Pulsed Light Therapy, commonly known as Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) therapy, is revolutionizing the treatment landscape for Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD) by offering a non-invasive approach to improve tear quality. This advanced therapy harnesses broad-spectrum light pulses to target and treat the underlying dysfunction of the meibomian glands, which play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy tear film. With IPL, patients experience reduced inflammation, improved gland function, and enhanced tear stability—all of which contribute to alleviating the discomfort associated with dry eye symptoms. As innovative research continues to support its efficacy, IPL therapy is fast emerging as a preferred treatment modality for those suffering from chronic ocular surface disorders. In the following sections, we explore the scientific underpinnings of IPL, how it is applied in clinical settings, the latest research breakthroughs, its safety and effectiveness, and cost considerations, providing you with a comprehensive guide to understanding this transformative therapy.
Exploring the Science Behind IPL: Innovative Insights into Tear Quality Improvement
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) therapy is founded on a sophisticated mechanism that employs high-intensity, broad-spectrum light pulses to target abnormal vascularization and reduce inflammation around the meibomian glands. In patients with Meibomian Gland Dysfunction, the quality of the tear film is compromised due to obstructed or dysfunctional glands, which leads to increased tear evaporation and chronic dry eye symptoms. IPL therapy works by delivering short bursts of light that are absorbed by the hemoglobin in the abnormal blood vessels surrounding the glands. This selective photothermolysis causes the targeted vessels to collapse, thereby reducing the inflammatory mediators that contribute to gland dysfunction.
One of the pivotal aspects of IPL is its ability to warm the meibomian glands gently. The thermal effect induced by the pulsed light helps to liquefy the thickened meibum (the oily secretion of the glands), facilitating its excretion onto the ocular surface. This warming effect is essential because it restores the normal flow of lipids, which are critical for stabilizing the tear film and preventing rapid evaporation. By improving the quality and consistency of the lipid layer, IPL directly enhances tear film stability, leading to better ocular comfort and reduced symptoms of dryness.
Moreover, the anti-inflammatory benefits of IPL extend beyond the direct effects on the blood vessels. The reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines and other mediators in the periocular area creates a more favorable environment for gland recovery. Studies have shown that IPL therapy can lead to a decrease in levels of inflammatory markers such as interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in the tear film, contributing to the overall health of the ocular surface. This dual action—both warming the glands and mitigating inflammation—makes IPL a highly effective treatment for improving tear quality in patients with MGD.
Additionally, IPL therapy has been found to promote cellular regeneration in the meibomian glands. Research suggests that the controlled light pulses may stimulate the proliferation of healthy glandular cells, potentially leading to a longer-term improvement in gland function. The innovative design of IPL devices allows clinicians to customize the wavelength, pulse duration, and energy output according to the specific needs of each patient, ensuring that the treatment is both safe and effective.
The scientific rationale behind IPL therapy is supported by a wealth of clinical data. For example, studies published in peer-reviewed journals such as the Journal of Ophthalmology and Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science have demonstrated significant improvements in tear film stability, meibomian gland expressibility, and patient-reported symptom scores following IPL treatment. These studies underscore the potential of IPL to not only provide immediate relief from dry eye symptoms but also to contribute to the long-term health of the ocular surface by restoring the natural function of the meibomian glands.
In summary, the innovative mechanism of IPL—combining selective photothermolysis, thermal stimulation, and anti-inflammatory effects—addresses the core issues underlying Meibomian Gland Dysfunction. By restoring the normal flow of lipids and reducing inflammation, IPL improves the quality of the tear film, which is essential for maintaining ocular comfort and visual clarity. As research in this area continues to evolve, IPL is poised to become an increasingly important tool in the management of dry eye conditions associated with MGD.
