limits
For many people, COVID prevention largely comes down to vaccination, a few sensible habits, and treating early if infection happens. But if your immune...
Peppermint Tea for Congestion: When It Helps and When It Triggers Reflux
Peppermint tea sits in that sweet spot between comfort and function: it is warm, soothing, and often makes breathing feel easier when your nose...