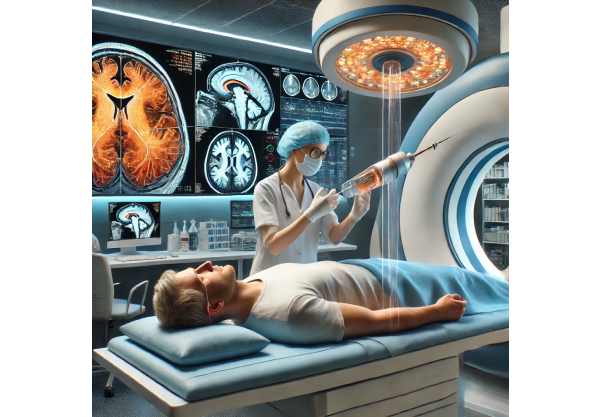
Orbital pseudotumor, also known as idiopathic orbital inflammation (IOI), is a non-cancerous inflammatory condition that affects the tissues of the orbit, the bony cavity that holds the eye. This condition is distinguished by a sudden onset of inflammation that can affect several orbital structures, including the extraocular muscles, lacrimal gland, optic nerve, and surrounding fat and connective tissue. The cause of orbital pseudotumors is unknown, hence the term “idiopathic.”
Patients with orbital pseudotumors typically experience pain, swelling, redness, and proptosis (eye protrusion). Diplopia (double vision), reduced visual acuity, and limited eye movement are all common. The condition can be acute, with symptoms appearing quickly, or chronic, with a slower onset and ongoing inflammation. A thorough clinical examination, imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and, in some cases, a biopsy are used to rule out other possible causes of orbital inflammation, such as infections or malignancies.
Understanding and diagnosing orbital pseudotumors is critical for prompt and effective treatment. Although the condition is not life-threatening, it can have a significant impact on a patient’s quality of life and, if not treated, can lead to complications such as permanent vision loss.
Standard Orbital Pseudotumor Management and Treatment
The management and treatment of orbital pseudotumors focuses on reducing inflammation, alleviating symptoms, and avoiding complications. Here are the standard treatments for this condition:
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids are the primary treatment for orbital pseudotumors because they are extremely effective at reducing inflammation. High-dose oral prednisone is usually prescribed first, followed by a gradual tapering of the dose based on the patient’s response. In cases of severe inflammation, intravenous corticosteroids may be given. Corticosteroids frequently produce dramatic responses, with symptoms improving rapidly.
- Immunosuppressive Therapy: Immunosuppressive agents may be used for patients who are intolerant to corticosteroids or have recurrent or refractory disease. Drugs like methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate mofetil can help control inflammation and reduce the need for long-term corticosteroid therapy. These agents must be closely monitored due to potential side effects and the risk of immunosuppression.
- Radiation Therapy: Low-dose radiation therapy may be considered for patients who do not respond well to corticosteroids or immunosuppressive therapy. Radiation can help reduce inflammation and symptoms, especially in chronic or recurring cases. However, it is typically reserved for situations in which other treatments have failed or are contraindicated.
- Biologic Agents: Some cases of orbital pseudotumor have been treated with biologic agents such as rituximab, especially when they are associated with systemic autoimmune diseases. These agents target specific immune system components and can help control inflammation. Their use is typically limited to refractory cases under the supervision of a specialist.
- Surgical Intervention: Surgery is rarely required for orbital pseudotumors, but it may be necessary in cases where there is significant structural involvement or a biopsy is required to confirm the diagnosis. In severe cases, orbital decompression surgery may be used to relieve pressure on the optic nerve and other structures.
- Supportive Care: Managing symptoms and promoting overall eye health are critical in the treatment of orbital pseudotumor. This includes using lubricating eye drops to prevent dryness and irritation, developing pain management strategies, and regularly monitoring visual function.
- Regular Follow-Up: Continuous follow-up is critical for monitoring the disease’s progression, adjusting treatment as needed, and detecting complications early. Patients usually require regular ophthalmologic evaluations and imaging studies to assess their response to therapy and detect any signs of recurrence.
Latest Breakthrough Innovations in Orbital Pseudotumor Treatment
Recent advances in medical research and technology have resulted in novel approaches that provide new hope for patients with orbital pseudotumor. These cutting-edge innovations include advanced diagnostic techniques, new therapeutic agents, precision medicine approaches, and integrative care models. Each of these innovations has distinct advantages and the potential to improve the management of orbital pseudotumor.
