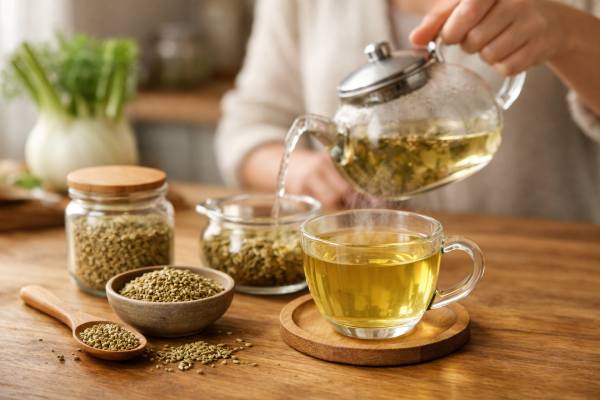
Fennel for Gas and Bloating: Tea, Seeds, and Evidence-Based Use
Bloating can feel deceptively simple—just “gas”—yet the causes range from fast eating and constipation to food sensitivities and stress-driven gut motility changes. Fennel (the...
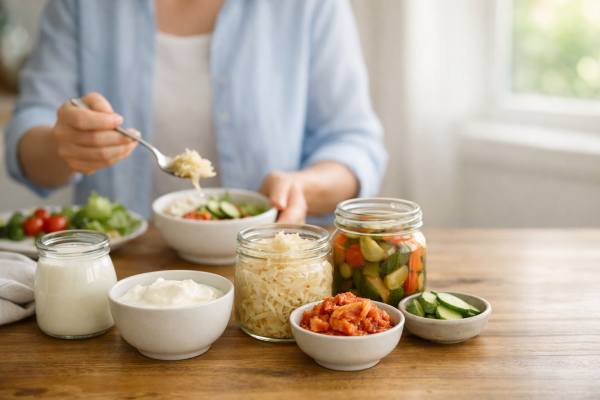
Fermented Foods for Gut Health: How to Start Without Getting Gassy
Fermented foods sit at an interesting crossroads of tradition and modern gut science. When they are made with live cultures and eaten consistently, they...
Fiber for Constipation: How Much You Need and Best Sources
Constipation is often treated as a problem of “not enough laxatives,” but for many people it is first a problem of daily structure: too...
Fiber Supplements and Medications: Timing Rules to Avoid Interactions
Fiber supplements can be a steady, low-drama way to support regularity, cholesterol goals, and post-meal blood sugar control—especially when food-based fiber is hard to...
Fibermaxxing: How to Increase Fiber Without Bloating or Constipation
Fibermaxxing has become shorthand for a simple idea: intentionally raising your daily fiber intake to support digestion and long-term health. Done well, it can...
Floating Stool: Causes, Fat Malabsorption, and When to Worry
Seeing stool float can be unsettling, especially when it seems to happen “out of nowhere.” The reassuring truth is that floating is a physical...
FODMAP Enzyme Powders: How They Work for Garlic, Onion, and Wheat Triggers
If garlic, onion, or wheat reliably leave you bloated and uncomfortable, you are not alone—and you are not imagining it. These foods are common...
Food Intolerance vs Food Allergy: Differences and When to Test
Many people use “food allergy” as a catch-all for any food that makes them feel unwell. In reality, true food allergies are immune reactions...
Food Poisoning Symptoms: Timeline, Home Care, and When to Go to the ER
Food poisoning can feel abrupt and alarming: nausea that rises fast, cramps that tighten in waves, and diarrhea that leaves you drained. Most cases...
Food Stuck in Throat Sensation: GERD, Anxiety, or Esophageal Issues?
That “food stuck in your throat” feeling can be unsettling—especially when it comes and goes, or shows up during stressful weeks. Sometimes it’s a...
Foods That Cause Gas: The Biggest Triggers and How to Reduce Symptoms
Gas is a normal byproduct of digestion, but it can feel anything but normal when it shows up as bloating, pressure, cramping, or frequent...
Foods That Firm Up Loose Stool: Soluble Fiber, Salt, and Simple Meal Ideas
Loose stool can turn an ordinary day into a careful negotiation with bathrooms, work, and meals. Food cannot fix every cause, but the right...
Foul-Smelling Stool: Common Reasons and When It’s Concerning
Most stool has an odor, but sometimes the smell turns unusually strong—sharp, rancid, “rotten egg,” or simply harder to ignore. That shift can be...
Fructose Malabsorption: Symptoms, Tests, and Diet Tips
Fructose malabsorption is a common, often overlooked reason for post-meal bloating, gas, and unpredictable bowel habits. It happens when the small intestine cannot absorb...
