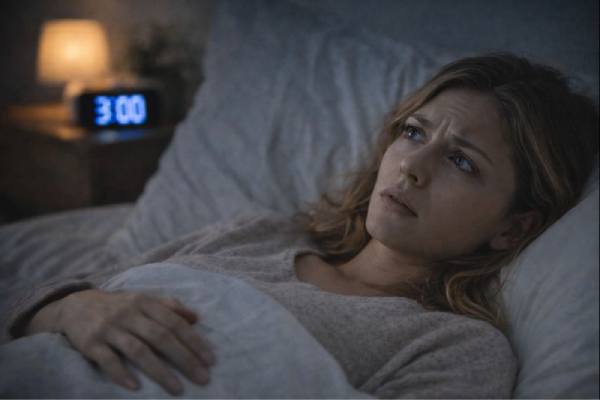
Why Do I Wake Up at 3 AM? Stress, Blood Sugar, and Sleep Cycles
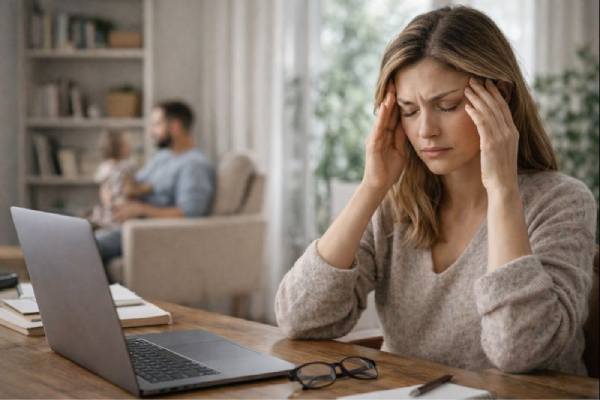
Waking up around 3 AM can feel oddly specific—like your body is running on a schedule you did not choose. In reality, that timing...
Window of Tolerance: Why You Flip Into Panic or Shutdown
Some days you can handle stress, think clearly, and recover after a hard moment. Other days, the same kind of challenge seems to tip...
Work Stress and Mental Health: Signs You’re Near Burnout and What to Change
Work stress is not just an uncomfortable feeling—it changes how your brain allocates attention, regulates emotion, and recovers after effort. When stress becomes a...
Working Memory Explained: The Skill Behind Focus and How to Train It
Working memory is the brain’s “hold and use” system. It lets you keep a small amount of information active—long enough to follow a conversation,...
Work-Life Balance: How to Prevent Burnout and Protect Your Mental Health
Work-life balance is not a perfect split between “work” and “life.” It is your ability to meet work demands without sacrificing sleep, relationships, physical...
Yoga Nidra (NSDR): How Non-Sleep Deep Rest Restores Your Brain
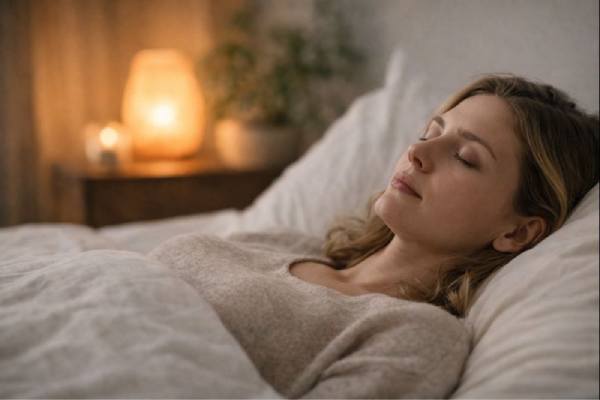
Modern fatigue is rarely just “tired.” It is overstimulation, fractured attention, and a nervous system that never fully downshifts. Yoga Nidra—often grouped under NSDR...
Zinc and Depression: Signs of Low Zinc and When Supplementation Helps
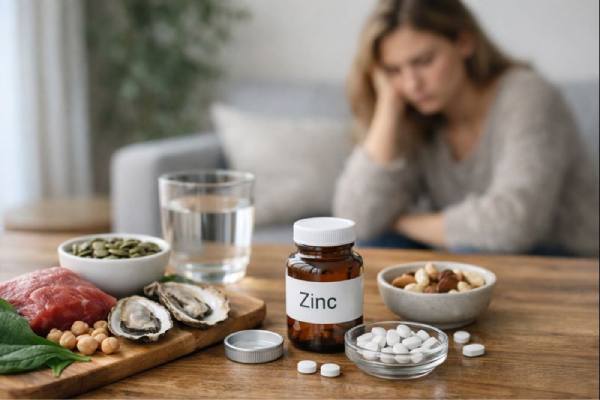
Zinc is a trace mineral with an outsized job description: it helps regulate immune signaling, supports wound healing and taste, and influences how neurons...
After the Flu: Post-Viral Dry Eye and Irritation That Won’t Go Away
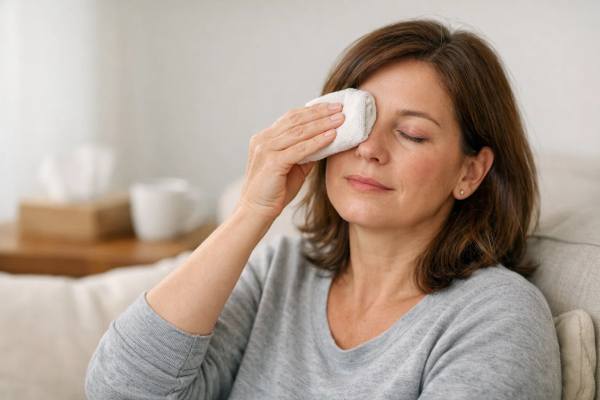
Getting over the flu can feel like crossing a finish line—until your eyes keep reminding you that your body is still resetting. Weeks after...
