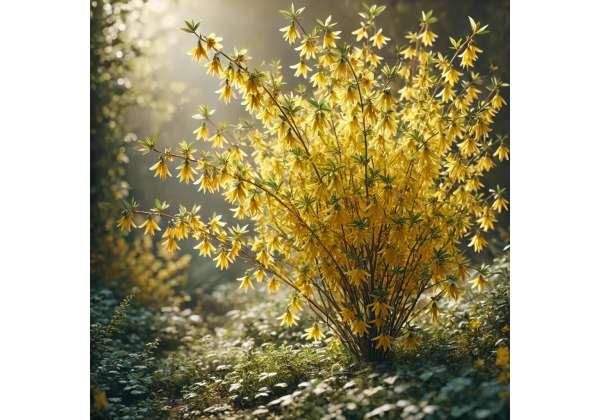
Are you looking for a vibrant herb revered for its potential medicinal powers and versatile applications? Golden Bell, often linked with radiant blooms and extensive therapeutic value, has earned recognition across various traditional practices. Beneficial for its antioxidant qualities, immune-enhancing properties, and topical uses, Golden Bell is a standout choice for natural wellness enthusiasts. In this guide, you’ll discover its botanical background, key active compounds, health-supporting traits, safety considerations, and the scientific studies that back its broad-ranging effects. By the end, you’ll have a complete understanding of how to harness Golden Bell’s profound benefits in daily life.
Table of Contents
- Plant Description and Key Characteristics
- Active Compounds and Chemical Profile
- Health Gains and Intrinsic Properties
- Applications, Safety, and Usage Tips
- Notable Research and Recent Findings
- FAQ
Plant Description and Key Characteristics
Golden Bell is widely admired for its striking flowers and longstanding use in traditional remedies. Below is a comprehensive look at its taxonomy, physical traits, and the conditions in which it thrives.
Taxonomic Classification
- Family: Oleaceae
- Genus: Forsythia
- Common Names: Golden Bell, Forsythia, Lian Qiao (in Traditional Chinese Medicine)
This genus comprises roughly 11 species, with Forsythia suspensa recognized for its historical medicinal applications. The plant is commonly referred to as Golden Bell due to its bright, bell-shaped blossoms.
Habitat and Geographic Distribution
Golden Bell naturally flourishes in East Asia, particularly in China, Korea, and Japan. Over time, its ornamental appeal and reputed healing potential have led to widespread cultivation in other regions, including Europe and North America.
Because Golden Bell can adapt to different climates, gardeners around the world frequently plant it in well-drained soil and regions with moderate rainfall. It tolerates both partial shade and full sun, but it typically blooms more abundantly when exposed to ample sunlight.
Physical Characteristics
- Leaves: Golden Bell’s leaves vary from simple, elliptical shapes to slightly serrated edges. They usually appear a few weeks after the flowers and are medium to bright green.
- Flowers: The most striking feature of the plant is its clusters of radiant yellow, bell-shaped blossoms, which often appear before the leaves. These flowers typically bloom in early spring, bringing a burst of color to landscapes.
- Stems and Branches: Golden Bell typically produces long, arching branches. Mature shrubs can grow to a height of 1–3 meters (around 3–10 feet), depending on the species and cultivation conditions.
- Root System: The roots are generally fibrous, providing the plant with stability and efficient nutrient absorption.
Growth Conditions and Requirements
- Soil Type: Prefers loamy, well-draining soil.
- Sunlight: Thrives in partial to full sun. More sunlight tends to produce more abundant blooms.
- Watering: Requires moderate watering. Overwatering can lead to root rot, but consistent moisture helps produce vigorous growth and vibrant flowers.
- Temperature: While Golden Bell generally tolerates temperature fluctuations, harsh winters or extreme heat can inhibit growth.
Traditional Roles and Cultural Significance
Golden Bell has been revered in certain regions for its purported healing properties as outlined in traditional medical texts. Its blossoms and fruits (often referred to as “fruits” or seed pods in herbal references) have been used for centuries in herbal preparations. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) values Golden Bell for its “heat-clearing” capacity, commonly pairing it with other herbs in formulas targeting respiratory infections, fevers, or skin complaints.
