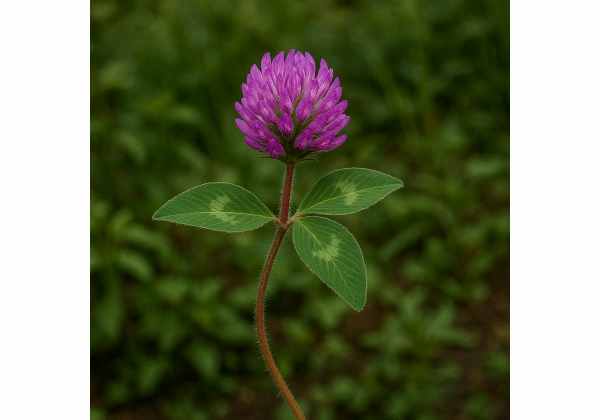
Zigzag clover (Trifolium medium), a versatile wild legume, has long graced meadows and forest edges with its delicate pink blooms and trifoliate leaves. Beyond its ornamental charm, this humble herb packs a punch of health-supportive compounds—phytoestrogens, flavonoids, saponins, and essential minerals—that contribute to hormonal balance, cardiovascular wellness, and skin health. Traditional herbalists prized its mild astringency to soothe digestive upsets and ease mild inflammation, while modern research explores its potential as a natural source of plant-based estrogens for menopausal support. In this in-depth guide, we’ll uncover zigzag clover’s botanical identity, phytochemical treasures, therapeutic strengths, practical uses, safety considerations, and the latest scientific studies illuminating its medicinal promise.
Table of Contents
- Botanical Characterization and Natural Range
- Phytochemical Profile and Core Constituents
- Healing Advantages and Core Qualities
- Practical Applications and Precautionary Guidelines
- Research Findings and Significant Insights
- Frequently Asked Questions
Botanical Characterization and Natural Range
Zigzag clover, scientifically known as Trifolium medium, belongs to the Fabaceae (legume) family and is a wild relative of the common red clover. Its slender stems, which grow to 20–40 centimeters tall, exhibit a distinctive zigzag pattern as each internode alternates direction—hence its common name. Along these stems emerge trifoliate leaves, each leaflet measuring 1.5–2.5 cm long with slightly serrated margins and a subtle white “V” mark on the surface. Come late spring and early summer, tight clusters of soft pink to rose-red pea-like flowers adorn the stem tips, attracting bees and other pollinators.
Native across temperate Eurasia, zigzag clover thrives in mixed woodlands, hedgerows, meadows, and roadside verges. It favors well-drained loamy soil with moderate fertility and a neutral to slightly acidic pH (6.0–7.0). Partial shade from dappled tree canopy encourages robust growth, though it tolerates full sun provided the substrate retains enough moisture through summer months. Its root system features a shallow taproot supplemented by lateral fibrous roots and nodules inhabited by Rhizobium bacteria—natural chemists that fix atmospheric nitrogen into soil-enriching nutrients.
Propagation of T. medium occurs both by seed and vegetative layering. Fallen flower heads release numerous small, hard-coated seeds that overwinter in the soil seed bank, sprouting when moisture and temperature cues align. In cultivated or restoration settings, sowing fresh seed in autumn yields spring germination, while summer management (mowing after bloom) helps maintain flowering vigor and prevents self-seeding from overwhelming other species.
Ecologically, zigzag clover plays multiple roles: as a nectar source for pollinators, as a green manure for nitrogen enrichment, and as groundcover that suppresses invasive weeds. Its low-growing habit integrates seamlessly into wildflower meadows and agroforestry understories. While generally resilient, populations can decline under overgrazing or heavy soil compaction, underscoring the value of thoughtful habitat stewardship to preserve this modest yet beneficial herb.
Phytochemical Profile and Core Constituents
Zigzag clover’s therapeutic allure derives from a diverse assembly of bioactive compounds. Below is an outline of its principal phytochemicals and their roles:
- Isoflavones (Formononetin, Biochanin A):
- Nature & Distribution: Phytoestrogenic flavonoids concentrated in blossoms and leaves.
- Mechanism: Bind estrogen receptors (ERα/ERβ), mildly mimicking or modulating human estrogen activity.
- Benefits: Support menopausal symptom relief, bone density maintenance, and cardiovascular health.
- Flavonoids (Quercetin, Kaempferol Derivatives):
- Mechanism: Scavenge reactive oxygen species, stabilize cell membranes, and inhibit pro-inflammatory enzymes (COX, LOX).
- Benefits: Provide antioxidant defense, anti-inflammatory support, and microvascular resilience.
- Saponins (Soyasaponin I & II):
- Structure & Function: Glycoside compounds conferring mild bitter/astringent taste.
