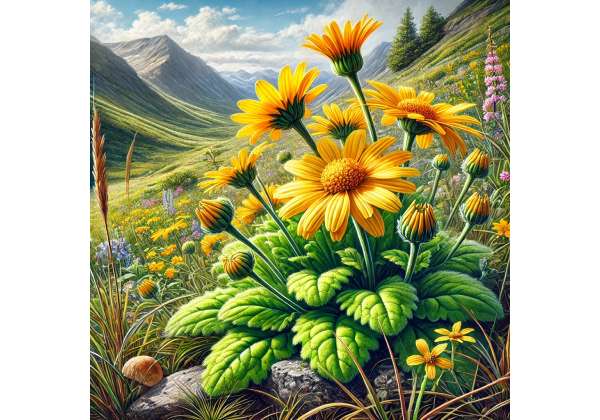
Arnica, most commonly known as Arnica montana or mountain arnica, is a perennial flowering plant native to the mountainous regions of Europe and parts of North America. Revered for centuries in folk and traditional medicine, Arnica is best known for its potent anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. This herb has long been used externally to treat bruises, sprains, and muscle pain, and more recently, its bioactive compounds have attracted the attention of modern research for their potential to accelerate healing and reduce inflammation. Beyond its medicinal applications, Arnica also plays a role in homeopathy and herbal remedies, and its vibrant yellow-orange flowers add ornamental value to alpine meadows and gardens.
Arnica is a fascinating herb that not only embodies the resilience of nature in harsh, mountainous terrains but also offers a wealth of therapeutic benefits. Its long history of traditional use, coupled with emerging scientific validation, makes Arnica a valuable natural remedy. Whether incorporated into topical ointments, infused in oils, or used in homeopathic preparations, Arnica continues to be an important herb for supporting musculoskeletal health and reducing discomfort after injuries.
- Traditional use in treating bruises, sprains, and muscle injuries
- Its rich content of bioactive compounds, including sesquiterpene lactones
- Long-standing historical use in European folk medicine and homeopathy
- Its ornamental value and adaptation to high-altitude, rugged landscapes
Table of Contents
- Arnica: Botanical Profile and Characteristics
- Arnica: Historical Background and Cultural Legacy
- Arnica: Active Compounds and Phytochemical Composition
- Arnica: Key Health Benefits and Therapeutic Properties
- Arnica: Uses, Applications, and Safety Guidelines
- Arnica: Recent Studies and Scientific Insights
- Arnica: Frequently Asked Questions
Arnica: Botanical Profile and Characteristics
Taxonomy and Botanical Description
Arnica montana, belonging to the Asteraceae family, is one of the best-known species of the Arnica genus. This herbaceous perennial grows in the alpine meadows and mountainous regions of Europe, particularly in the Pyrenees, Alps, and Carpathian Mountains. Its scientific classification is as follows:
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Order: Asterales
- Family: Asteraceae
- Genus: Arnica
- Species: A. montana
Morphology
- Stems and Leaves:
Arnica features robust, erect, and branching stems that can reach up to 60 centimeters (24 inches) in height. The leaves are broad, oval to lanceolate, and have a rough, slightly hairy surface. They are arranged alternately along the stems and are typically a deep green, providing a strong contrast to the bright, showy flowers. - Flowers:
The inflorescences of Arnica are daisy-like and radiate a brilliant yellow or orange color. Each composite flower head is made up of numerous tiny florets, with prominent ray florets surrounding a central disc. The striking appearance of its blooms is not only aesthetically pleasing but also serves as a signal for pollinators. - Fruit:
After flowering, Arnica produces small, dry, one-seeded fruits known as achenes. These fruits are dispersed by the wind, enabling the plant to colonize the open, rocky soils of its native habitat.
Habitat and Cultivation
- Native Environment:
Arnica montana thrives in nutrient-poor, well-drained, and slightly acidic soils typical of alpine and subalpine regions. It prefers cool, moist climates with full sun exposure and is adapted to the rigorous conditions of high-altitude environments. - Cultivation Challenges:
Due to its specialized habitat requirements, cultivating Arnica outside its native range can be challenging. It demands careful attention to soil pH, drainage, and microclimate conditions. However, modern horticultural techniques have made it possible to grow Arnica in controlled environments for both ornamental and medicinal purposes. - Ecological Importance:
In its natural habitat, Arnica plays a significant role in supporting local biodiversity. Its flowers attract various pollinators, including bees and butterflies, contributing to the overall health of alpine ecosystems.