Historically, the bright yellow blossoms also symbolize renewal and vitality, aligning with the spring season. As a result, ornamental plantings of Golden Bell are strongly associated with new beginnings and celebratory occasions in some cultures.
Active Compounds and Chemical Profile
Golden Bell contains a complex array of phytochemicals. These compounds are central to the herb’s physiological and biochemical actions, contributing to its well-known effects in herbal medicine. Below is a detailed overview of the key constituents.
- Forsythiaside A and Forsythiaside B
- Description and Effects: These phenylethanoid glycosides exhibit marked antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. They may help neutralize free radicals and support the body’s immune responses.
- Mechanisms of Action: Known to inhibit bacterial strains and decrease inflammation by moderating pro-inflammatory mediators.
- Rutin
- Description and Effects: A flavonoid frequently found in many plants, rutin supports the maintenance of healthy blood vessels. Studies suggest it can help reduce capillary fragility and address oxidative stress.
- Mechanisms of Action: Rutin enhances antioxidant enzyme activity, which can protect the body from oxidative damage and improve circulatory health.
- Phillyrin (Forsythin)
- Description and Effects: A lignan compound prominent in Golden Bell. It demonstrates antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-regulating potentials in preliminary studies.
- Mechanisms of Action: Phillyrin is thought to modulate inflammatory pathways and may inhibit certain viral replication processes, thereby supporting immune defense.
- Matairesinol
- Description and Effects: Another notable lignan that may be beneficial for cardiovascular well-being and possess mild estrogenic or anti-estrogenic activities, depending on physiological factors.
- Mechanisms of Action: Like other lignans, matairesinol is metabolized into enterolactone and enterodiol, compounds that can act on hormonal and immune pathways in the human body.
- Essential Oils (Terpenoids and Volatile Constituents)
- Description and Effects: Golden Bell’s flowers and other aerial parts contain volatile oils—compounds responsible for the herb’s distinctive aroma. They often exhibit antiseptic, mild sedative, or mood-lifting effects.
- Mechanisms of Action: Terpenoids can combat microbial invasions and reduce oxidative stress by influencing cellular signaling cascades.
- Pinoresinol
- Description and Effects: Pinoresinol, another lignan found in various plants, is recognized for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory attributes.
- Mechanisms of Action: It interacts with free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative damage, and can support the body’s anti-inflammatory processes.
- Phenolic Acids
- Description and Effects: Compounds such as caffeic acid, syringic acid, and related substances also appear in Golden Bell, contributing to its overall antioxidant strength.
- Mechanisms of Action: Phenolic acids can donate electrons to neutralize free radicals, positively affecting cellular health and possibly slowing age-related deterioration.
- Sterols (e.g., β-Sitosterol)
- Description and Effects: Plant sterols are known to promote healthy cholesterol levels when consumed regularly as part of a balanced diet.
- Mechanisms of Action: By inhibiting cholesterol absorption in the intestines, β-sitosterol may contribute to cardiovascular support.
Significance of the Compound Synergy
A crucial aspect of Golden Bell’s efficacy lies in the synergy among these compounds. While certain chemicals like forsythiaside A and Phillyrin have been studied individually, many herbalists assert that the combined action of multiple constituents offers more pronounced and holistic effects than isolated components could provide.
This inherent synergy underpins the traditional usage of Golden Bell in decoctions, tinctures, and topical applications, where the entire spectrum of phytochemicals works together to support wellness.
Health Gains and Intrinsic Properties
Golden Bell benefits span a wide range of bodily systems, from immune support to skin health. Below is an exploration of the key advantages and properties attributed to this herb.
1. Immune Support and Antimicrobial Activity
Golden Bell’s active compounds—particularly forsythiasides and lignans—have been studied for their broad-spectrum antimicrobial capacities. Traditionally, Golden Bell has been paired with other herbs to manage seasonal colds, respiratory issues, and mild infections. Through its antibacterial and antiviral actions, this herb may help the body combat invading pathogens more efficiently.
