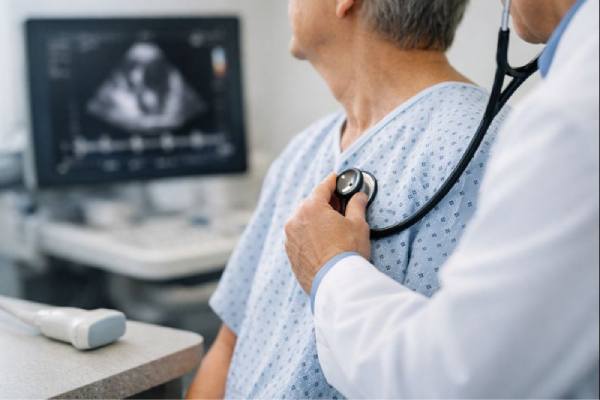
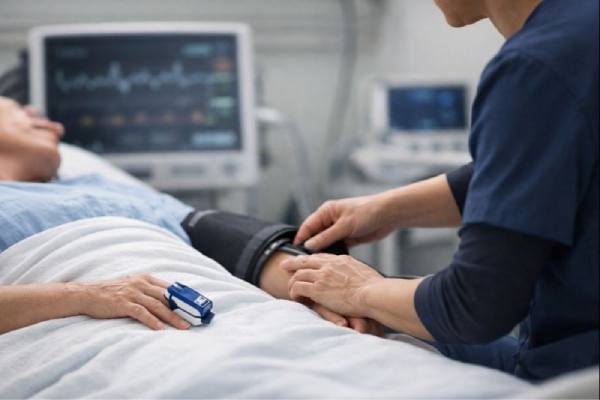
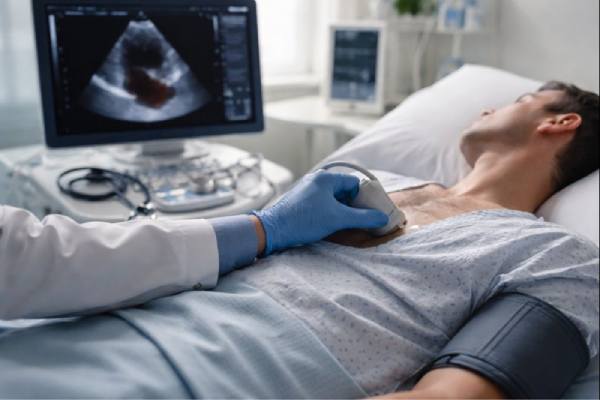
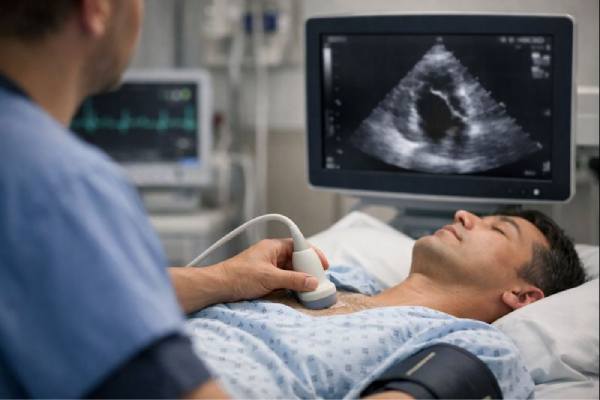
Heart valve disease: Types, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
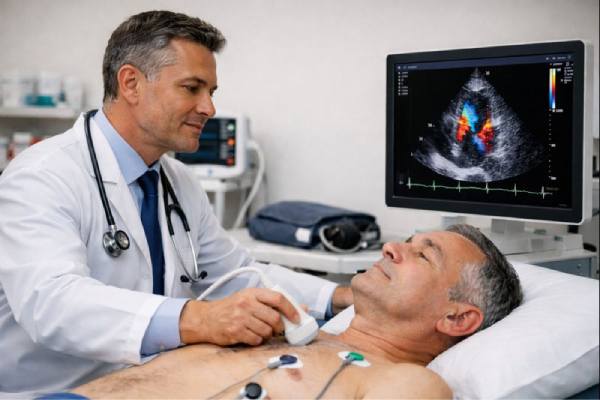
Heart valve disease is a problem with one or more of the heart’s “doors,” which open and close to keep blood moving in the...
Heart Valve Infection: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Recovery Guide
A heart valve infection can feel deceptively ordinary at first—fatigue that won’t lift, a fever that keeps returning, or shortness of breath you blame...
Heart valve prolapse: Causes, Risk Factors, Complications, and Management
Heart valve prolapse means a valve leaflet bows backward more than it should when the heart squeezes. Most people hear about it after a...
Heart valve regurgitation: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
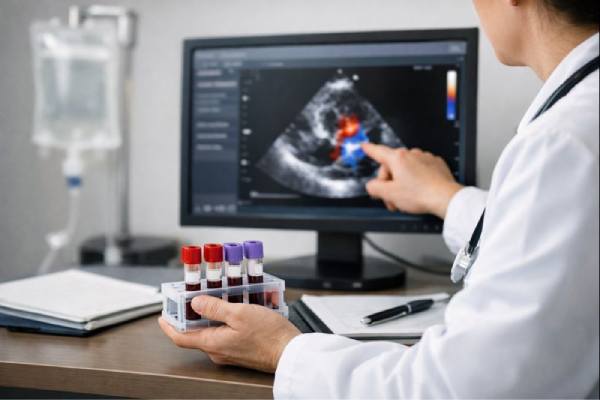
Heart valve regurgitation means a heart valve does not seal tightly, so a portion of blood leaks backward with each heartbeat. Many people first...
