Sore Throat Causes: Cold, Flu, Strep, Reflux, and Allergies
A sore throat seems simple until you try to answer the one question that actually matters: Why does it hurt? The cause determines what...
Sore Throat on One Side: Tonsil Stone, Peritonsillar Abscess, Strep, or Reflux?
A sore throat that stays on one side can feel more alarming than a typical “scratchy both sides” cold—and sometimes it should. The throat...
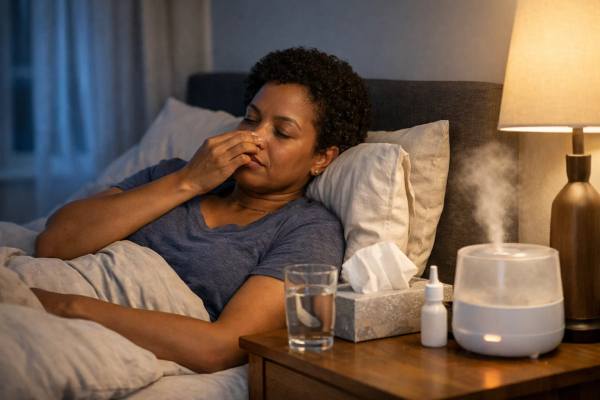
Sore Throat Remedies That Work: Salt Water, Sprays, Lozenges, and Hydration
A sore throat can feel deceptively intense: swallowing hurts, your voice turns thin, and even breathing cold air can sting. The good news is...
Spices for Congestion: Capsaicin, Horseradish, and When “Hot” Foods Irritate Airways
Congestion has a way of turning ordinary breathing into work, which is why many people reach for “hot” foods the moment their nose stuffs...
Spicy Foods for Congestion: Why They Help and When They Backfire
When your nose is stuffed and your head feels heavy, a bowl of spicy soup can feel like a small miracle. The first bite...
Steam Inhalation for Congestion: Benefits, Risks, and Safer Options
Steam has a long history as a “blocked nose” remedy, and it can feel reassuring: warm air, a little loosened mucus, and the sense...
Steroids for Viral Cough or “Chest Inflammation”: When They Help, When They Harm, and Red Flags
A cough that settles into your chest can feel alarming. It is common to hear phrases like “chest inflammation,” “bronchitis,” or “tight lungs,” and...
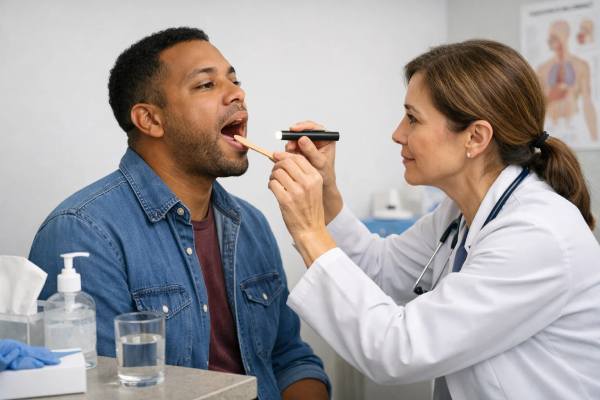
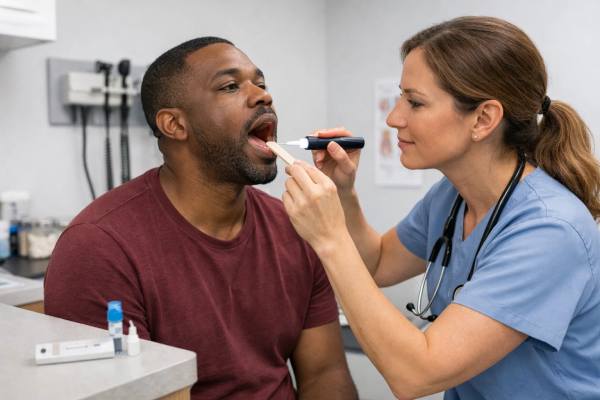
Strep Throat Symptoms: Signs, Testing, and When to Treat
A sore throat can feel deceptively simple—until swallowing becomes sharply painful, fever climbs, and you start wondering whether you need antibiotics. Strep throat is...