Step-by-Step Guide: Clinical Application and Treatment Protocols for IPL
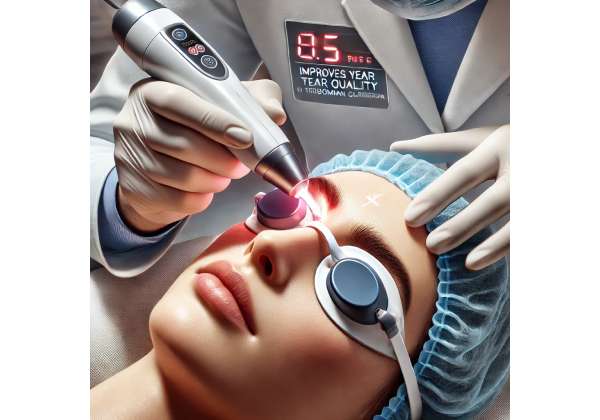
The clinical application of IPL therapy for Meibomian Gland Dysfunction is a well-structured process that emphasizes both precision and patient comfort. Treatment typically begins with a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s ocular surface and meibomian gland function. During this assessment, clinicians use diagnostic tools such as tear break-up time (TBUT), meibography, and slit-lamp examinations to identify the severity of gland dysfunction and determine the appropriate treatment settings.
Once the evaluation is complete, patients are prepped for IPL therapy in a controlled clinical environment. The procedure is usually performed in a darkened room to maximize the effectiveness of the light treatment. Before the treatment begins, protective eyewear is provided to shield the eyes from the intense light pulses, ensuring patient safety throughout the procedure.
During an IPL session, the clinician applies a coupling gel to the periocular area. This gel not only enhances the conductivity of the light but also provides a smooth surface for the IPL handpiece to glide over the skin. The device is then carefully positioned adjacent to the eyelids, targeting the areas around the meibomian glands without directly exposing the globe. The clinician adjusts the settings on the IPL device—such as pulse duration, energy level, and wavelength—based on the patient’s skin type, severity of MGD, and overall treatment goals.
Each treatment session typically lasts between 15 and 30 minutes, depending on the number of passes and the area being treated. A standard protocol may involve multiple passes over the affected areas to ensure even coverage and thorough treatment of the dysfunctional glands. Patients may experience a mild warming sensation or slight discomfort during the procedure, but the treatment is generally well tolerated. The non-invasive nature of IPL means that there is no need for anesthesia, and patients can resume normal activities immediately following the session.
Following the treatment, patients are provided with post-procedural care instructions. These usually include guidelines for managing any transient redness or mild swelling, as well as recommendations to avoid excessive sun exposure and to use soothing eye drops if needed. Follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor the patient’s progress, assess improvements in tear quality, and determine if additional treatment sessions are necessary. Most treatment protocols for MGD involve a series of IPL sessions—often spaced a few weeks apart—to achieve optimal results and maintain long-term benefits.
The integration of IPL therapy into a comprehensive dry eye management plan often involves combining the treatment with other supportive therapies. For example, patients may also use warm compresses, lid scrubs, and omega-3 supplements to further enhance meibomian gland function and tear film stability. The synergistic effect of these combined approaches can lead to more significant and sustained improvements in ocular surface health.
Clinicians emphasize the importance of patient education during the IPL treatment process. Clear communication about what to expect before, during, and after the procedure helps to alleviate any anxiety and fosters a collaborative treatment environment. Patients are encouraged to share any concerns or discomfort during the procedure so that adjustments can be made in real time. This patient-centric approach not only improves the overall treatment experience but also enhances the likelihood of achieving the desired therapeutic outcomes.
In summary, the clinical application of IPL for Meibomian Gland Dysfunction is characterized by its precision, customization, and ease of integration into existing treatment regimens. The step-by-step process—from initial evaluation to post-treatment follow-up—ensures that each patient receives a tailored therapy designed to improve tear quality and alleviate dry eye symptoms effectively. As IPL technology continues to advance, its role in the management of MGD is expected to expand, offering even greater benefits for patients seeking non-invasive, long-term relief.
What the Latest Research Reveals: Breakthrough Studies on IPL for Meibomian Gland Dysfunction
Recent research has provided compelling evidence supporting the efficacy of IPL therapy in managing Meibomian Gland Dysfunction and improving tear quality. A series of breakthrough studies, published in reputable journals, has highlighted the multifaceted benefits of IPL, not only in reducing inflammation but also in enhancing the functionality of the meibomian glands.