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
Advances in diagnostic technologies have greatly improved the ability to accurately diagnose and monitor orbital pseudotumor.
High-Resolution Imaging: High-resolution imaging modalities, such as enhanced CT and MRI scans, enable detailed visualization of orbital structures and inflammation levels. These advanced imaging techniques enable early and precise diagnosis, which aids in treatment decision-making and therapy response monitoring. High-resolution imaging can also help distinguish orbital pseudotumor from other conditions that cause similar symptoms, such as infections or cancer.
Molecular and Genetic Profiling: Molecular and genetic profiling of orbital tissues can reveal information about the underlying mechanisms of inflammation and identify specific biomarkers associated with orbital pseudotumor. Techniques such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) and gene expression analysis enable the identification of molecular signatures that can be used to develop targeted therapies. This personalized approach to diagnosis has the potential to improve treatment outcomes while also lowering the risk of complications.
Novel Therapeutic Agents
Innovative therapeutic agents have been developed to improve the efficacy of orbital pseudotumor treatment while reducing the side effects associated with conventional therapies.
Monoclonal Antibodies: Monoclonal antibodies, such as tocilizumab and infliximab, target specific cytokines involved in the inflammatory response. These biologic agents can help control inflammation and alleviate symptoms in patients with refractory orbital pseudotumor. The use of monoclonal antibodies represents a targeted approach to therapy, with minimal impact on the overall immune system.
JAK Inhibitors: Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, including tofacitinib and ruxolitinib, disrupt the signaling pathways that cause inflammation. These oral medications have shown promise in treating a variety of inflammatory conditions and are being investigated for their potential use in the treatment of orbital pseudotumors. JAK inhibitors are a convenient and effective alternative to traditional immunosuppressants.
** Small Molecule Inhibitors**: Imatinib and sunitinib are small molecule inhibitors that target specific pathways involved in inflammatory cell proliferation and survival. These agents have been used successfully to treat other inflammatory conditions and are now being tested for their efficacy in orbital pseudotumor. Small molecule inhibitors enable a more precise and targeted approach to therapy, lowering the risk of systemic side effects.
Precision Medicine
Precision medicine tailors treatment plans to each patient’s unique characteristics, such as genetic profile, disease manifestations, and general health. This approach seeks to maximize treatment efficacy while minimizing side effects.
Genetic Testing: Advances in genetic testing have enabled the identification of genetic mutations and alterations that cause inflammation in orbital pseudotumor. Understanding these genetic factors allows clinicians to choose targeted therapies that are most likely to work for each patient. Genetic testing can also help predict treatment response and monitor for resistance, allowing for adjustments to the treatment plan.
Biomarker-Based Treatment: Biomarker-based therapy refers to the use of specific biomarkers to guide treatment decisions. Clinicians can create personalized treatment plans that maximize efficacy while minimizing side effects by identifying biomarkers linked to disease activity and therapy response. Biomarker-based therapy provides a targeted and personalized approach to treating orbital pseudotumors.
Integrative and Complementary Approaches
Integrative approaches combine conventional medical treatments with complementary therapies to provide comprehensive care for patients with orbital pseudotumor.
Nutritional Support: Proper nutrition is critical for supporting the immune system and promoting recovery from inflammation. Nutritional interventions, such as the use of certain vitamins and minerals that promote immune health, can supplement medical treatments and improve patient outcomes.
Mind-Body Therapies: Acupuncture, yoga, and mindfulness meditation can all help with symptom management, stress reduction, and overall well-being. These therapies offer comprehensive support to patients being treated for orbital pseudotumor, improving their quality of life and promoting emotional resilience.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation: Physical therapy and rehabilitation are critical in restoring function and mobility following treatment for orbital pseudotumor. Specialized exercises and therapies can assist patients in regaining strength, improving eye movement, and reducing pain and stiffness. Physical therapy programs are tailored to each patient’s specific needs, resulting in optimal recovery and functional outcomes.
Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning
The application of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in healthcare has the potential to transform the treatment of orbital pseudotumor.
AI-Powered Diagnostics: Artificial intelligence algorithms can analyze large datasets of imaging and clinical data to identify patterns and predict disease progression. AI-powered diagnostics can improve the accuracy and efficiency of detecting orbital pseudotumors, allowing for earlier intervention and personalized treatment strategies.
Predictive Modeling: Machine learning models can forecast the likelihood of complications and guide treatment decisions based on individual patient data. Predictive modeling assists clinicians in developing proactive management plans, which improves long-term outcomes for patients with orbital pseudotumor.