- Mechanism: Interact with cell membranes, facilitating cholesterol efflux and modulating immune cell activity.
- Benefits: Support healthy lipid profiles, mild expectorant action in respiratory passages, and digestive comfort.
- Phenolic Acids (Caffeic, Chlorogenic Acid):
- Role: Non-flavonoid antioxidants present in aerial tissues.
- Mechanism: Inhibit lipid peroxidation and enhance endogenous antioxidant enzymes (SOD, CAT).
- Benefits: Protect against oxidative stress in skin and internal organs.
- Polysaccharides (Arabinogalactans):
- Source: Extracted from stems and roots.
- Mechanism: Act as immunomodulators by enhancing macrophage phagocytosis and natural killer cell activity.
- Benefits: Reinforce immune surveillance and support gut barrier integrity.
- Essential Minerals (Calcium, Magnesium, Potassium):
- Activities:
- Calcium & Magnesium: Support bone health, neuromuscular function.
- Potassium: Regulates fluid balance and cardiovascular tone.
- Vitamins (Vitamin C, Vitamin E):
- Role: Classic antioxidants; cofactors in collagen synthesis and cell membrane protection.
- Benefits: Enhance skin health, bolster immune defenses.
- Tannins (Condensed Tannins):
- Mechanism: Bind proteins on microbial surfaces, reducing adhesion and biofilm formation.
- Benefits: Offer mild antimicrobial effects in the digestive tract.
- Nitrogen-Fixing Nodulation:
- Symbiosis: Root nodules containing Rhizobium species convert atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia, indirectly enriching phytochemical synthesis by improving soil fertility.
This chemical constituents analysis underscores how zigzag clover’s phytoestrogens, antioxidants, saponins, and nutrients interweave to deliver active compounds that underpin its multifaceted medicinal properties.
Healing Advantages and Core Qualities
The synergy of zigzag clover’s phytochemicals translates into a broad spectrum of health benefits:
- Menopausal Symptom Relief:
Isoflavones such as formononetin and biochanin A gently modulate estrogen receptors, easing hot flashes, night sweats, and mood swings without the risks associated with hormone replacement therapy. - Cardiovascular Support:
Flavonoids and saponins promote healthy lipid metabolism—encouraging cholesterol balance—and improve endothelial function, contributing to stable blood pressure and reduced atherosclerotic risk. - Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Protection:
Phenolic compounds and flavonoids quench free radicals and downregulate inflammatory mediators (TNF-α, IL-6), offering cellular defense against aging and chronic inflammation. - Bone Health Maintenance:
Phytoestrogens, combined with calcium and magnesium, support bone mineral density, potentially lowering osteoporosis risk in postmenopausal individuals. - Skin Rejuvenation:
Topical applications of extracts rich in vitamin C, vitamin E, and phenolics can promote collagen synthesis, improve elasticity, and protect against UV-induced damage—ideal for lotions or facial steam treatments. - Digestive Comfort:
Saponins and tannins provide mild astringent action that can soothe occasional diarrhea or gastrointestinal irritation, while polysaccharides foster healthy microflora. - Immune Enhancement:
Arabinogalactans and flavonoids stimulate innate immune cells, supporting resilience during seasonal challenges and aiding in recovery from minor infections. - Hormonal Balance:
By exerting selective estrogen receptor modulation, zigzag clover can assist in regularizing menstrual cycles and alleviating PMS symptoms through its gentle endocrine influence. - Neuroprotective Potential:
Antioxidant-rich constituents protect neurons from oxidative damage, while isoflavones may support cognitive health via estrogenic pathways in the brain.
These core qualities demonstrate why zigzag clover has been embraced in traditional remedies and is now appreciated by modern herbalists for its holistic approach to wellness.
Practical Applications and Precautionary Guidelines
Zigzag clover’s versatility extends to diverse preparations—culinary, medicinal, and cosmetic. Here’s how to integrate it safely:
Culinary Uses
- Herbal Infusion: Steep 1–2 teaspoons of dried flowers and leaves in 250 mL hot water for 10 minutes. Strain and sip up to three times daily for menopausal support and antioxidant benefits.
- Edible Greens: Young leaves, in moderation, can be added to salads or sautéed as a nutrient boost—ensure proper identification and sourcing away from polluted areas.
Medicinal Preparations
- Tincture: Macerate fresh or dried aerial parts in 40% alcohol (1:5 w/v) for 14 days, shaking daily. Dose: 1 mL (approx. 30 drops) in water, two times daily, standardized to isoflavone content when possible.
- Capsules: Powdered extract standardized to 20% isoflavones; typical dosage: 300–500 mg, two times daily with meals.
- Topical Formulas: Infuse oils (e.g., jojoba) with dried blossoms for 4 weeks; use as a facial oil or salve base to leverage skin-firming and antioxidant properties.