2. Anti-inflammatory Effects
Inflammation lies at the root of many chronic conditions, including arthritis, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular issues. Research on the forsythiasides and lignans in Golden Bell suggests potential to lower levels of inflammatory markers in the body. This could be helpful for those seeking natural ways to alleviate discomfort or manage chronic inflammatory states.
3. Antioxidant Potential
Antioxidants play a key role in neutralizing free radicals—unstable molecules that can cause cellular damage and contribute to aging, cancer, and other diseases. Compounds like rutin, phenolic acids, and pinoresinol in Golden Bell help maintain oxidative balance within the body, fostering cellular health and potentially slowing down age-related decline.
4. Skin Health and Wound Care
Thanks to its antimicrobial qualities, Golden Bell has been used to formulate topical solutions, poultices, or creams. Historical evidence suggests its use in addressing minor wounds, cuts, and skin irritations. Its soothing components may also help reduce redness and inflammation on the skin’s surface, making it a choice herb for those seeking gentle, herbal-based skincare solutions.
5. Respiratory Function
Golden Bell has long been featured in respiratory-support formulas in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Its expectorant properties may aid in loosening mucus, making breathing easier during common respiratory conditions. Though modern studies are limited, anecdotal reports affirm its longstanding use as a supportive agent for coughs and congestion.
6. Detoxification and Heat-clearing in TCM
In TCM, Golden Bell is traditionally classified as a “heat-clearing” herb. This classification indicates that it can help eliminate heat (or internal excesses) from the body, thereby reducing symptoms like fever, sore throat, or irritability. By restoring internal balance, Golden Bell is said to promote faster recovery from infections or inflammatory conditions.
7. Possible Cardiovascular Support
Some research points to potential cardiovascular advantages. Lignan compounds, for example, might help regulate lipid levels, which supports healthy cholesterol management. When coupled with an antioxidant-rich diet, Golden Bell may contribute to overall heart health and circulatory function.
8. Relief for Mild Gastrointestinal Discomfort
In some folk remedies, Golden Bell extracts have been used to address occasional digestive upset. While not widely studied in modern contexts, historical herbal traditions indicate that its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory actions can offer a gentle remedy for mild GI irritations. However, more clinical data is needed to confirm these uses.
9. Potential for Hormonal Balance
Certain lignans in Golden Bell can act as phytoestrogens, substances that mimic or modulate estrogen in the body. Though the effects are typically milder than synthetic hormone treatments, these plant-based compounds may support individuals seeking natural approaches to managing hormone-related fluctuations. Nonetheless, caution and professional guidance are advised when using phytoestrogen-rich herbs.
Summarizing the Key Benefits
- Golden Bell Benefits for Immune Health: Helps ward off infections and bolster the body’s defenses.
- Golden Bell Properties for Skin: Addresses minor wounds and irritations due to its antimicrobial constituents.
- Golden Bell Uses for Circulation: May assist in lipid regulation and offer antioxidant protection.
- Golden Bell Applications for Inflammation: Aims to reduce inflammatory markers and soothe affected areas.
In essence, Golden Bell’s synergy of phytochemicals brings together antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant qualities that can support holistic well-being.
Applications, Safety, and Usage Tips
Golden Bell is versatile, with applications that span culinary, medicinal, and cosmetic domains. However, proper guidance is crucial to ensure both effectiveness and safety. Below, we explore its diverse uses, along with dosage recommendations and important cautions.
Culinary Uses
While Golden Bell is not commonly recognized as a mainstream culinary ingredient in Western cuisine, some cultures use its blossoms in teas or as ornamental garnishes. The flowers can be steeped to produce a delicate infusion, often combined with other fragrant herbs to create a refreshing spring beverage.
- Tea Preparation Tip: Lightly rinse the fresh flowers or dried Golden Bell pods to remove any debris. Steep in hot water (about 80–90°C / 176–194°F) for 5–7 minutes. Add honey or a compatible sweetener if desired.
- Flavor Profile: Mildly floral with subtle earthy undertones, pairing well with green tea or herbal blends like chamomile or mint.
Medicinal Applications
- Decoctions and Herbal Formulas: Traditionally used in conjunction with other herbs—like Lonicera japonica (honeysuckle) or Licorice—to address respiratory complaints and mild infections.