Heart valve stenosis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Modern Treatment Options
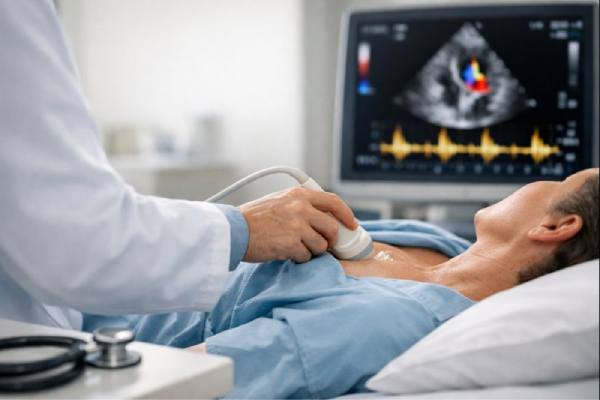
Heart valve stenosis means a valve opening has become too narrow, forcing the heart to push blood through a tighter space. Many people live...
Hemodynamic instability: Sepsis, Bleeding, and Management
Hemodynamic instability is a clinical warning that the body may not be getting steady, adequate blood flow. It often shows up as low blood...
Hemopericardium: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Emergency Treatment
Hemopericardium means blood has collected in the sac around the heart. The sac is normally a thin, slippery space; when blood fills it, the...
Hemorrhagic cardiac tamponade: Causes, Red Flags, Diagnosis, and Emergency Treatment
Hemorrhagic cardiac tamponade happens when blood collects around the heart and builds enough pressure to limit how the heart fills between beats. That pressure...
Hemorrhagic pericarditis: How It’s Diagnosed, Echocardiogram Findings, and Treatment
Hemorrhagic pericarditis is inflammation of the sac around the heart that leads to a blood-tinged or bloody fluid build-up in that space. Sometimes it...
Hemorrhagic shock: Risk Factors, Red Flags, Testing, and ICU Care Explained
Hemorrhagic shock happens when a person loses so much blood that the body can’t deliver enough oxygen to the brain, heart, and other organs....
Hemorrhagic stroke: Causes, Warning Signs, Diagnosis, and Emergency Treatment
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in or around the brain breaks and bleeding damages brain tissue. (“Hemorrhage” means bleeding from a...
Hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Overview, Causes, Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Hemorrhagic telangiectasia is a condition where fragile, widened blood vessels sit close to the surface of the skin and lining tissues, making bleeding more...
Hepatic vein thrombosis: Overview, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Hepatic vein thrombosis is a condition where a blood clot blocks the veins that drain blood out of the liver. It is often discussed...
Hepatocardiac syndrome: Heart Changes in Advanced Liver Disease, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
When the liver is under long-term strain, the heart often has to “work around” the consequences. Hepatocardiac syndrome is a practical umbrella term for...
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Overview, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is a genetic condition that makes certain blood vessels form abnormally. Many people first notice frequent nosebleeds or tiny red...
Hibernating myocardium: What It Means, Viability Testing, and Recovery Potential
Hibernating myocardium is heart muscle that has gone quiet to survive. When a coronary artery delivers too little blood for a long time, the...
High blood pressure: Overview, Causes, Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management
High blood pressure is common, often quiet, and highly treatable—but it still drives a large share of heart attacks, strokes, kidney disease, and heart...
High-output heart failure: What It Is, Why It Happens, and How It’s Managed
High-output heart failure can feel confusing: the heart may be pumping more blood than usual, yet the body still behaves as if it isn’t...
Holt-Oram syndrome: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Cardiac Monitoring Plan
Holt-Oram syndrome is a rare condition that links two parts of the body that develop early in pregnancy: the hands/arms and the heart. Some...
Hughes-Stovin syndrome: Causes, Hemoptysis Warning Signs, and Treatment Options
Hughes-Stovin syndrome is a very rare condition in which inflammation in blood vessels can lead to two dangerous problems at the same time: blood...
Hydropericardium: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Hydropericardium means an abnormal buildup of clear fluid around the heart. That fluid collects inside the pericardial sac, a thin “sleeve” that normally holds...
Hypercholesterolemia: Causes, LDL Goals, and Evidence-Based Treatment
Hypercholesterolemia means your blood cholesterol is higher than is healthy for your arteries over time. The concern is not the number alone, but what...
Hyperchylomicronemia: Causes, Pancreatitis Risk, and Treatment Strategies
Hyperchylomicronemia is a condition where fat-rich particles called chylomicrons build up in the bloodstream, often driving triglycerides to extremely high levels. Chylomicrons normally appear...
Hypercoagulability: Blood Clot Risk, Key Triggers, Testing, and Prevention
Hypercoagulability means the body is more likely than usual to form blood clots. Sometimes this tendency is mild and never causes problems. Other times,...