Carnivore Diet and Gut Health: IBS Relief Claims, Microbiome Risks, and What Studies Show
The carnivore diet is one of the most extreme elimination diets in mainstream nutrition: animal foods only, with little to no fiber, and typically...
Castor Oil Packs for Bloating: What People Claim and What Experts Say
Castor oil packs sit at the intersection of folk medicine and modern wellness culture: a warm, oil-soaked cloth placed on the abdomen in hopes...
Celiac Disease Symptoms: Digestive and Non-Digestive Signs
Celiac disease is an immune condition triggered by gluten that can affect far more than the digestive tract. Some people develop obvious gut symptoms—diarrhea,...
Celiac Testing: What to Eat Before the Test and What Results Mean
Celiac disease testing is most accurate when your immune system is actively “seeing” gluten—yet many people start cutting gluten the moment they suspect it...
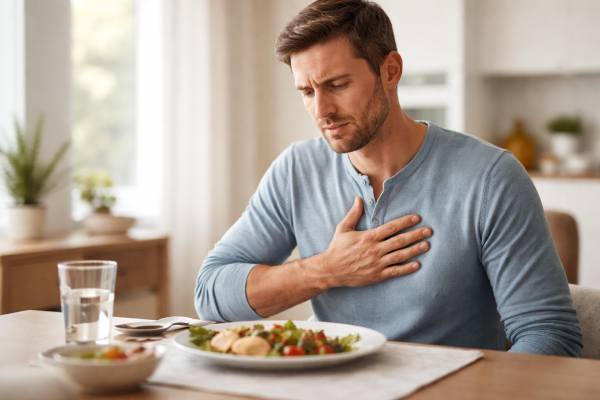
Chest Pain After Eating: Reflux, Spasm, or Something Serious?
Chest pain after eating can feel alarming because the chest is shared territory: the esophagus, stomach, heart, lungs, and chest wall all send pain...
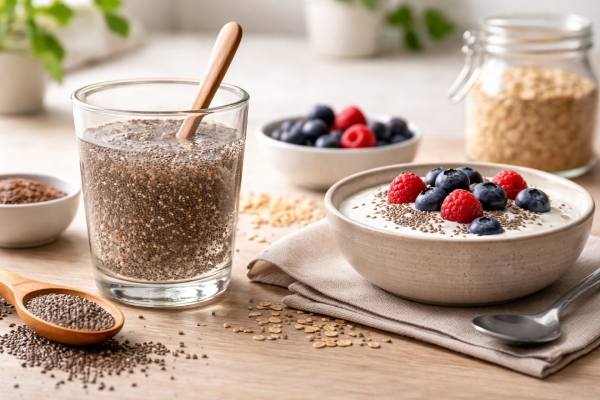
Chia Seeds for Constipation: How Much Helps and Common Mistakes
Chia seeds are small, but they behave like a powerful “hydration sponge” in the digestive tract. When soaked, they form a gel that can...
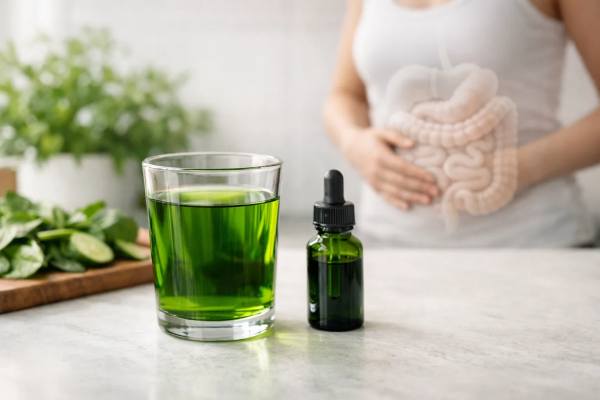
Chlorophyll Water for Digestion: Trend Claims, Benefits, and Side Effects
Chlorophyll water has become a popular “gut reset” ritual: a few green drops in water, taken daily with the promise of easier digestion, less...
Chronic Constipation: Causes, Tests, and Treatment Options
Chronic constipation is more than “not going often enough.” It can mean hard stools, straining, a sense of incomplete emptying, or feeling blocked—even when...
Chronic Diarrhea: Common Causes and Which Tests Help
Chronic diarrhea can quietly take over daily life—planning meals around bathrooms, avoiding travel, and wondering whether each episode is “just something you ate” or...
Collagen for Gut Health: Does It Help Digestion or Just Hype?
Collagen has become a staple supplement for people who want calmer digestion, less bloating, and a “stronger gut lining.” The idea sounds intuitive: collagen...
Colon Cancer Symptoms: Early Signs Many People Miss
Colon cancer often starts quietly. For many people, the earliest clues are subtle—small shifts in bowel habits, a nagging sense that something feels “off,”...
Colon Polyps: What They Are and Why Screening Matters
Colon polyps are common growths that form on the inner lining of the large intestine. Most are harmless, but some are the early “starting...
