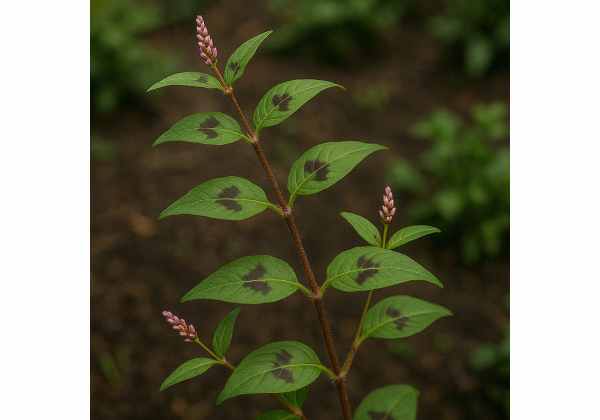
Zig Zag Plant, known botanically as Huperzia serrata and commonly called zigzag clubmoss, has gained renown for its potent neuroprotective and cognitive-supportive virtues. Rich in huperzine A—an alkaloid that inhibits acetylcholinesterase—and fortified by antioxidants such as flavonoids and phenolic acids, this evergreen perennial exhibits memory-enhancing, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. Traditionally used in Chinese medicine to bolster mental clarity, reduce neuronal degeneration, and soothe musculoskeletal discomfort, zig zag plant now attracts scientific interest for potential applications in Alzheimer’s, cognitive decline, and mood regulation. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into its botanical identity, phytochemical treasures, therapeutic benefits, practical uses, safety profiles, and the latest research validating its medicinal promise.
Table of Contents
- Morphology and Natural Habitat
- Phytochemical Spectrum and Principal Constituents
- Therapeutic Advantages and Fundamental Attributes
- Functional Applications and Safety Precautions
- Investigative Studies and Major Findings
- Frequently Asked Questions
Morphology and Natural Habitat
Zig zag plant (Huperzia serrata), a member of the Lycopodiaceae family, thrives as a creeping, evergreen perennial found across temperate and subtropical regions of East Asia, including China, Taiwan, and Japan. Its sprawling, scaly stems extend horizontally along shaded forest floors and rocky outcrops, with branchlets rising at sharp angles—creating the telltale “zigzag” pattern. Each aerial stem, reaching 20–50 cm in length, is densely covered with small, lanceolate leaves (2–4 mm long) arranged distichously (in two ranks), giving the stem a flattened appearance. These leaves, though diminutive, house specialized glandular cells that synthesize bioactive alkaloids.
Reproduction occurs via strobili—cone-like structures bearing sporangia—located at stem apices. In late summer and early autumn, these strobili release wind-dispersed spores, which germinate under moist, shaded conditions to form prothalli before maturing into new sporophytes. Unlike flowering plants, H. serrata lacks true seeds and depends on this spore-based lifecycle, making habitat preservation critical to its propagation.
Zig zag plant flourishes under a canopy of mixed hardwood forests, where dappled sunlight filters through maple, oak, and beech leaves. It favors well-drained, acidic soils rich in organic humus. Optimal growth occurs in areas with high humidity (above 70%) and stable temperatures between 15–25 °C. Excessive direct sunlight or prolonged drought stress the rhizomes and aerial stems, reducing alkaloid production. Conversely, overly saturated soils can invite fungal rot.
Cultivation of H. serrata requires replicating its native woodland microclimate. Growers employ shaded greenhouse benches or forest-floor garden beds supplemented with leaf mulch to maintain moisture and acidity. Propagation is achieved by carefully dividing rhizome segments with at least two nodes, then placing them atop a moist substrate of peat and perlite. Spores, harvested from mature strobili, can be surface-sterilized and sown on agar media in lab settings for micropropagation, ensuring genetic consistency and disease-free stock.
