Cerebral embolism, Causes, Risk Factors, and How to Prevent Recurrence
A cerebral embolism happens when a traveling blood clot (or other material) suddenly blocks an artery in the brain, cutting off oxygen to the...
Cerebral infarction, Causes and Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Recovery
Cerebral infarction is the medical term for a part of the brain being injured because it did not get enough blood and oxygen. Most...
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Imaging Tests, and Treatment Options
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) is an uncommon type of stroke caused by a blood clot in the brain’s venous drainage system—most often the...
Cerebrovascular disease: Overview, Causes, Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management
Cerebrovascular disease is an umbrella term for conditions that disrupt blood flow to the brain. Because brain tissue is highly “energy-hungry,” even a brief...
Chagas cardiomyopathy: Causes, Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Chagas cardiomyopathy is the heart form of Chagas disease, a long-term infection caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. For many people, the infection is...
Cholesterol embolism: Overview, Causes, Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management
Cholesterol embolism is a vascular emergency that often hides in plain sight. It happens when tiny cholesterol crystals break loose from an atherosclerotic plaque—most...
Chronic Arterial Insufficiency: Claudication Symptoms, ABI Testing, and Treatment Options
Chronic arterial insufficiency is a long-term reduction in blood flow through an artery—most often to the legs—usually because fatty plaque has narrowed the vessel...
Chronic cerebrovascular disease: Small Vessel Disease, White Matter Changes, and Cognitive Symptoms
Chronic cerebrovascular disease is a long-term problem of blood vessels in and around the brain. Instead of a single sudden blockage, it reflects years...
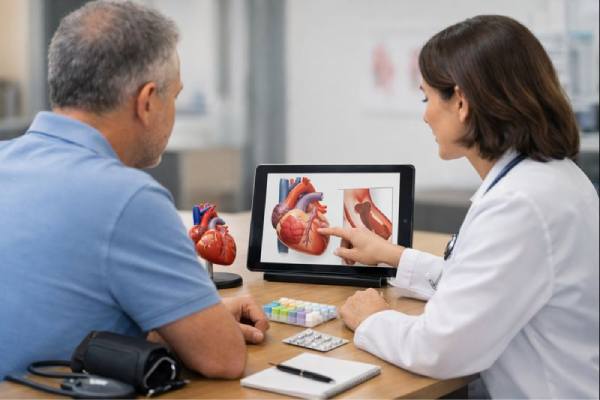
Chronic Coronary Artery Disease: Overview, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management
Chronic coronary artery disease (often called chronic coronary disease) is a long-term condition where the arteries that feed the heart muscle become narrowed, stiff,...
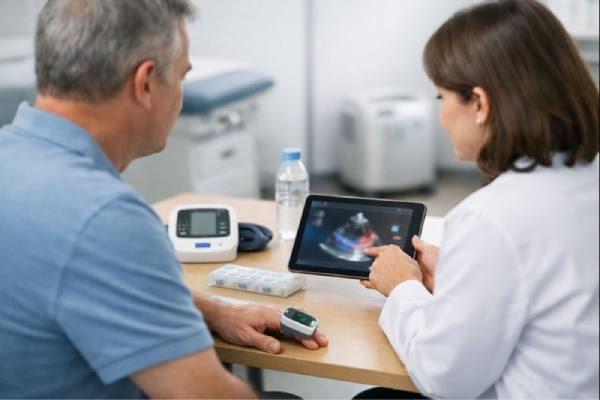
Chronic coronary syndrome: Angina Symptoms, Stress Testing, and Treatment Options
Chronic coronary syndrome (CCS) is the long-term form of coronary artery disease—when the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle gradually lose their ability...
Chronic heart failure: Causes, Risk Factors, Management, and How to Prevent Flare-Ups
Chronic heart failure is a long-term condition in which the heart cannot pump enough blood—or cannot fill properly—to meet the body’s needs during daily...
Chronic ischemic heart disease: What Causes Ischemia, Who’s at Risk, and How to Prevent Heart Attack
Chronic ischemic heart disease is a long-term condition where the heart muscle does not consistently get enough oxygen-rich blood—most often because the coronary arteries...
Chronic pericarditis, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Long-Term Management
Chronic pericarditis is inflammation of the pericardium—the thin, two-layered sac around the heart—that persists, returns, or smolders for months. For many people, it starts...
Chronic Stroke Syndrome: Long-Term Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Recovery Strategies
Living with the long-term effects of a stroke can feel less like a single event and more like a new health chapter—one that touches...
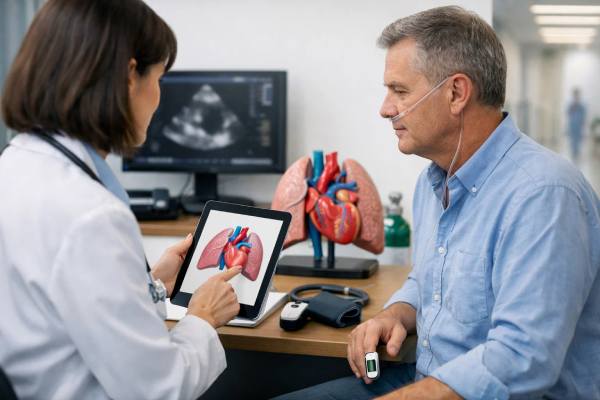
Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options
Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) is a form of high blood pressure in the lung arteries that develops after blood clots fail to clear...
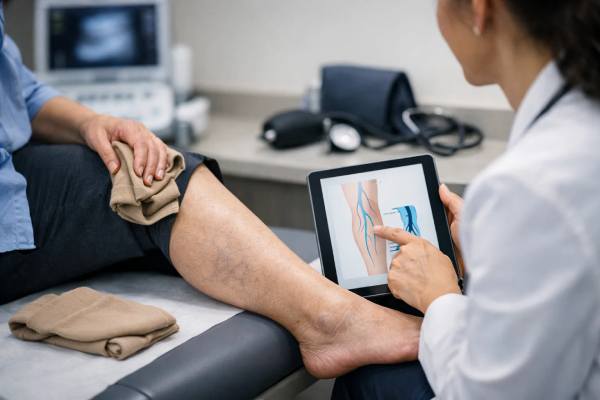
Chronic venous insufficiency: Early signs, diagnosis, and proven treatments
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) happens when the veins in your legs struggle to send blood back to the heart efficiently. Instead of moving upward,...