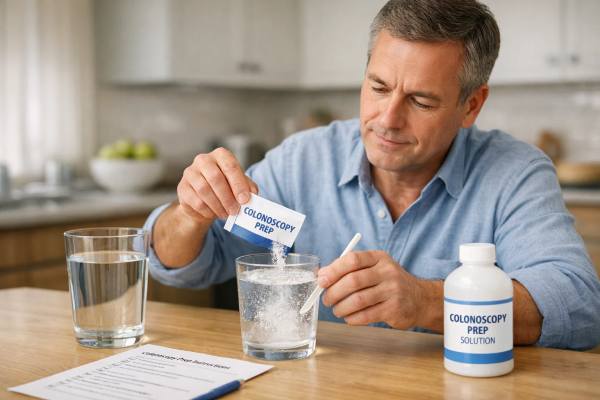
Colonoscopy Prep: Tips to Make It Easier and More Effective
A colonoscopy can do something few medical tests can: it can both find early changes and prevent future cancer by removing polyps during the...
Constipation After Antibiotics: Gut Changes and Recovery Tips
Antibiotics can be life-saving, but they rarely act in isolation. Alongside clearing an infection, they can temporarily disrupt the gut’s normal rhythm—changing your microbiome,...
Constipation and Bloating: Why They Happen Together and What Helps
Constipation and bloating often arrive as a pair: your abdomen feels tight or swollen, yet bowel movements are infrequent, incomplete, or difficult. This combination...
Constipation: Causes, Symptoms, and Relief That Works
Constipation is more than “not going often enough.” It can mean hard stools, straining, a sense of incomplete emptying, or feeling backed up even...
Cramping After Meals: IBS, Intolerance, or Infection?
Cramping that flares after you eat can feel confusing: the trigger is obvious (food), but the cause is not. Sometimes it is a predictable...
Crohn’s Disease Symptoms: Digestive Signs and Red Flags
Crohn’s disease can be difficult to recognize early because symptoms often come and go, and they can resemble more common problems like IBS, a...
Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome: Episodes, Triggers, and When to Get Evaluated
Cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS) is a condition where intense nausea and repeated vomiting arrive in waves—often abruptly—then disappear, leaving stretches of relative normalcy in...
DAO Supplements for Histamine Intolerance: When They Help and What to Expect
Diamine oxidase (DAO) supplements are designed to help break down dietary histamine in the gut before it triggers symptoms. For some people with suspected...
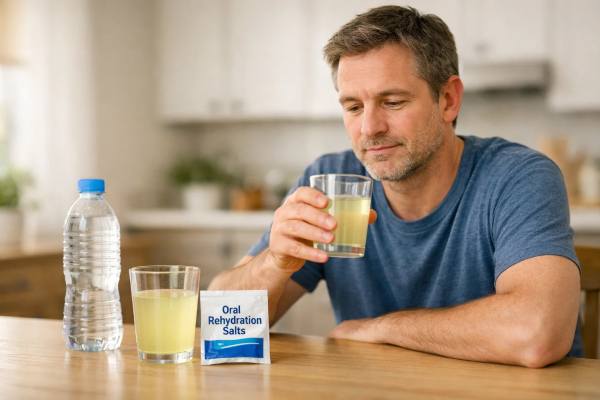
Dehydration From Diarrhea: Signs, ORS, and When to Get Help
Diarrhea can drain the body faster than many people expect. It is not only the water loss that matters, but also the loss of...
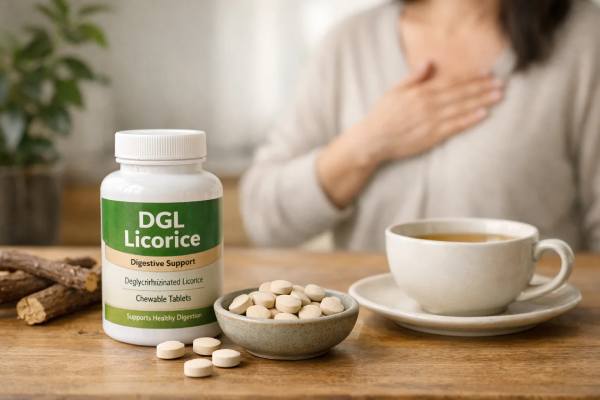
DGL Licorice for Heartburn: Benefits, Dosing, and Who Should Avoid It
Heartburn can feel deceptively simple—burning behind the breastbone after a meal—yet the causes range from classic acid reflux to sensitive esophageal nerves that overreact...
Diarrhea After Antibiotics: Causes, C. diff Warning Signs, and What to Do
Diarrhea after antibiotics is common, unsettling, and often misunderstood. In many cases, it is a short-lived side effect caused by temporary shifts in gut...
Diarrhea After Eating: Triggers, Food Intolerances, and Next Steps
Diarrhea that reliably follows meals can feel like your digestive system has a mind of its own. Sometimes the cause is simple—too much caffeine,...