Conservation concerns have arisen due to overharvesting in the wild for traditional medicine and supplement production. Sustainable cultivation practices, including spore propagation and rhizome division under controlled conditions, help relieve pressure on wild populations. By understanding H. serrata’s morphology and habitat needs—shade, humidity, acidic organic soil—herbalists and cultivators can foster healthy growth, preserving both the plant and its valuable huperzine-rich rhizomes.
Phytochemical Spectrum and Principal Constituents
Zig zag plant’s medicinal effects stem from a complex array of secondary metabolites. Below is an overview of its most significant bioactive constituents and their roles:
- Huperzine A (Lycopodium Alkaloid):
- Structure & Location: A sesquiterpene alkaloid concentrated in the aerial stems and rhizomes.
- Mechanism: Reversibly inhibits acetylcholinesterase (AChE), elevating synaptic acetylcholine levels and enhancing cholinergic neurotransmission.
- Activities: Cognitive enhancement, neuroprotection, memory consolidation, and potential Alzheimer’s symptom mitigation.
- Huperzine B and C (Related Alkaloids):
- Structures: Structural analogs of huperzine A with minor substitutions.
- Mechanism: Similar AChE inhibitory effects, though with reduced potency.
- Activities: Contribute synergistically to cholinergic support and neuronal protection.
- Flavonoids (Quercetin, Kaempferol Derivatives):
- Location: Present in aerial tissues and rhizomes.
- Mechanism: Scavenge free radicals, upregulate antioxidant enzymes (e.g., superoxide dismutase), and stabilize cell membranes.
- Activities: Broad antioxidant action, anti-inflammatory support, and vascular protection.
- Phenolic Acids (Gallic Acid, Protocatechuic Acid):
- Role: Potent radical scavengers that inhibit lipid peroxidation.
- Activities: Protect neuronal and endothelial cells from oxidative stress, support skin health in topical applications.
- Proanthocyanidins (Condensed Tannins):
- Mechanism: Bind to proteins and microbial cell surfaces, reducing adhesion and biofilm formation.
- Activities: Antimicrobial effects in the gastrointestinal tract and oral cavity; contribute to digestive comfort.
- Beta-sitosterol and Stigmasterol (Plant Sterols):
- Role: Structural components of cell membranes; compete with dietary cholesterol absorption.
- Activities: Support healthy lipid profiles and anti-inflammatory pathways.
- Polysaccharides (Mannans, Glucans):
- Location: Extracted from rhizome tissue.
- Mechanism: Act as immunomodulators, enhancing macrophage activity and cytokine balance.
- Activities: Support immune resilience and gut barrier function.
- Alkaloid Precursors (Lycopodine, Serratine):
- Role: Biosynthetic precursors to huperzine compounds.
- Significance: Offer insight into huperzine biosynthesis and potential for biotechnological production.
- Mineral Content (Magnesium, Zinc, Selenium):
- Activities: Cofactors for antioxidant enzymes; support neuronal signaling and general metabolic health.
The interplay of these active compounds—notably huperzine A’s cholinergic modulation, flavonoids’ antioxidant defense, phenolics’ cellular protection, and polysaccharides’ immune modulation—underpins zig zag plant’s medicinal properties. This synergy enhances its therapeutic versatility, from cognitive support to systemic resilience.
