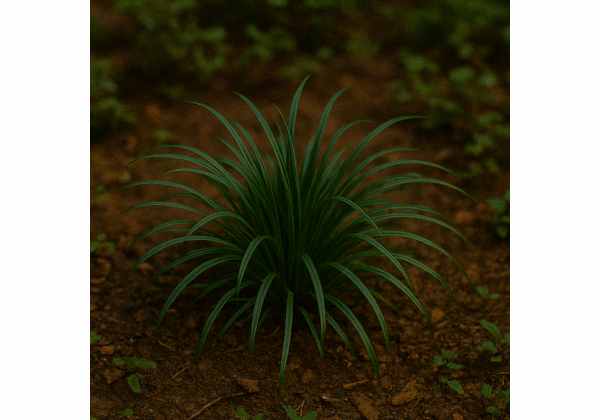
Ophiopogon japonicus is a time-honored herb in traditional Chinese medicine, renowned for its nourishing, yin-enhancing, and moistening properties. Rich in bioactive compounds such as ophiopogonins, polysaccharides, flavonoids, and phenolic acids, this herb supports cardiovascular, respiratory, and immune health while offering potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Traditionally used to treat dry coughs, thirst, and other yin-deficient conditions, Ophiopogon japonicus is now embraced in modern wellness practices. Its versatility allows for various applications, including decoctions, extracts, and topical formulations, making it an essential natural remedy for holistic health and preventive care.
Table of Contents
- Botanical Profile and Taxonomic Overview
- Phytochemical Composition and Active Constituents
- Health Benefits and Essential Properties
- Practical Applications, Usage, and Safety Precautions
- Scientific Studies and Research Insights
- Frequently Asked Questions about Ophiopogon japonicus
Botanical Profile and Taxonomic Overview
Ophiopogon japonicus, commonly known as “dwarf lilyturf” or Mai Men Dong in traditional Chinese medicine, is a perennial herbaceous plant revered for both its ornamental and medicinal value. Native to East Asia, particularly China, Japan, and Korea, this herb has been cultivated for centuries for its therapeutic attributes. It grows in clumps with slender, arching leaves and produces small, inconspicuous flowers that yield tiny, dark berries. Its robust rhizomatous root system enables it to thrive in shaded, well-drained soils—conditions typical of forest margins, stream banks, and cultivated gardens.
Taxonomic Classification and Morphological Features
Ophiopogon japonicus belongs to the Asparagaceae family and is closely related to other monocotyledonous plants. The genus name “Ophiopogon” derives from Greek, meaning “snake beard,” which is a nod to the plant’s long, filamentous styles visible in its flowers. Morphologically, the herb is characterized by:
- Leaves: Narrow, lanceolate, and glossy, with a rich green hue that can appear almost black under certain lighting. The leaves emerge in a basal rosette and are known for their resilience.
- Flowers: Small, star-shaped, and typically white or pale violet. These flowers appear in loose clusters at the apex of the stems and are less showy than those of ornamental lilies, yet they carry significant medicinal value.
- Rhizomes: A dense network of underground rhizomes that store nutrients and water, enabling the plant to survive adverse conditions and facilitate vegetative reproduction.
- Berries: Tiny, dark fruits that follow the flowering phase and aid in seed dispersal, ensuring the propagation of the species in natural settings.
Growth Habits and Preferred Habitats
Ophiopogon japonicus thrives in areas with partial shade and well-drained, slightly acidic to neutral soils. It is commonly found in forest understories, along streams, and in traditional herb gardens where it is cultivated for its medicinal properties. The plant’s adaptability to low-light conditions and its modest water requirements make it an ideal candidate for sustainable cultivation in both rural and urban landscapes. Moreover, its ability to form dense groundcover not only contributes to its ornamental appeal but also helps prevent soil erosion.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Historically, Ophiopogon japonicus has held an esteemed place in East Asian herbal medicine. Known as “Mai Men Dong” (literally, “wheat straw herb”) in Chinese medicine, it has been used for over 2,000 years to nourish yin, moisten the lungs, and clear heat. Ancient texts describe its use in treating symptoms of dryness such as chronic coughs, thirst, and constipation. Beyond its medicinal applications, the plant has been integrated into traditional landscape designs and is appreciated for its understated beauty in gardens and courtyard plantings. Its enduring cultural significance is a testament to its holistic benefits, which bridge the realms of physical health and aesthetic pleasure.
Modern Cultivation and Propagation
Today, Ophiopogon japonicus is cultivated both for its medicinal extracts and as an ornamental groundcover. Modern horticultural practices favor propagation by division of clumps, ensuring uniformity and vigor in new plants. Cultivators employ organic fertilizers and natural pest control methods to maintain the herb’s purity and potency. Advances in controlled-environment agriculture have further enhanced its availability throughout the year, making it a reliable resource for herbal practitioners worldwide.
In summary, the botanical and taxonomic profile of Ophiopogon japonicus reveals a plant that is as robust as it is graceful. Its adaptive growth habits, distinctive morphology, and deep-rooted cultural history combine to make it a cornerstone of traditional herbal medicine and modern phytotherapy.
Phytochemical Composition and Active Constituents
The therapeutic efficacy of Ophiopogon japonicus is largely attributed to its complex array of bioactive compounds. Extensive phytochemical studies have identified a range of constituents that work synergistically to provide antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects. Below is a detailed analysis of the key compounds present in this remarkable herb.