Arnica’s botanical profile, characterized by its robust stems, vibrant flowers, and adaptability to challenging environments, underscores its importance as both an ornamental and medicinal plant. Its ability to thrive in harsh conditions reflects its resilience, which is mirrored in its potent therapeutic properties.
Arnica: Historical Background and Cultural Legacy
Traditional European Herbalism
Arnica has a long and storied history in European folk medicine. Its use dates back to ancient times, and it was highly regarded by herbalists for its potent healing properties. Traditional texts and folklore have preserved the knowledge of Arnica’s applications for centuries.
- Medieval and Renaissance Use:
During the medieval period, Arnica was a staple in the apothecaries of Europe. Herbalists utilized its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties to treat bruises, sprains, and other injuries. It was often prepared as an ointment or tincture, applied topically to alleviate pain and reduce swelling. - Homeopathy:
In the 18th and 19th centuries, Arnica became a foundational remedy in homeopathy. Homeopathic preparations of Arnica montana are still among the most widely used remedies, particularly for trauma, muscle soreness, and shock. The belief in its “like cures like” principle has contributed significantly to its global reputation.
Cultural Significance and Folklore
- Symbol of Healing:
Arnica’s vibrant yellow blooms and its reputation for rapid healing made it a symbol of recovery and rejuvenation in various European cultures. It was often associated with the idea of natural resilience and the restorative power of the earth. - Mythology and Ritual:
Some folklore traditions imbued Arnica with mystical properties, associating it with protection against evil spirits and as a charm for recovery. Its use in ceremonial remedies underscored its importance as a natural healer.
Modern Revival and Global Usage
- Contemporary Herbal Medicine:
In recent decades, there has been a resurgence of interest in traditional herbal remedies, and Arnica has experienced renewed popularity. Today, it is widely used in both conventional herbal medicine and homeopathy for its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and wound-healing properties. - Cosmetic Applications:
Beyond its medicinal uses, Arnica is also valued in the cosmetic industry. It is incorporated into creams, gels, and ointments designed to reduce bruising, promote skin healing, and improve the appearance of scars. - Commercial Cultivation:
Given its high demand, Arnica is now cultivated in several European countries and in North America under controlled conditions. Advances in agricultural practices have enabled the production of high-quality Arnica extracts that meet modern safety and efficacy standards.
The cultural legacy of Arnica, deeply embedded in European traditional medicine and homeopathy, continues to influence its contemporary applications. Its historical reputation as a natural healer is matched by its modern use in both medicinal and cosmetic formulations, making it a timeless herb of significant global interest.
Arnica: Active Compounds and Phytochemical Composition
The potent therapeutic effects of Arnica are attributed to its rich array of bioactive compounds. These phytochemicals work synergistically to deliver the herb’s renowned anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and healing properties.
Sesquiterpene Lactones
- Key Constituents:
The primary active compounds in Arnica are sesquiterpene lactones, such as helenalin and dihydrohelenalin. These compounds are largely responsible for Arnica’s anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. - Mechanisms of Action:
Helenalin, in particular, has been shown to inhibit the activity of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a protein complex that plays a key role in regulating the inflammatory response. This inhibition helps reduce inflammation and pain in injured tissues.
Flavonoids and Phenolic Compounds
- Antioxidant Properties:
Arnica contains various flavonoids, including quercetin and kaempferol, which contribute to its antioxidant activity. These antioxidants help scavenge free radicals, protecting cells from oxidative stress and supporting overall tissue repair. - Polyphenols:
The polyphenolic compounds in Arnica further enhance its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, which are critical in promoting wound healing and reducing infection risks.
Essential Oils
- Volatile Components:
Arnica also contains a range of essential oils that contribute to its aromatic profile and mild antimicrobial activity. These volatile compounds can enhance the overall therapeutic effect when Arnica is applied topically.
