Cirrhotic cardiomyopathy: Early Symptoms, Diagnostic Tests, and Management Strategies
Cirrhotic cardiomyopathy is a pattern of heart dysfunction that develops in people with liver cirrhosis. Many patients feel “fine” at rest because cirrhosis often...
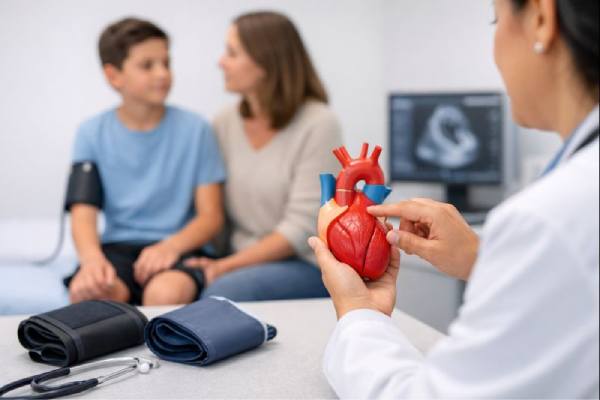
Cleft mitral valve: Overview, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
A cleft mitral valve is a congenital (present-from-birth) split or indentation in one leaflet of the mitral valve—the “gate” that controls blood flow from...
Coarctation of the aorta: Causes, Risk Factors, Complications, and Long-Term Management
Coarctation of the aorta is a narrowing in the body’s main artery that makes the heart pump against extra resistance. The condition is usually...
Collateral circulation disorder: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
When a major artery narrows or closes, your body may try to “detour” blood through smaller connecting vessels called collaterals. In some people, these...
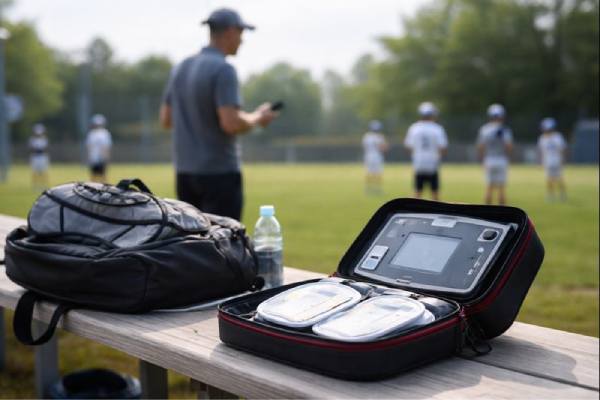
Commotio cordis: Causes, Risk Factors, Symptoms, and Rapid Treatment
Commotio cordis is one of the most sudden and unsettling medical emergencies in sport: a healthy person takes a seemingly routine blow to the...
Complete heart block, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and modern pacing treatment
Complete heart block (also called third-degree atrioventricular, or AV, block) is a condition where the heart’s upper chambers (atria) and lower chambers (ventricles) stop...
Conduction disorder of the heart, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options
A conduction disorder of the heart is a problem in the electrical wiring that tells your heart when to beat. Instead of a smooth,...
Congenital aortic stenosis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Long-Term Care
Congenital aortic stenosis is a narrowing at or near the aortic valve that is present from birth. The aortic valve is the heart’s “front...
Congenital coronary artery anomaly: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Imaging, and Treatment Options
A congenital coronary artery anomaly is an “as-built” difference in the way one or more coronary arteries arise, travel, or connect. Many variants never...
Congenital heart block: Complete AV Block Explained, Risks, Testing, and Long-Term Care
Congenital heart block is a problem with the heart’s electrical wiring that is present before birth. Instead of signals moving smoothly from the upper...
Congenital heart disease: Types, Early Signs, Diagnosis, and Modern Treatments
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is an umbrella term for heart and blood-vessel differences that form before birth. Some are mild and never cause symptoms;...
Congenital mitral valve anomalies: Types, Severity Grading, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Congenital mitral valve anomalies are structural differences in the mitral valve that develop before birth. The mitral valve sits between the left atrium and...
Congenital pericardial defect: Types, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
A congenital pericardial defect means a person is born with a missing or incomplete pericardium—the thin, tough “sac” that normally surrounds the heart and...
Congenital valve defects: Types, Stenosis vs Regurgitation, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Congenital valve defects are structural differences in one or more heart valves that develop before birth. A valve may be too narrow to open...
Congenital valvular heart disease: Causes, Genetic Risk, Associated Defects, and Complications
Congenital valvular heart disease means you are born with a heart valve that formed differently—too narrow, too leaky, or built with an unusual shape...
Congestive heart failure: Symptoms, Stages, and When It Becomes an Emergency
Congestive heart failure (often shortened to “heart failure” or CHF) means the heart cannot keep up with the body’s needs without extra pressure and...