- Tinctures: Tinctures may offer a convenient way to incorporate Golden Bell for those seeking a more concentrated dose. Dosages vary, but 1–2 mL taken two to three times daily is a common practice in herbal medicine, subject to individual tolerance.
- Capsules and Powders: Commercial herbal supplements containing Golden Bell extracts are available. Always follow manufacturer guidelines or consult a qualified herbalist for dosing based on your specific needs.
Cosmetic and Topical Uses
- Skin Ointments: Golden Bell’s antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties make it a promising addition to creams formulated for minor skin irritations, blemishes, or redness.
- Bath Soaks: In some holistic traditions, Golden Bell flowers or extracts are added to bathwater. Believers in herbal balneotherapy assert that this practice can calm irritated skin and improve overall relaxation.
Safety and Possible Side Effects
Golden Bell is generally regarded as safe when consumed in moderate amounts. However, there are certain considerations:
- Potential Allergies: As with any herb, some individuals may experience allergic reactions such as rashes or itching. Discontinue use and consult a healthcare professional if you notice adverse skin reactions or respiratory discomfort.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Data on the safety of Golden Bell during pregnancy and lactation remains limited. Consultation with a trained professional is strongly recommended before introducing any new herb into your regimen.
- Medication Interactions: Golden Bell may interact with prescribed drugs, especially those targeting immunity, inflammation, or hormones. If you are on medication for a chronic health condition, seek medical advice prior to use.
- Excessive Dosage Risks: Consuming large quantities of any herb can lead to unwanted side effects, including digestive upset or altered heart rate. Always adhere to recommended dosages.
Dosage Considerations
- Teas and Infusions: 1–2 cups daily, using 1–2 teaspoons of dried Golden Bell (fruits, flowers, or a blend).
- Tinctures: 1–2 mL, two to three times a day, depending on the tincture strength (usually 1:5 or 1:3).
- Capsules: Follow the product label, but typical ranges are 300–600 mg of standardized extract, once or twice daily.
Practical Tips for Safe Use
- Source Quality Herbal Products: Purchase from reputable suppliers to ensure purity and accurate labeling.
- Test for Tolerance: Begin with a smaller amount to see how your body responds. Gradually increase dosage if no adverse effects occur.
- Store Properly: Keep dried herbs in an airtight container, away from direct sunlight and moisture, to preserve potency.
- Consult a Professional: When in doubt, seek guidance from an herbalist or healthcare provider knowledgeable about botanical remedies.
By understanding these safety guidelines and usage suggestions, you can maximize Golden Bell’s beneficial properties while minimizing potential risks.
Notable Research and Recent Findings
Modern investigations have begun to validate several of the traditional claims surrounding Golden Bell. Below is a numbered list of selected scientific studies and their key takeaways:
- 2020 – “Evaluation of the Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Potential of Forsythia suspensa”
- Journal: Journal of Medicinal Plant Research
- Key Findings: This study measured the antioxidant activity of various extracts from Golden Bell and confirmed significant free radical scavenging capacity. Researchers also tested the plant’s extracts against common bacterial strains, noting marked inhibition in vitro.
- Additional Notes: Concluded that the phenylethanoid glycosides, including forsythiaside, were primary contributors to both the antioxidant and antimicrobial properties.
- 2018 – “Phillyrin and Its Influence on Viral Replication in Cell Cultures”
- Journal: Virology & Immunology
- Key Findings: Focused on the antiviral activity of phillyrin, a lignan in Golden Bell. Researchers discovered that phillyrin reduced viral replication rates in certain influenza strains.
- Additional Notes: Preliminary but promising results indicate Golden Bell’s potential for broader viral inhibition, particularly when used alongside other antiviral agents or supportive treatments.
- 2016 – “Forsythia suspensa and Respiratory Health: Clinical Observations”
- Journal: Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine
- Key Findings: This clinical pilot study explored the effect of Golden Bell-based formulations on patients with mild upper respiratory tract infections. Participants reported reduced fever intensity and faster symptom resolution compared to a control group.