A landmark study published in the Journal of Ophthalmology in 2020 involved a randomized controlled trial comparing IPL therapy with conventional treatments for MGD. The study reported that patients who underwent IPL treatment exhibited a significant increase in tear film stability, as measured by improved tear break-up time (TBUT) and a reduction in ocular surface staining. Additionally, the trial demonstrated that IPL led to a marked improvement in meibomian gland expressibility, which is directly associated with better lipid secretion and overall tear quality. These findings underscore the potential of IPL to provide both symptomatic relief and long-term improvements in ocular surface health.
Another influential study, featured in Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science in 2021, focused on the anti-inflammatory effects of IPL. Researchers observed that IPL treatment resulted in a significant reduction in inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and TNF-α in the tear film. The study utilized advanced imaging techniques and biochemical assays to quantify these changes, revealing that the reduction in inflammation was accompanied by improved glandular function. This study provided critical insights into the mechanism by which IPL reduces ocular surface inflammation, reinforcing its role as a therapeutic tool in managing chronic MGD.
Complementing these controlled trials, observational studies have also shed light on the real-world benefits of IPL therapy. In a multicenter case series published in Clinical Ophthalmology in 2019, patients with refractory MGD underwent a series of IPL sessions over several months. The results were promising: not only did the majority of patients report a significant reduction in dry eye symptoms and discomfort, but there were also measurable improvements in tear film lipid layer thickness and overall ocular surface health. These real-world outcomes support the clinical trial data and suggest that IPL can be an effective option for a diverse patient population with varying degrees of gland dysfunction.
Emerging research has begun to explore the potential of combining IPL with other treatment modalities for enhanced outcomes. A pilot study presented at the 2022 International Dry Eye Symposium investigated the synergistic effects of IPL combined with thermal pulsation therapy. Preliminary data indicated that the combined approach resulted in superior improvements in meibomian gland function and tear film stability compared to either treatment alone. This integrated treatment strategy is particularly exciting as it offers a comprehensive approach to managing MGD by addressing both the gland obstruction and the inflammatory components of the disease.
Moreover, long-term follow-up studies are now being conducted to evaluate the durability of IPL’s therapeutic effects. Early data from these studies suggest that the benefits of IPL—such as improved tear quality and reduced ocular surface inflammation—can be maintained over extended periods with periodic maintenance sessions. This durability is a crucial consideration for chronic conditions like MGD, where sustained management is necessary to prevent symptom recurrence and to promote ongoing ocular health.
Overall, the latest research consistently demonstrates that IPL therapy is an effective, safe, and innovative treatment for Meibomian Gland Dysfunction. The studies emphasize its dual action of reducing inflammation and enhancing meibomian gland function, which together contribute to improved tear quality and a reduction in dry eye symptoms. As ongoing research continues to refine treatment protocols and explore synergistic therapies, the role of IPL in the comprehensive management of MGD is poised to expand even further.
Evaluating Effectiveness and Safety: Clinical Outcomes of IPL for MGD
Clinical experience with IPL therapy for Meibomian Gland Dysfunction consistently shows significant improvements in tear quality and symptom relief. Patients typically report reduced dryness, less irritation, and improved overall comfort following treatment. Objective measures, such as increased tear break-up time and enhanced gland expressibility, corroborate these subjective improvements. The safety profile of IPL is particularly notable; adverse effects are minimal and usually limited to temporary redness or mild discomfort during the procedure. With a non-invasive approach that avoids the complications associated with more aggressive treatments, IPL offers a balanced and effective solution for managing chronic MGD while ensuring patient safety.
Therapy Price: Cost Considerations for IPL Treatment
The cost of IPL therapy for Meibomian Gland Dysfunction generally ranges between \$300 and \$500 per session. With many patients requiring a series of treatments for optimal results, the overall expense remains competitive compared to other advanced dry eye therapies, offering significant long-term benefits.
Medical Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is intended for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider for personalized diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
If you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it on your favorite social platforms such as Facebook or X.