Degos disease: Causes, Risk Factors, Complications, and Long-Term Monitoring
Degos disease is a very rare condition in which small blood vessels become damaged and blocked. That injury can show up first on the...
Dehydration-induced hypotension: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Fast Rehydration Treatment
Dehydration-induced hypotension happens when your body loses enough fluid that your blood pressure drops. For some people, it starts as a subtle “off” feeling—lightheaded...
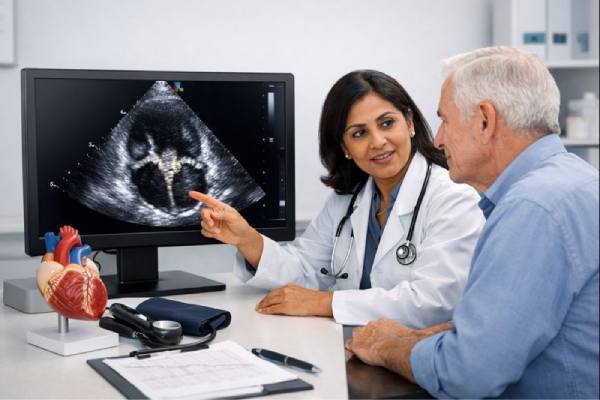
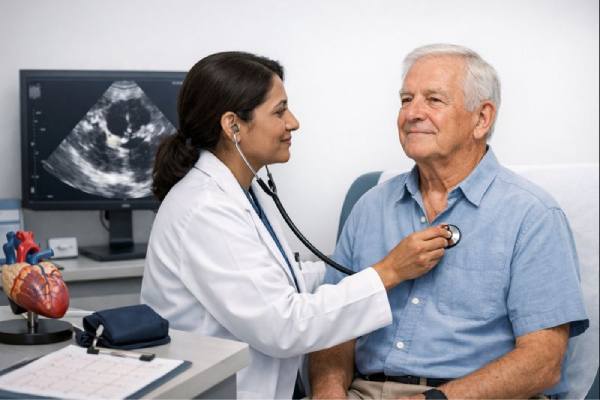
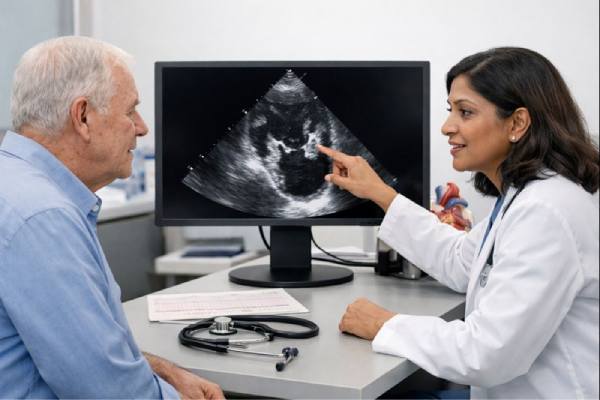
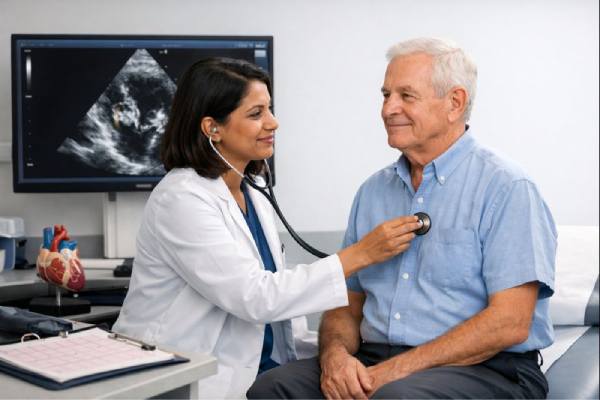
Dextrocardia: Causes, Associated Heart Defects, and Long-Term Management
Dextrocardia means the heart sits on the right side of the chest instead of the left. For some people, it is an incidental finding...
Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Causes, Fibrosis, Stiff Heart, and Key Risk Factors
Diabetic cardiomyopathy is a heart muscle problem that develops in some people with diabetes, even when they do not have blocked arteries or long-standing...