Other Bioactive Compounds
- Tannins:
Tannins present in Arnica may contribute to its astringent properties, helping to contract tissues and reduce bleeding in wounds. - Coumarins:
Some coumarin derivatives in Arnica also exhibit mild anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, complementing the action of sesquiterpene lactones.
Nutritional Content
- Trace Minerals and Vitamins:
Although not consumed in large quantities, Arnica contains small amounts of essential vitamins and minerals that support cellular health and the overall healing process.
The complex interplay of these bioactive compounds underpins Arnica’s long-standing use in traditional medicine and homeopathy. Together, they provide a robust pharmacological profile that supports its use in reducing inflammation, alleviating pain, and promoting the healing of wounds and bruises.
Arnica: Notable Health Benefits and Therapeutic Properties
Arnica is celebrated for its broad spectrum of health benefits, particularly its ability to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and accelerate the healing process. Its applications span a variety of conditions, from minor injuries and bruises to muscle soreness and chronic inflammatory disorders.
1. Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Effects
- Pain Reduction:
Arnica’s sesquiterpene lactones, particularly helenalin, are potent anti-inflammatory agents that help reduce swelling and relieve pain. Topical applications of Arnica creams and gels are widely used to manage the pain associated with bruises, sprains, and muscle soreness. - Inflammation Control:
By inhibiting inflammatory mediators such as NF-κB, Arnica can reduce the inflammatory response, which in turn helps decrease discomfort and promote faster recovery following injury.
2. Wound Healing and Tissue Repair
- Accelerated Healing:
Traditional use of Arnica in herbal medicine includes its application to wounds, cuts, and abrasions. Its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties help to prevent infection and accelerate the healing process. - Reduction of Bruising:
Arnica is perhaps best known for its ability to reduce the appearance of bruises. Regular topical application to the affected area can help speed up the reabsorption of blood, thereby diminishing discoloration and pain.
3. Musculoskeletal Relief
- Treatment of Sprains and Strains:
Arnica is a popular remedy for relieving the pain and swelling associated with sprains, strains, and other soft tissue injuries. It is often applied in the form of creams, ointments, or compresses immediately after injury to reduce inflammation and support recovery. - Muscle Soreness:
Athletes and active individuals use Arnica to ease muscle soreness and stiffness after strenuous exercise. Its analgesic properties help to relieve pain and promote relaxation of overworked muscles.
4. Anti-Oxidant and Immune Support
- Cellular Protection:
The flavonoids and polyphenols in Arnica provide antioxidant benefits, protecting cells from oxidative stress and potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases. - Immune System Modulation:
Some studies suggest that Arnica may support the immune system by reducing inflammation and oxidative damage, thereby enhancing the body’s natural defense mechanisms.
5. Applications in Homeopathy
- Homeopathic Remedy:
Arnica montana is one of the most widely used remedies in homeopathy. It is employed to treat a range of conditions including trauma, shock, and bruising. Homeopathic preparations of Arnica are highly diluted and are believed to stimulate the body’s natural healing response without causing significant side effects.
6. Additional Uses
- Skin Care:
Arnica is used in cosmetic formulations to promote skin healing, reduce the appearance of scars, and improve overall skin tone. Its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties make it a beneficial ingredient in anti-aging products. - Circulatory Support:
By improving blood circulation and reducing capillary fragility, Arnica may help in managing conditions associated with poor circulation, such as varicose veins and minor circulatory disturbances.
Overall, the health benefits of Arnica are well-documented in both traditional and modern contexts. Its ability to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, promote wound healing, and support overall tissue repair makes it an invaluable herb in integrative and alternative medicine.
Arnica: Uses, Applications, and Safety Guidelines
Common Applications
- Topical Preparations:
- Creams, Ointments, and Gels:
Arnica is most commonly used topically. Creams and gels containing Arnica extract are applied to bruises, sprains, and muscle soreness to reduce pain and inflammation. - Compresses and Poultices:
Fresh or reconstituted Arnica can be used in compresses or poultices for acute injuries. This method is especially popular in traditional European medicine.
- Homeopathic Remedies:
- Low-Dilution Preparations:
In homeopathy, Arnica montana is used in highly diluted forms to treat trauma, shock, and general pain. These remedies are available as pellets, liquid drops, or tablets.
