Persistent Cough After a Cold: Post-Viral Cough Timeline and Relief
A cold can fade in a week, yet the cough may linger—sometimes long enough to feel like a second illness. This “post-viral” or “postinfectious”...
Pertussis vs Bronchitis vs Post-Viral Cough: The Pattern Clues That Matter
When a cough drags on, the label matters less than the pattern. Pertussis (whooping cough), acute bronchitis, and post-viral cough can all start after...
Pink Eye with Cold Symptoms: When It’s Viral and What to Do
Pink eye that shows up alongside a runny nose, sore throat, or cough often points to a viral cause—especially when it begins in one...
Pink Eye with Respiratory Symptoms: Adenovirus vs Allergies vs “Something Else” (When to Worry)
A red, watery eye that appears alongside a sore throat, congestion, or cough is often viral—frequently linked to adenovirus—but the overlap can be misleading....
Pneumococcal Vaccine at Age 50: Which Shot You Need Now (PCV15 vs PCV20 vs PCV21)
Turning 50 is more than a birthday milestone—it is also a point where the risk of serious pneumococcal illness begins to rise. Streptococcus pneumoniae...
Pneumonia Symptoms: Early Signs and When to Go to the ER
Pneumonia can start like an ordinary cold and then quietly change the rules: breathing becomes harder, fatigue deepens, and the body struggles to keep...
Pneumonia Vaccines: Who Needs Them and When
When people say “pneumonia vaccine,” they usually mean vaccines that protect against pneumococcal disease—a common bacterial cause of serious pneumonia, bloodstream infection, and meningitis....
Pneumonia vs Bronchitis: Differences in Symptoms and Treatment
A cough can make everything feel the same—tight chest, fatigue, restless sleep, and the uneasy question: Is this just bronchitis, or is it pneumonia?...
Positive Flu Test at Home: When Antivirals Help and When to Just Support Symptoms
A positive home flu test can feel oddly decisive: one line, one answer, and suddenly you are doing mental math about missed work, contagious...
Post-COVID Cough: How Long It Lasts and When It Needs Workup
A lingering cough after COVID can be unsettling, especially when everything else has improved. The good news is that most post-viral coughs—including those after...
Postnasal Drip: Causes, Best Treatments, and When It Means Infection
Postnasal drip is one of those symptoms that sounds minor until you have it: a constant throat “coating,” frequent clearing, a cough that worsens...
Post-Viral Fatigue: Why You’re Exhausted After a Cold and How to Recover
You expect a cold to end when the sore throat and congestion fade—but sometimes the exhaustion hangs on. Post-viral fatigue is that “heavy battery”...
Preventing Colds in Kids: School Germs, Hygiene, and Sleep
If your child seems to bring home a new cold every other week, you are not imagining it—schools and daycares are efficient sharing networks...
Probiotic Foods for Cold Season: Yogurt, Kefir, and What Strains Matter
Cold season invites a familiar question: is there anything you can eat that meaningfully lowers your odds of catching “every bug going around”? Probiotic...
Probiotics for Immune Health: Can They Reduce Colds?
Probiotics are often marketed as an easy way to “boost immunity,” especially when colds start circulating at school and work. The reality is more...
Propolis for Sore Throat: Throat Sprays, Evidence, and Allergy Risks
A sore throat can feel deceptively simple—just scratchiness, pain with swallowing, maybe a hoarse voice—yet it can disrupt sleep, appetite, and concentration for days....
Pulse Oximeter Readings Explained: What Numbers Are Normal and When to Worry
A pulse oximeter can turn a vague worry—“Am I getting enough oxygen?”—into a number you can track at home. That is powerful during colds,...
Quercetin for Colds and Allergies: What It May Help and Dosage Safety
Quercetin is a plant compound found in foods like onions, apples, and tea, and it has become a popular supplement during cold and allergy...
Quit Smoking During a Respiratory Infection: What Happens First Week and How to Make It Easier
Trying to quit while you have a cold, flu, bronchitis, or another respiratory infection can feel like choosing the hardest week to start. But...
Rebound Congestion: How Overusing Nasal Sprays Makes Stuffiness Worse
A nasal decongestant spray can feel like a small miracle: two sprays, a deep breath, and you can finally sleep. The problem is that...
Repeat Testing After a Negative Rapid Test: When It’s Worth Doing (COVID and Flu)
A negative rapid test can feel like a green light—especially when you are tired, congested, and hoping to get back to normal. But rapid...
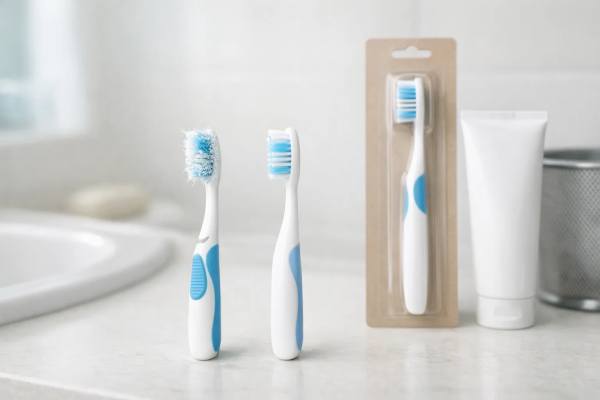
Replace Your Toothbrush After a Cold? The Evidence, the Myths, and Practical Rules
When you are getting over a cold, it is easy to look at your toothbrush and wonder whether it is quietly keeping you sick....
Respiratory Illness in Pregnancy: Safe Medications and When to Call Your OB
A sore throat or a tight cough can feel different when you are pregnant. Symptoms that might be “just a cold” at other times...
Respiratory Viruses When You’re Immunocompromised: Lower Fever Doesn’t Mean “Less Sick”
When you are immunocompromised, a respiratory virus can follow different rules. You might not spike a high fever, even with a significant infection, because...