Strep Throat vs Viral Sore Throat: Key Differences and Next Steps
Most sore throats feel similar at first: scratchiness, pain with swallowing, and a low desire to talk or eat. The next step, though, depends...
Stuffy Nose at Night: Why It Gets Worse Lying Down and How to Sleep
A stuffy nose that flares the moment you lie down can feel unfair: you breathe fine on the couch, then struggle the second your...
Sudafed and High Blood Pressure: Safer Options for Congestion
When your nose is blocked, it is tempting to reach for the fastest fix. But if you live with high blood pressure, oral decongestants...
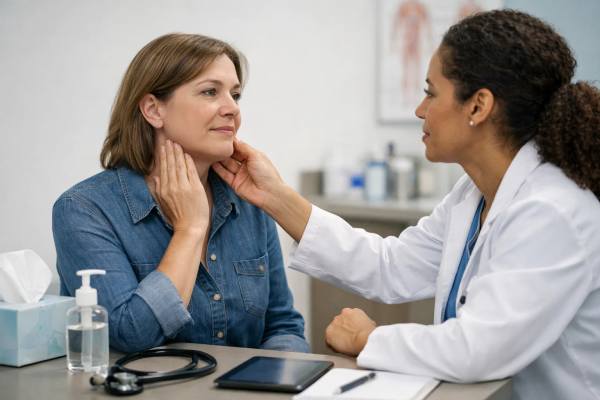
Swollen Lymph Nodes in the Neck: Cold vs Strep vs Something Else?
A tender lump along the jawline or a “ropey” swelling under the ear can feel alarming, especially when it shows up with a sore...
Swollen Tonsils: Causes, Home Care, and When to See a Doctor
Swollen tonsils can turn an ordinary day into a struggle—swallowing hurts, sleep feels shallow, and your voice may sound different. Tonsils are part of...
Tamiflu (Oseltamivir): When It Helps, Timing, and Side Effects
Tamiflu, the brand name for oseltamivir, is one of the most familiar prescription antivirals for influenza. It does not “cure” the flu overnight, but...
Throat Clearing All Day: Postnasal Drip, Reflux, and Habit Cough
Throat clearing can start as a small annoyance and quietly become an all-day reflex—during meetings, meals, and even in the quiet moments when you...
Throat Tickling Cough: Dry Air, Postnasal Drip, and Irritant Triggers
A throat tickle that keeps setting off a dry cough can feel small at first, then strangely relentless—especially when talking, laughing, or trying to...
Thyme Tea for Cough and Congestion: Traditional Remedy and How to Make It
A mug of thyme tea is more than a comforting ritual. Warmth, steam, and steady hydration can make breathing feel easier when you are...
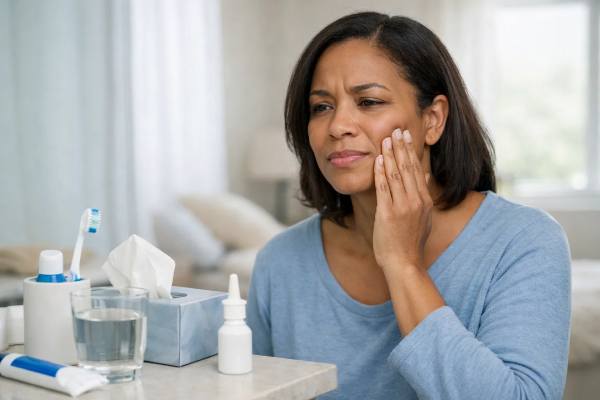
Tooth Pain from Sinus Congestion: Why It Happens and What Helps
When your upper teeth suddenly ache during a cold or allergy flare, it can feel confusing and a little alarming. Teeth are supposed to...