- Cosmetic Formulations:
- Skincare Products:
Arnica extract is included in various skincare products such as creams, serums, and lotions aimed at reducing inflammation, promoting wound healing, and improving the appearance of bruises and scars.
Dosage Guidelines
- Topical Application:
- Apply Arnica cream or gel to the affected area 2–3 times daily. Do not use on broken skin unless specified by a professional.
- Homeopathic Remedies:
- Follow the dosing instructions provided on the product. Common regimens involve taking 3–5 pellets every few hours during acute trauma, then gradually reducing the frequency.
- Over-the-Counter Supplements:
- Arnica supplements are less common due to potential toxicity concerns with oral ingestion. When used, they should be taken strictly as directed by a healthcare professional.
Safety Precautions
- Avoid Ingestion of Unprocessed Arnica:
- Raw or unprocessed Arnica can be toxic if ingested. Always use products that have been properly processed and standardized.
- Do Not Apply to Broken Skin (Unless Advised):
- Topical Arnica should not be applied to open wounds or broken skin as it may cause irritation or systemic absorption of its compounds.
- Consultation for Sensitive Groups:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women, as well as individuals with underlying health conditions, should consult a healthcare provider before using Arnica products.
- Monitor for Allergic Reactions:
- Although allergic reactions are rare, some people may experience skin irritation or other sensitivities. Discontinue use if any adverse reaction occurs.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines:
- Always adhere to the dosage and usage instructions provided on commercial Arnica products, whether they are creams, gels, or homeopathic preparations.
By following these guidelines, Arnica can be safely incorporated into your regimen to harness its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and healing properties. It is important to use Arnica under the guidance of a healthcare professional, especially in cases of severe injury or chronic conditions.
Arnica: Recent Studies and Emerging Scientific Insights
Modern scientific research is increasingly validating the traditional uses of Arnica, particularly its efficacy in reducing inflammation and promoting wound healing.
1. Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Research
- Study (2017), Phytotherapy Research:
A controlled study on Arnica montana extracts demonstrated a significant reduction in inflammatory markers, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). The research provided evidence that topical Arnica preparations can reduce pain and swelling in soft tissue injuries.
2. Wound Healing Efficacy
- Clinical Trial (2018), Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine:
In a clinical trial, patients with mild to moderate bruising and sprains who applied Arnica cream experienced faster recovery times and a reduction in bruise size compared to a placebo group. The study concluded that Arnica is effective in accelerating the healing process in superficial injuries.
3. Homeopathic Applications
- Review (2019), Homeopathy Journal:
A comprehensive review of clinical trials involving homeopathic Arnica preparations confirmed their effectiveness in reducing pain and inflammation in trauma cases. Although the mechanism remains controversial due to the high dilution levels, the clinical outcomes support its continued use in homeopathy.
4. Safety and Toxicological Assessments
- Toxicity Study (2020), Toxicology Reports:
Research into the toxicological profile of Arnica demonstrated that while topical use in controlled doses is generally safe, ingestion of raw Arnica can lead to systemic toxicity. The study underscores the importance of using properly processed and standardized Arnica products.
Arnica: Frequently Asked Questions
Is Arnica safe for topical use on bruises and sprains?
Yes, Arnica is widely used topically to reduce bruising and relieve pain associated with sprains and soft tissue injuries. However, it should not be applied to broken or open wounds unless directed by a healthcare professional.
Can Arnica be used in homeopathic preparations?
Yes, Arnica montana is one of the most commonly used remedies in homeopathy, particularly for trauma, shock, and bruising. Homeopathic preparations are highly diluted and considered safe when used as directed.
What forms of Arnica are available for medicinal use?
Arnica is available in several forms, including topical creams, gels, tinctures, and homeopathic pellets. It is also used in some over-the-counter supplements, though oral use is generally not recommended due to potential toxicity.
Are there any side effects associated with Arnica?
When used topically in recommended doses, Arnica is generally safe. However, some individuals may experience skin irritation or allergic reactions. Oral ingestion of unprocessed Arnica can be toxic, so it is important to follow usage guidelines carefully.
Disclaimer:
This article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before starting any new herbal regimen, particularly if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
If you found this comprehensive guide on Arnica valuable, please share it on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or your preferred social media platform. Sharing this information helps others discover the natural healing potential of this time-honored herb!