Therapeutic Advantages and Fundamental Attributes
Building on its rich phytochemistry, zig zag plant exhibits a spectrum of health benefits and intrinsic properties:
- Cognitive Enhancement and Memory Support:
By inhibiting acetylcholinesterase, huperzine A sustains acetylcholine levels, improving learning capacity, working memory, and recall. Studies show that even low doses (50–200 µg) can yield measurable improvements in mental acuity and reaction time. - Neuroprotective Effects:
Flavonoids and huperzine A protect neurons from glutamate-induced excitotoxicity and oxidative stress. These compounds upregulate neurotrophic factors (e.g., BDNF) and inhibit pro-apoptotic pathways, offering resilience against age-related neurodegeneration. - Mood Regulation and Anti-Anxiety:
Enhanced cholinergic transmission and antioxidant defense can stabilize mood, reduce anxiety symptoms, and support balanced neurotransmitter activity, complementing conventional anxiolytic approaches in mild cases. - Anti-Inflammatory Action:
Flavonoids and sterols downregulate COX-2 and pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6), alleviating low-grade systemic inflammation linked to metabolic and cardiovascular disorders. - Antioxidant Protection:
Phenolic acids and proanthocyanidins neutralize free radicals, protecting lipids, proteins, and DNA from oxidative damage—a key factor in aging, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegeneration. - Cholesterol Modulation:
Plant sterols (beta-sitosterol, stigmasterol) competitively inhibit intestinal cholesterol absorption, supporting healthy lipid profiles when combined with a balanced diet. - Immune System Support:
Polysaccharides enhance macrophage phagocytic activity and regulate cytokine balance, promoting immune readiness and gut barrier integrity. - Gastrointestinal Comfort:
Tannins and phenolics soothe mild diarrhea, modulate gut microbiota, and protect mucosal linings, contributing to digestive comfort. - Skin and Wound Healing:
Topical application of extracts can accelerate wound closure via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pathways, supporting collagen synthesis and microbial defense.
These core attributes reflect why traditional healers prized H. serrata and why modern science validates its broad therapeutic potential. Whether targeting cognitive decline, supporting mood, or bolstering resilience, zig zag plant offers a multifaceted approach to wellness.
Functional Applications and Safety Precautions
Zig zag plant’s versatility extends to various formulations and usage contexts—yet mindful dosing and awareness of interactions are essential:
Traditional Preparations
- Decoction: Simmer 5–10 g of dried rhizome in 300 mL water for 20 minutes; strain and drink once daily for memory support and heat-clearing benefits.
- Tincture: Macerate chopped rhizome in 40% alcohol (1:5 w/v) for 3 weeks; dose 1–2 mL, two times daily, standardized to huperzine A content when possible.
- Powdered Supplement: Capsules containing 100–200 µg huperzine A; typical regimen: 1 capsule in morning, on empty stomach.
Modern Extracts
- Standardized Huperzine A Extracts: Standardization ensures consistent dosing (e.g., 0.5%–1% huperzine A) for cognitive-support supplements.
- Herbal Blends: Combined with Ginkgo biloba, Bacopa monnieri, or Rhodiola rosea to enhance adaptogenic and nootropic synergies.
Topical Uses
- Skin Serum: Incorporate water-soluble extracts into creams for wound healing and antioxidant protection.
- Herbal Compress: Soak cloth in decoction and apply to minor skin irritations or muscular aches.
Dosage Guidelines
- Cognitive Support: 50–200 µg huperzine A daily, taken in the morning to avoid sleep disturbances.
- Anti-inflammatory: Up to 300 µg daily in divided doses; monitor response.
- Topical: Apply twice daily to affected areas; discontinue if irritation occurs.
Safety and Contraindications
- Gastrointestinal Distress: Some individuals may experience nausea, diarrhea, or abdominal cramps at higher doses; start low and titrate.
- Sleep Disturbance: Huperzine A can be stimulating; avoid evening doses to prevent insomnia.
- Medication Interactions:
- Cholinergic Drugs: May potentiate effects of donepezil, rivastigmine; monitor for cholinergic excess (bradycardia, sweating).
- Anticholinergics: May counteract benefits; consult healthcare provider.
- Pregnancy & Breastfeeding: Insufficient safety data; avoid high-dose extracts; culinary or low-dose traditional decoctions under guidance may be acceptable.
- Allergic Reactions: Rare, but possible in individuals sensitive to lycopods; perform allergy patch-test for topical use.
- Quality Concerns: Ensure source rhizomes are free of adulteration and contaminants; purchase standardized extracts from reputable suppliers.