Functional Dyspepsia: Symptoms, Triggers, and What Helps
Functional dyspepsia is a long-running pattern of upper-abdominal discomfort that can make eating feel unpredictable: a few bites and you are uncomfortably full, or...
Functional GI Disorders: What They Are and How They’re Diagnosed
Functional gastrointestinal (GI) disorders are some of the most common reasons people seek digestive care—yet they’re also among the most misunderstood. These conditions can...
Camu Camu for immunity, skin support, and antioxidant health
Camu camu (Myrciaria dubia) is a small, intensely sour Amazonian fruit that has become popular well beyond its native riverbanks for one simple reason:...
Caralluma weight loss, appetite suppression, dosage, and side effects
Caralluma (Caralluma fimbriata) is a succulent plant traditionally eaten in parts of India, often described as a “famine food” used during long travel or...
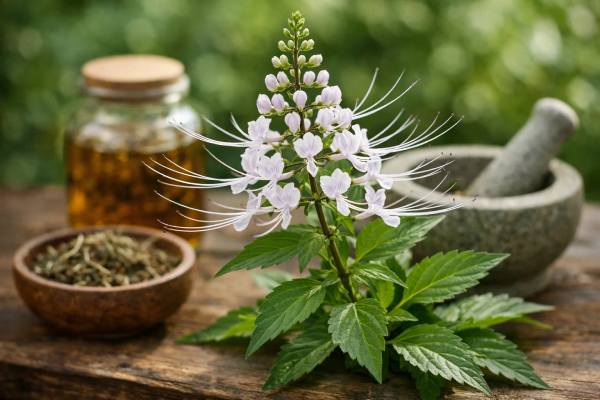
Cat’s Whiskers, urinary tract support, kidney health, and diuretic tea benefits
Cat’s whiskers (Orthosiphon aristatus), often called Java tea, is a traditional herbal leaf used most famously for “urinary tract flushing” and gentle fluid support....
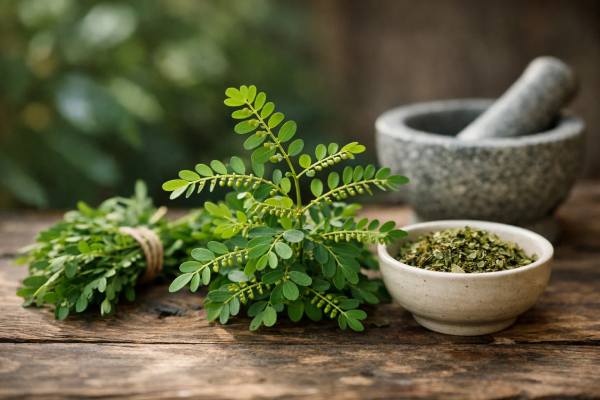
Chanca Piedra for kidney stones, urinary health, and evidence-based use
Chanca piedra, often called “stone breaker,” is a small tropical plant traditionally used to support urinary comfort and help manage kidney stone tendencies. In...
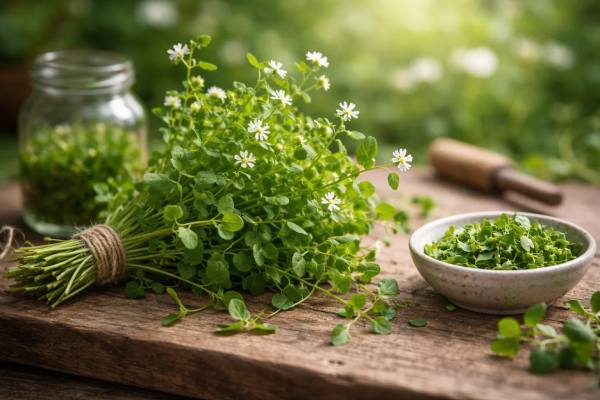
Chickweed benefits, uses, dosage, and side effects
Chickweed (Stellaria media) is one of those humble plants that quietly earns a permanent place in traditional herbalism: soft, green, and often growing at...
Chinese Goldthread benefits, berberine content, uses, dosage, and safety guide
Chinese goldthread (Coptis chinensis)—often called Huanglian in traditional East Asian medicine—is a very bitter rhizome valued for its “cooling” and cleansing character. In modern...
Chlorella for Detox and Immunity, How It Works, Dosage, and Safety Precautions
Chlorella is a bright-green, single-celled freshwater microalga best known as a nutrient-dense “greens” supplement. Unlike leafy plants, it packs protein, chlorophyll, carotenoids, minerals, and...
Cissus Quadrangularis benefits, bone healing, joint support, and safety
Cissus quadrangularis (Cissus quadrangularis) is a vine-like plant long used in traditional systems for bone and connective tissue support—earning the well-known nickname “bone setter.”...