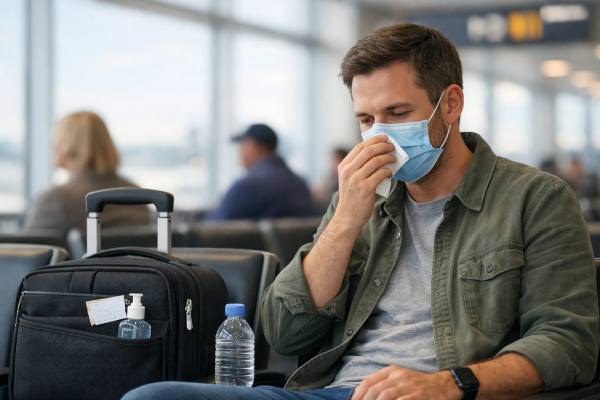
Traveling While Sick: Flying, Public Transport, and How to Reduce Spread
Getting sick right before a trip creates a difficult choice: protect your plans, or protect the people around you. Respiratory viruses spread most easily...
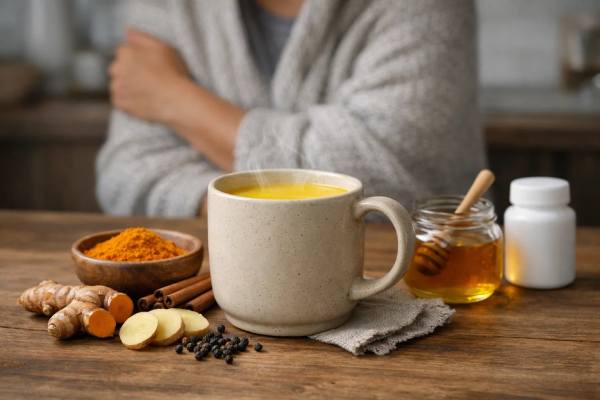
Turmeric Milk (Golden Milk): Cold-Season Benefits, Recipe, and Who Should Avoid It
When you feel a cold coming on, turmeric milk—often called golden milk—can be a comforting ritual that supports the basics your body leans on...
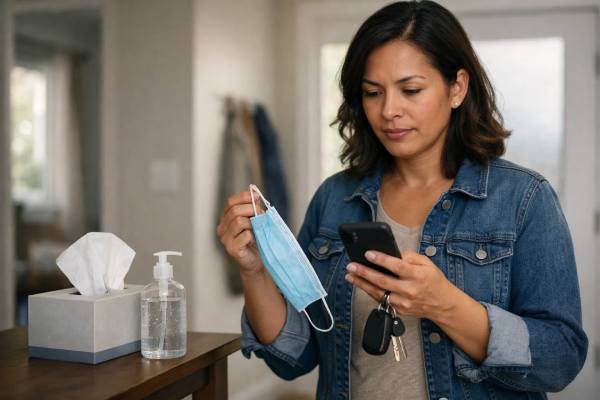
Updated CDC Respiratory Virus Guidance: What It Means for Staying Home and Masks
When you wake up with a sore throat or a tight, tired cough, the hardest decision is rarely the tissues or tea—it is whether...
Vaping and Respiratory Symptoms: Cough, Wheeze, and When to Get Checked
A new cough that lingers, a faint wheeze you never had before, or tight breathing after climbing stairs can be unsettling—especially if you vape....
Vaping While Sick: Does It Prolong a Cold, Bronchitis, or Asthma Flare?
When you are sick, your airways are already working overtime—swollen lining, thicker mucus, and a cough reflex that fires faster than usual. Vaping adds...
Viral vs Bacterial Sinus Infection: How to Tell and What to Do
A “sinus infection” can feel unmistakable—pressure behind the cheeks, a heavy head, and mucus that seems determined to stay put. The tricky part is...