Diabetic vascular disease: Overview, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies
Diabetic vascular disease is the umbrella term for blood-vessel damage linked to diabetes. It includes problems in large arteries that supply the heart, brain,...
Diastolic dysfunction: What It Means, Risk Factors, and How It’s Treated
Diastolic dysfunction means the heart has trouble relaxing and filling between beats. That “resting” phase is called diastole (the heart’s relaxation phase). When filling...
Diastolic heart failure: Overview, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Diastolic heart failure is a form of heart failure where the heart’s squeeze may look normal, but the heart does not relax and fill...
Dilated cardiomyopathy: Overview, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Dilated cardiomyopathy is a condition where the heart’s main pumping chamber stretches and weakens over time. When that chamber loses strength, the heart can’t...
Diminished peripheral pulses: What They Mean, Common Causes, and Next Steps
Diminished peripheral pulses means a pulse in the arms or legs feels weaker than expected—or weaker on one side than the other—when checked by...
Diphtheritic endocarditis: How It Spreads, Who’s at Risk, and Prevention
Diphtheritic endocarditis is an uncommon but serious infection of the heart valves caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae, the bacterium best known for causing diphtheria. While...
Dissection of the aorta: Causes, Genetic Risks, Family Screening, and Management
An aortic dissection is a medical emergency where the inner lining of the aorta—the body’s main artery—tears and blood forces its way between the...
Disseminated intravascular coagulation: What It Is, Why It Happens, and Management.
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a dangerous loss of balance in the body’s clotting system. Instead of making clots only where they’re needed, the...
Dressler syndrome: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment After a Heart Attack
Dressler syndrome is an inflammatory reaction that can appear after the heart has been injured—most often after a heart attack or heart surgery. It...
Drug-induced cardiomyopathy: Causes, Early Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Drug-induced cardiomyopathy is a form of heart muscle weakness caused or triggered by a medication or drug exposure. In some people it develops slowly,...
Duchenne cardiomyopathy: Early Detection, Symptoms, and Heart Protection
Duchenne cardiomyopathy is the heart-related part of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (Duchenne), a genetic condition that weakens muscles over time. While most families first notice...
Dunbar syndrome: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Best Treatment Options
Dunbar syndrome—also called median arcuate ligament syndrome (MALS)—is an uncommon cause of persistent upper abdominal pain, especially after eating. In this condition, a band...
Dyslipidemia: Causes, Risk Factors, and What Your Lipid Panel Means
Dyslipidemia means your blood fats are out of balance—most often LDL cholesterol (“bad” cholesterol) is too high, HDL cholesterol (“good” cholesterol) is too low,...
Dysrhythmia: Types, Symptoms, and When It’s Dangerous
A dysrhythmia (also called an arrhythmia) is an abnormal heart rhythm—too fast, too slow, or irregular. Some dysrhythmias are harmless and temporary, like a...
Calcific aortic stenosis: Aortic Valve Narrowing, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Calcific aortic stenosis is a common valve condition in which the aortic valve becomes stiff and narrowed as calcium builds up in the valve...
Calcific aortic valve disease: Causes, Risk Factors, Early Signs, and Disease Progression
Calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD) is a slow, progressive condition where the aortic valve leaflets become thicker, stiffer, and increasingly coated with calcium. Early...
Calcific mitral stenosis: Overview, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management
Calcific mitral stenosis is a narrowing of the mitral valve caused by calcium buildup and stiffening around the valve ring (the mitral annulus) and,...
Calcific mitral valve disease: Symptoms and Complications and When to Seek Urgent Care
Calcific mitral valve disease is a spectrum of problems caused by calcium buildup in and around the mitral valve, most often starting in the...
Capillary leak syndrome: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Capillary leak syndrome is a serious condition where fluid and proteins escape from the bloodstream into surrounding tissues. When that “leak” becomes widespread, blood...
Cardiac allograft vasculopathy: Symptoms, Surveillance, Diagnosis, and Treatment After Heart Transplant
Cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV) is a form of coronary artery disease that develops only in transplanted hearts. Instead of creating a few isolated blockages,...