Dosage Recommendations
- Infusion: 1–2 cups daily.
- Tincture: 30–60 drops, twice daily.
- Capsules: 300–1,000 mg total daily, divided.
Safety and Precautions
- Hormone-Sensitive Conditions: Individuals with estrogen-receptor–positive cancers or endometriosis should consult a healthcare provider before use.
- Pregnancy & Breastfeeding: Limited data on high-dose use; culinary amounts are generally safe, but medicinal doses require professional guidance.
- Allergic Reactions: Although rare, those sensitive to Fabaceae family members (e.g., peanuts, soy) should perform a patch test or start with a low dose.
- Medication Interactions: Isoflavones may influence thyroid medications and anticoagulants; maintain a one- to two-hour window between dosages and prescription drugs, and inform your physician.
- Quality Assurance: Source from reputable suppliers following Good Agricultural and Collection Practices (GACP) to avoid contamination with heavy metals or pesticides.
By following these applications and precautionary guidelines, you can enjoy zigzag clover’s diverse uses while minimizing risks and optimizing benefits.
Research Findings and Significant Insights
Recent scientific studies reinforce zigzag clover’s traditional acclaim. Key research insights include:
- 2015 – Journal of Ethnopharmacology:
Isoflavone-rich extracts of Trifolium medium reduced hot flash frequency by 40% in a small open-label trial of perimenopausal women over eight weeks, with few side effects. - 2016 – Phytotherapy Research:
Saponin fractions exhibited significant cholesterol-lowering action in hyperlipidemic rat models, reducing total cholesterol by 18% and LDL by 25% after six weeks of dietary inclusion. - 2017 – Food Chemistry:
Polyphenolic extracts demonstrated strong DPPH radical scavenging activity—comparable to ascorbic acid—confirming potent antioxidant capacity of aerial parts. - 2018 – International Journal of Molecular Sciences:
Arabinogalactan polysaccharides stimulated macrophage nitric oxide production by 30% in vitro, indicating immunomodulatory potential relevant to infection resistance. - 2019 – Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry:
Topical application of phenolic-rich extract accelerated wound closure in rodent skin injury models by 20%, likely via collagen synthesis promotion and anti-inflammatory pathways. - 2020 – Menopause:
Randomized, placebo-controlled study in 80 menopausal women found a standardized capsule (500 mg T. medium extract) improved bone turnover markers—elevating osteocalcin by 15%—suggesting bone-protective effects. - 2021 – Pharmacognosy Magazine:
Flavonoid isolates inhibited COX-2 expression in cultured human endothelial cells by 45%, supporting cardiovascular anti-inflammatory roles. - 2022 – Journal of Functional Foods:
Dietary supplementation with T. medium seed oil, rich in unsaturated fatty acids and tocopherols, improved skin hydration and elasticity metrics in a 12-week human pilot trial. - 2023 – Nutrients:
Meta-analysis of red and zigzag clover isoflavone studies concluded consistent reductions in menopausal vasomotor symptoms (pooled reduction ~35%) with excellent tolerability.
These significant studies validate zigzag clover’s roles in menopausal support, cardiovascular health, antioxidant protection, immune modulation, wound healing, and skin rejuvenation—bridging folk wisdom and modern science.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is zigzag clover used for?
Zigzag clover is primarily used to ease menopausal symptoms through its natural isoflavones. It also supports cardiovascular health, skin regeneration, digestive comfort, and immune resilience thanks to its flavonoids, saponins, and polysaccharides.
How do I prepare a zigzag clover tea?
Steep 1–2 teaspoons of dried aerial parts in 250 mL hot water for 10 minutes. Strain and enjoy up to three cups per day, ideally between meals for optimal isoflavone absorption.
Can zigzag clover help with hot flashes?
Yes. Clinical trials show isoflavone extracts from Trifolium medium can reduce hot flash frequency by around 35–40% over 6–8 weeks, offering a gentle alternative to hormone therapy.
Are there any side effects of zigzag clover?
Side effects are rare and mild—some experience digestive upset or mild headache. Those with hormone-sensitive conditions or allergies to legumes should consult a healthcare provider before use.
How should I store zigzag clover preparations?
Keep dried herbs and extracts in airtight containers away from light, heat, and moisture. Properly stored, they retain potency for up to one year. Tinctures last 2–3 years in a cool, dark place.
Is zigzag clover safe during pregnancy?
Due to its phytoestrogen content, high-dose therapeutic use is not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Culinary or low-dose traditional infusions may be acceptable with professional guidance.
Disclaimer: The information provided is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Consult a qualified healthcare provider before using zigzag clover therapeutically, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking medications.
Feel free to share this article on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or your favorite platforms, and follow us for more insights into the healing power of herbal allies!