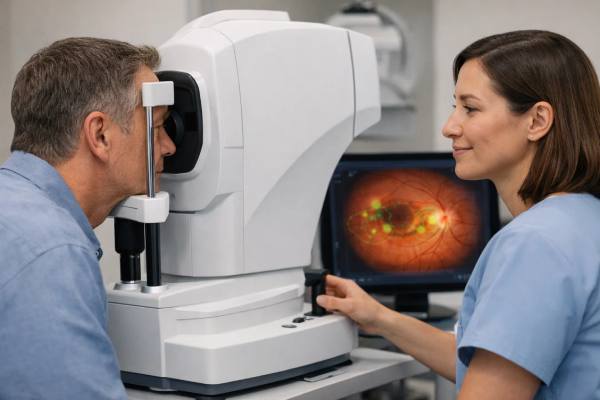
AI Retinal Screening: How New Eye Scans Detect Disease Earlier
Retinal screening used to mean scheduling an eye specialist visit, dilating the pupils, and waiting for a human reader to interpret photos. New AI-enabled...
Amblyopia (Lazy Eye) in Adults: Can It Be Treated and What Helps?
Amblyopia—often called “lazy eye”—is usually discussed as a childhood condition, which can leave adults feeling stuck with a diagnosis they were told was “too...
Amniotic Membrane for Ocular Surface Healing: When It’s Used and Recovery Timeline
When the front of the eye is injured or inflamed, healing can stall in ways that feel disproportionate to the original problem—persistent pain, light...
Anti-Reflective Coating: Benefits for Night Driving and Screen Glare
If you have ever noticed headlights “blooming” across your lenses at night or a bright window reflected on your glasses during a video call,...
Anti-VEGF Eye Injections: What They Treat and What to Expect at Each Visit
Anti-VEGF eye injections have changed what “saving vision” looks like for many retinal diseases. They are used when abnormal blood vessels leak fluid or...
AREDS2 Vitamins for Macular Degeneration: Who Should Take Them and Why
AREDS2 vitamins are not “eye vitamins” in the casual sense. They are a specific, research-tested combination of antioxidants and minerals created to slow progression...
Autologous Serum Tears vs Platelet-Rich Plasma Drops: Which Helps Severe Dry Eye More?
Severe dry eye is not just “dryness.” It can feel like burning, stabbing grit, light sensitivity, and fluctuating vision that makes screens and driving...
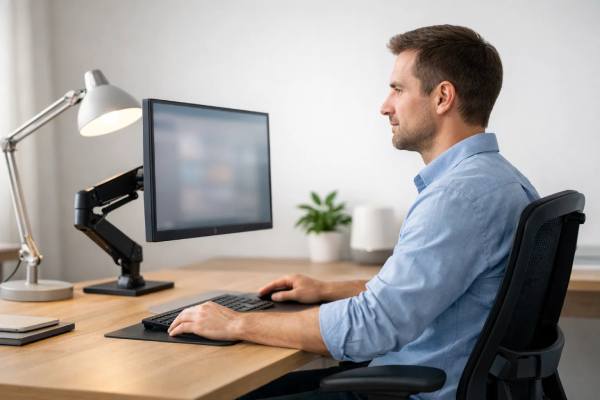
Best Monitor Setup for Eye Health: Distance, Height, and Brightness
A comfortable monitor setup is one of the few “eye health” upgrades you can feel within a single workday. When your screen is the...
Black Spots in Vision: Causes, Red Flags, and Next Steps
A black spot in your vision can be harmless, urgent, or somewhere in between—and the difference often comes down to a few specific details....
Blocked Tear Duct in Babies: Signs, Massage Tips, and When to See a Doctor
A blocked tear duct in a baby can look dramatic—constant watering, sticky lashes, and a crusty inner corner—yet it is often a temporary plumbing...
Blue-Light Blocking Glasses: Do They Help Eye Strain or Sleep?
Blue-light blocking glasses sit at the intersection of modern life and modern discomfort. Many of us spend hours under LED lighting, switching between monitors,...
Blurry Vision: Common Causes, Quick Checks, and When to See an Eye Doctor
Blurry vision is one of the most common and most unsettling eye symptoms because it can mean almost anything—from a simple need for updated...
Blurry Vision During COVID-19: Possible Causes and When to Get Checked
Blurry vision during COVID-19 can feel unsettling because it is hard to tell what is “just part of being sick” and what deserves urgent...
Brain Fog With Eye Strain: Vision Fatigue, Screens, and What Helps
If your eyes feel tired and your thinking feels slow at the same time, you are not imagining the connection. Eye strain can act...
Burning Eyes: Dry Eye, Irritants, and Relief That Works
Burning eyes can feel deceptively simple—until you realize how many everyday exposures can set them off. For some people, the burn is a dry,...
Can Eye Rubbing Damage Your Eyes? Keratoconus Risk and Safer Alternatives
Rubbing your eyes can feel like the quickest way to quiet an itch, clear a blur, or relieve fatigue. But the eye’s surface and...