Light Sensitivity With COVID-19: Why It Happens and What Helps
Light sensitivity (photophobia) can feel like an unexpected twist in a COVID-19 illness. One day you’re dealing with fatigue, congestion, or fever; the next,...
Long COVID and Eye Symptoms: Blurry Vision, Eye Pain, and Photophobia
For many people, COVID-19 ends in a week or two. For others, recovery is slower and stranger: energy returns unevenly, headaches linger, and vision...
Low-Dose Atropine for Myopia Control: Best Concentrations, Side Effects, and New Data
Myopia control has shifted from a “wait and see” approach to proactive care—because the goal is not only clearer vision today, but also a...
Low-Level Light Therapy for Dry Eye: What the Research Shows
Dry eye is not just “not enough tears.” For many people, it is an unstable tear film driven by inflamed eyelids, thickened meibomian gland...
Lutein and Zeaxanthin for Eye Health: Benefits, Food Sources, and Dosage
Lutein and zeaxanthin are the two carotenoids most concentrated in the macula—the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision. They act...
Makeup Irritation: Why Your Eyes React and How to Prevent Flare-Ups
Eye makeup should enhance comfort and confidence—not leave you with burning, watering, or swollen lids by late afternoon. The challenge is that the eyelid...
Myopia Control: What Works (Atropine, Ortho-K, and Special Lenses)
Myopia control is not about “curing” nearsightedness—it is about slowing how quickly myopia increases as a child grows. That matters because higher myopia is...
Myopia in Kids: Early Signs, Risk Factors, and Prevention Tips
Myopia (nearsightedness) can feel like it appears overnight: a child who used to spot a friend across the playground starts squinting at the whiteboard,...
New Glasses Feel Weird: Adjustment Time, Headaches, and When to Recheck
Getting new glasses can be surprisingly disorienting—even when the prescription is correct. Your brain has spent months or years interpreting the world through a...
Nicotinamide (Vitamin B3) for Glaucoma: Neuroprotection Research and Safety Notes
Glaucoma treatment has long centered on lowering eye pressure, and for good reason. Yet many people continue to lose vision even when pressure looks...
Nicotinamide Plus Pyruvate for Eye Health: The Metabolic Therapy Approach Explained
Glaucoma and other optic nerve disorders are often described in mechanical terms—pressure, blood flow, or “wear and tear.” Yet the tissues that fail in...
Night Vision Problems: Glare, Halos, and What Might Be Causing Them
Glare and halos at night can make driving, walking, or even reading street signs feel far more difficult than your daytime vision would suggest....
Ocular Migraine: Visual Aura, Triggers, and When to Worry
The term “ocular migraine” can sound like an eye disease, yet most of the time it describes a brain-based visual event: a migraine aura...
Ocular Rosacea: Symptoms, Triggers, and Treatment Options
Ocular rosacea is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the eyelids, tear film, and the surface of the eye. For some people it arrives...
Omega-3 for Dry Eyes: Who Benefits and What the Evidence Says
Dry eye can feel deceptively simple—“my eyes are dry”—yet the root problem is often inflammation and tear-film instability, not just a lack of tears....
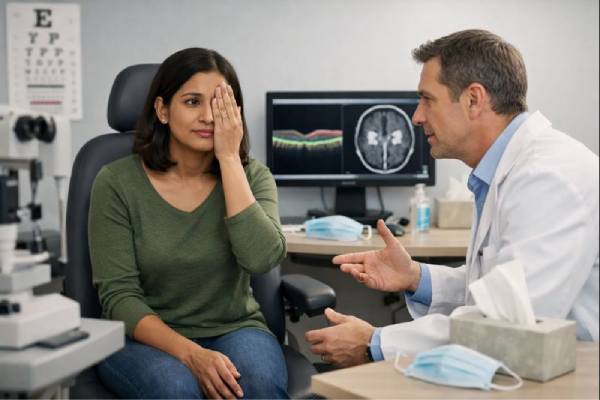
Optic Neuritis After COVID-19: Symptoms, Risks, and When to Act Fast
Optic neuritis is an inflammation of the optic nerve that can cause rapid vision changes, often with pain when moving the eye. Since the...