- Additional Notes: Suggested synergy with other TCM herbs, highlighting the complexity of multi-herb formulations.
- 2021 – “Investigation of Forsythiaside A’s Anti-inflammatory Mechanisms”
- Journal: Phytotherapy Insights
- Key Findings: Lab tests exposed immune cells to forsythiaside A. The researchers found a significant decrease in pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-6.
- Additional Notes: Although these findings remain at the cellular level, they suggest that Golden Bell’s components can modulate inflammatory pathways.
- 2019 – “Golden Bell Extract and Lipid Metabolism in Animal Models”
- Journal: Plant-Based Nutrition & Biochemistry
- Key Findings: Rats given a supplement containing forsythia extracts demonstrated improved lipid profiles, with lower total cholesterol and LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels.
- Additional Notes: The authors propose that the lignans and plant sterols in Golden Bell may collaborate to enhance lipid metabolism and thus offer cardiovascular benefits.
- 2022 – “Combined Antibacterial Efficacy of Forsythia suspensa and Honeysuckle Flower”
- Journal: Frontiers in Herbal Medicine
- Key Findings: This investigation highlighted how combining Golden Bell with honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica) produced a stronger antibacterial effect against resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains than either herb alone.
- Additional Notes: The enhanced effect underscores the importance of herbal synergy, reflecting longstanding TCM practice where multi-herb formulas are the norm.
- 2017 – “Topical Application of Forsythia suspensa in Dermatological Treatments”
- Journal: Dermato-Herbal Therapeutics
- Key Findings: Focused on a cream formulated with Golden Bell extract, which displayed beneficial outcomes in soothing mild eczema and inflammatory skin lesions.
- Additional Notes: The improvement was primarily attributed to the plant’s anti-inflammatory and antibacterial components. Further research is needed to validate these results in large-scale human trials.
Collectively, these investigations suggest that Golden Bell’s benefits extend beyond anecdotal reports, showing promise in immunological support, inflammation management, and possibly cardiovascular health. While most of these studies remain preliminary, they lay the groundwork for future research, emphasizing Golden Bell’s potential to complement modern therapeutic approaches.
FAQ
Is Golden Bell the same as forsythia?
Golden Bell is a common name for forsythia shrubs, especially Forsythia suspensa. They share the same bright yellow flowers and active compounds, so the terms are often used interchangeably.
Does Golden Bell help boost the immune system?
Golden Bell contains compounds like forsythiasides and lignans, which may support immune defenses. However, individual results may vary, and more extensive human research is needed to confirm its full immunological impact.
Can I use Golden Bell flowers to make tea at home?
Yes, you can brew the dried or fresh flowers into a mild tea. Ensure they are harvested from a safe, pesticide-free source. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Is it safe to consume Golden Bell during pregnancy?
Limited data exists regarding its safety for pregnant or breastfeeding individuals. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for specific recommendations related to your circumstances.
What are the potential side effects of using Golden Bell?
Possible side effects include allergic reactions or digestive upset if taken in excess. Discontinue use and consult a professional if you experience any adverse symptoms.
How do I store dried Golden Bell herbs?
Keep them in an airtight container, away from sunlight and moisture. This helps maintain their potency and prolongs shelf life.
Can Golden Bell interact with medications?
Yes. It might interact with certain drugs, especially those affecting immunity or inflammation. Check with a healthcare professional to avoid adverse interactions.
Are there cosmetic uses for Golden Bell?
Absolutely. Creams or ointments containing Golden Bell extracts may help soothe minor skin irritations and support natural wound healing processes.
Is there scientific backing for Golden Bell’s benefits?
Various studies have begun to highlight its antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory capacities. While promising, further research is needed for definitive conclusions.
Should I combine Golden Bell with other herbs?
Many traditional formulas pair Golden Bell with herbs like honeysuckle. Synergy may enhance benefits, but consult an herbalist or medical professional before combining remedies.
Disclaimer
The information in this article is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult with a qualified healthcare practitioner before making decisions related to your health and well-being.
Feel free to share this guide with friends, family, or on your social media platforms like Facebook and X (formerly Twitter) if you found it valuable and informative.