Therapy Types Explained: CBT vs ACT vs DBT vs EMDR
Choosing a therapy can feel like learning a new language—especially when the options sound similar and everyone claims their approach “works.” The reassuring truth...
Thyroid Problems and Brain Fog: Hypothyroid Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Brain fog can feel like walking through your day with the lights turned down—slower thinking, weaker memory, and a constant sense that you are...
Time Blindness Explained: ADHD, Stress, and Better Planning
Time blindness is the uneasy gap between clock time and felt time. You look up and an hour is gone, or you swear you...
Time Management for ADHD: Tools That Reduce Overwhelm
If you have ADHD, time management is rarely about laziness or willpower. It is usually about executive function: the brain skills that translate intentions...
Tingling Hands and Face With Anxiety: Why It Happens
Tingling in your hands, lips, or face can feel suddenly alarming—especially when it arrives alongside racing thoughts, chest tightness, or the sense that you...
Tinnitus and Anxiety: Why They Feed Each Other and What Helps
Tinnitus can be deceptively simple to describe—ringing, buzzing, hissing—yet surprisingly complex to live with. For many people, the sound is not just an “ear...
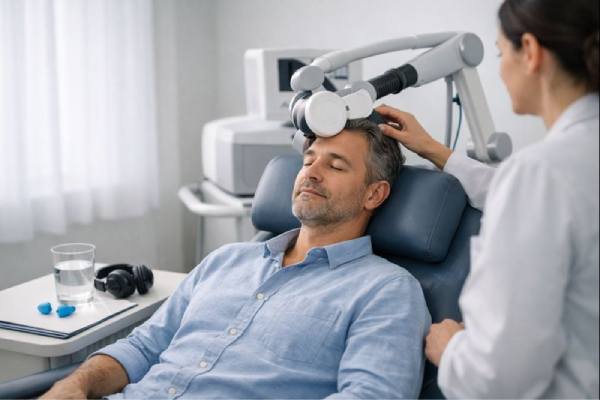
TMS for Depression: How It Works, Success Rates, and Side Effects
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive treatment for depression that uses brief magnetic pulses to influence activity in brain networks linked to mood....
Toxic Relationships: Signs, Emotional Effects, and How to Protect Yourself
Some relationships feel hard because life is hard: work stress, family demands, health worries. A toxic relationship feels different. It repeatedly drains your energy,...
Trauma and the Brain: How It Shapes Emotions, Behavior, and Triggers
Trauma is not just something that happened in the past—it can become a pattern the brain keeps replaying in the present. After overwhelming stress,...
Trauma Bonding: Why It’s Hard to Leave and How Healing Works
Trauma bonding is one of those experiences that can feel impossible to explain from the inside. You may know a relationship is harming you,...
TRE Shaking Exercises: What They Are and How to Try Them Safely
TRE (Tension and Trauma Releasing Exercises) is a structured way of using gentle fatigue and positioning to trigger involuntary shaking or tremoring—often starting in...
Treatment-Resistant Depression: Options Beyond Standard Antidepressants
Depression can be relentless—not only because of how it feels, but because it can distort hope and shrink your sense of options. When symptoms...
Tryptophan and “Serotonin Foods”: Mood, Sleep, and Smart Food Pairings
If you have ever searched for “serotonin foods,” you have probably seen lists that promise calmer moods and better sleep from a handful of...
Turmeric and Mood: Curcumin for Depression, Inflammation, and Absorption Tips
Turmeric has moved far beyond the spice rack, largely because of curcumin—the bright yellow polyphenol that gives turmeric its color and much of its...
Ultra-Processed Foods and Mental Health: What We Know So Far
Ultra-processed foods are no longer a niche nutrition topic. For many people, they make up a large share of daily calories because they are...
Understanding Depression: Symptoms, Causes, and How to Cope
Depression is more than “feeling down.” It can change how you think, sleep, eat, move, and relate to other people. It often dulls pleasure,...