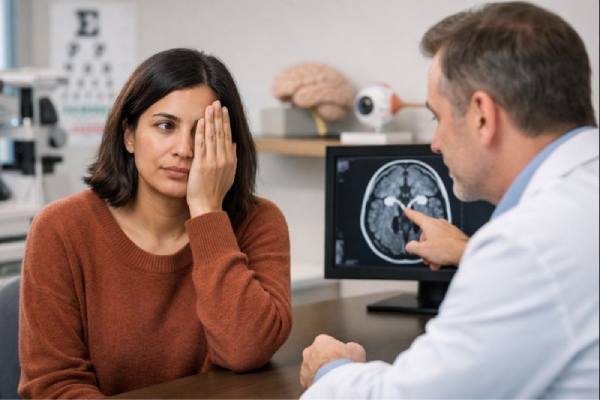
Optic Neuritis: Early Signs, MS Links, and When to Act Fast
Optic neuritis is inflammation of the optic nerve, the cable that carries visual signals from the eye to the brain. It often arrives quickly,...
Ozempic/Wegovy and Vision Changes: What’s Known and When to Get an Eye Exam
Ozempic and Wegovy (both forms of semaglutide) have reshaped treatment for type 2 diabetes and obesity by improving blood sugar control, supporting weight loss,...
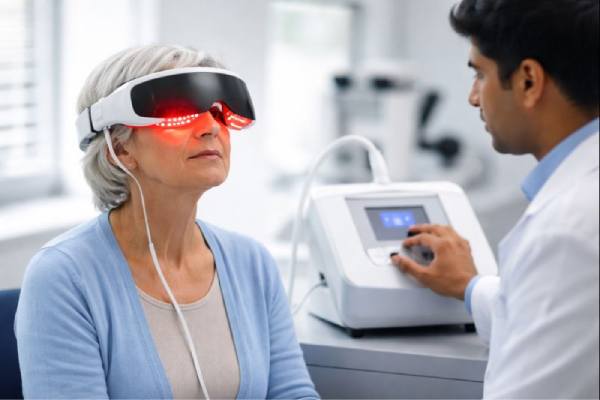
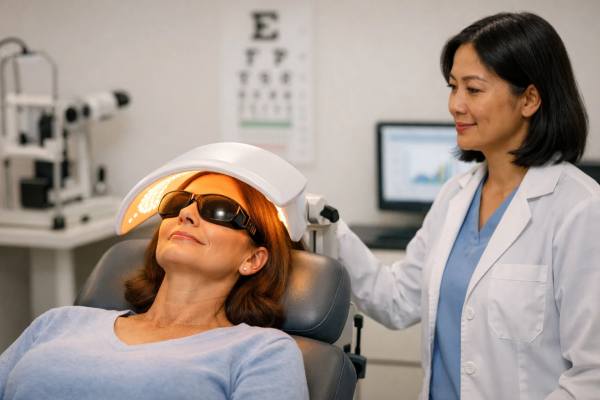
Photobiomodulation (Light Therapy) for Dry AMD: Evidence Update and Who May Benefit
Photobiomodulation (PBM) is a form of light therapy that delivers carefully calibrated, low-intensity wavelengths to retinal tissue. For people with dry age-related macular degeneration...
Pinguecula vs Pterygium: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
If you have noticed a small yellowish bump on the white of your eye or a wedge-shaped growth creeping toward the cornea, you have...
Pink Eye (Conjunctivitis): Types, Contagious Period, and Home Care
Pink eye, medically called conjunctivitis, is inflammation of the thin clear tissue that covers the white of the eye and lines the inner eyelids....
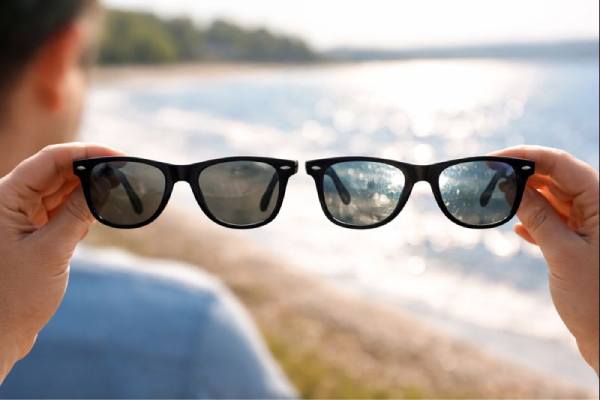
Polarized vs Non-Polarized Sunglasses: Which Protects Better?
Sunglasses can feel like a style choice, but for eye health they are a form of protective equipment. The important question is not only...
Presbyopia Explained: Why Near Vision Gets Worse After 40 and What Helps
Presbyopia is the quiet reason many people start holding menus farther away or increasing the font on their phone in their early-to-mid 40s. It...
Prescription Dry Eye Treatments: Restasis vs Xiidra vs Cequa vs Miebo vs Eysuvis
Dry eye disease is rarely just “not enough tears.” For many people it is a cycle of inflammation, surface damage, and unstable tear film—often...