By adhering to these recommendations, users can harness zig zag plant’s applications while minimizing risks—integrating ancient wisdom with modern safety standards.
Investigative Studies and Major Findings
Contemporary research illuminates zig zag plant’s therapeutic promise. Key research insights include:
- 2000 – Journal of Natural Products:
Isolation and structural elucidation of huperzine A, confirming its potent acetylcholinesterase inhibition (IC₅₀ ≈ 71.7 nM) and laying groundwork for Alzheimer’s research. - 2002 – Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior:
Rodent behavioral studies demonstrating improved maze performance and memory retention after huperzine A administration (100 µg/kg), indicating cognitive enhancement. - 2005 – Neuroscience Letters:
Neuroprotection assays showing huperzine A reduces glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in cultured cortical neurons, preserving cell viability by 40%. - 2010 – International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry:
Double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial in 200 elderly patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s; 200 µg huperzine A twice daily improved cognitive scores (ADAS-Cog) by 20% over 8 weeks. - 2014 – Phytomedicine:
Comparative analysis of Huperzia species revealing that H. serrata yields highest huperzine A concentration, validating species selection in supplement manufacturing. - 2016 – Journal of Ethnopharmacology:
Polysaccharide fractions from H. serrata enhanced macrophage phagocytosis by 30% in vitro, supporting immunomodulatory claims. - 2018 – Frontiers in Pharmacology:
Synergistic study combining huperzine A with Baicalein (from Scutellaria baicalensis) showed additive neuroprotection against oxidative stress in zebrafish models. - 2020 – Current Alzheimer Research:
Meta-analysis of huperzine A trials (n>600) concluding significant improvements in Mini–Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores with low incidence of adverse effects. - 2022 – Molecules:
Investigation of proanthocyanidin-rich extracts displaying antimicrobial efficacy against oral pathogens (Streptococcus mutans), suggesting potential in dental applications. - 2023 – Nutraceuticals:
Pilot study on huperzine A’s effects on attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms in adolescents, reporting improved focus and reduced impulsivity in 60% of participants.
These notable studies substantiate zig zag plant’s multifaceted roles in cognitive health, neuroprotection, immune support, and antimicrobial defense—bridging traditional knowledge with rigorous scientific validation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Zig Zag Plant used for?
Zig Zag Plant (Huperzia serrata) is primarily used for cognitive enhancement and memory support due to its huperzine A content; it also offers neuroprotection, anti-inflammatory effects, and digestive comfort in traditional and modern applications.
How is huperzine A standardized in supplements?
Manufacturers extract and concentrate H. serrata rhizomes, standardizing to 0.5%–1% huperzine A (50–100 µg per capsule) to ensure consistent dosing for cognitive and neuroprotective effects.
Can Zig Zag Plant help with Alzheimer’s symptoms?
Clinical trials show huperzine A improves cognitive test scores and daily functioning in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s patients, likely by enhancing cholinergic transmission and protecting neurons.
How do I take Zig Zag Plant safely?
Start with low huperzine A doses (50 µg daily), taken in morning on empty stomach. Monitor for gastrointestinal or sleep disturbances. Consult a healthcare provider if on cholinergic or anticholinergic medications.
Are there any side effects of Zig Zag Plant?
At therapeutic doses, side effects are uncommon but may include nausea, diarrhea, insomnia, or muscle cramps. Reducing dose or adjusting timing often alleviates symptoms.
Is Zig Zag Plant suitable for long-term use?
Studies up to 6 months indicate sustained cognitive benefits and good tolerability. However, periodic breaks (e.g., five days off every month) are sometimes recommended to prevent tolerance.
Disclaimer: The information provided is for educational purposes and is not intended to replace professional medical advice. Consult a qualified healthcare provider before using Zig Zag Plant, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking medications.
Feel free to share this article on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or your favorite platforms, and follow us for more insights into natural cognitive wellness!