- Ophiopogonins
Ophiopogonins are steroidal saponins unique to Ophiopogon japonicus. They are renowned for their capacity to modulate inflammatory responses and protect cardiac tissues. Studies have shown that these saponins improve myocardial function and reduce arterial stiffness, making them critical in cardiovascular support. Additionally, ophiopogonins exhibit immunomodulatory effects by balancing cytokine production, which may contribute to overall immune health. - Polysaccharides
The herb is rich in complex polysaccharides that are instrumental in its traditional use as a yin-nourishing agent. These polysaccharides stimulate the immune system, enhance mucosal immunity, and promote overall vitality. They also exhibit antioxidant properties by scavenging free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative stress and contributing to cellular repair and regeneration. This action is particularly beneficial in maintaining respiratory and gastrointestinal health. - Flavonoids
Ophiopogon japonicus contains several flavonoid compounds, including luteolin, apigenin, and quercetin. These molecules are powerful antioxidants that protect cells from damage caused by reactive oxygen species. Flavonoids also contribute to the herb’s anti-inflammatory properties by inhibiting the release of pro-inflammatory mediators. Their presence is crucial for supporting vascular health and reducing the risk of chronic degenerative diseases. - Phenolic Acids
Phenolic acids such as caffeic acid and ferulic acid are found in significant concentrations in Ophiopogon japonicus. These compounds are known for their potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. They help stabilize cellular membranes, inhibit lipid peroxidation, and may reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease by protecting blood vessels from oxidative damage. - Steroidal Glycosides and Triterpenoids
In addition to ophiopogonins, other steroidal glycosides and triterpenoids contribute to the herb’s pharmacological profile. These compounds have been implicated in anti-tumor activity, as well as in the modulation of metabolic pathways. Their ability to interact with cellular receptors and signaling pathways underscores their potential role in preventing the progression of certain chronic diseases. - Amino Acids and Micronutrients
Although present in smaller quantities, essential amino acids, vitamins (notably vitamin C and several B vitamins), and minerals (such as potassium, magnesium, and calcium) enhance the nutritional profile of Ophiopogon japonicus. These micronutrients support overall metabolic functions, aid in enzymatic reactions, and contribute to tissue repair and regeneration. - Additional Bioactive Compounds
Emerging research has identified additional compounds such as coumarins and lignans in Ophiopogon japonicus. These molecules further contribute to its antioxidant capacity and may have neuroprotective effects, adding another layer to the herb’s extensive health benefits.
The combined actions of these phytochemicals endow Ophiopogon japonicus with a wide spectrum of therapeutic properties. Their synergistic interactions not only underpin the herb’s traditional use in nourishing yin and moistening the lungs but also support its modern applications in cardiovascular, respiratory, and immune health. Ongoing research continues to elucidate the molecular mechanisms behind these bioactive compounds, paving the way for the development of standardized extracts and novel therapeutic formulations.
Health Benefits and Essential Properties
Ophiopogon japonicus is celebrated for its diverse health benefits, many of which have been validated by both traditional Chinese medicine and modern scientific research. Its array of bioactive compounds contributes to a holistic therapeutic profile that addresses multiple physiological systems. Below, we explore the primary health benefits and intrinsic properties of this remarkable herb.
Cardiovascular Support
Ophiopogon japonicus plays a vital role in supporting heart health. The steroidal saponins (ophiopogonins) and flavonoids help improve blood circulation, reduce arterial stiffness, and lower cholesterol levels. By enhancing myocardial function and promoting vascular relaxation, the herb reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension and atherosclerosis. Regular consumption may contribute to improved cardiac output and overall cardiovascular resilience.
Respiratory and Pulmonary Benefits
One of the hallmark uses of Ophiopogon japonicus in traditional Chinese medicine is for the treatment of respiratory ailments. The herb is prized for its ability to moisten the lungs and clear internal heat. Its polysaccharides stimulate mucus secretion in a beneficial way, alleviating dry coughs and easing bronchial irritation. These properties make it an effective remedy for conditions like chronic dry cough, bronchitis, and other respiratory disorders.
Immune System Enhancement and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
The immunomodulatory properties of Ophiopogon japonicus are largely attributed to its rich polysaccharide content. These compounds stimulate the production and activity of immune cells, thereby fortifying the body’s defenses against infections. Additionally, the herb’s flavonoids and phenolic acids help reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, mitigating chronic inflammation. This dual action is particularly beneficial for individuals with autoimmune conditions or those recovering from illness.
Antioxidant and Anti-Aging Benefits
Oxidative stress is a major contributor to cellular aging and the development of degenerative diseases. Ophiopogon japonicus is a potent source of antioxidants, thanks to its flavonoids and phenolic acids. These compounds scavenge free radicals, protect cellular structures, and promote tissue repair. As a result, regular use of the herb may slow the aging process, improve skin health, and reduce the risk of age-related conditions, contributing to overall longevity.
Digestive and Metabolic Regulation
The digestive benefits of Ophiopogon japonicus are well recognized in traditional medicine. The herb’s polysaccharides not only boost immune function but also promote healthy gut flora. Improved digestion leads to better nutrient absorption and stable blood sugar levels. For individuals with metabolic concerns, such as insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes, incorporating Ophiopogon japonicus into the diet can support more balanced metabolic processes and sustained energy levels.
Neuroprotective and Cognitive Enhancing Properties
Recent studies have begun to explore the neuroprotective potential of Ophiopogon japonicus. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties extend to neural tissues, where they help reduce oxidative damage and promote cognitive function. Preliminary research suggests that the herb may enhance memory, improve concentration, and protect against neurodegenerative conditions. These benefits make it a promising natural supplement for maintaining mental clarity and overall brain health.
Skin, Hair, and Cosmetic Applications
Ophiopogon japonicus is also valued for its cosmetic benefits. The antioxidants and vitamins present in the herb support collagen production, enhance skin elasticity, and help protect against environmental damage. When used topically, extracts of Ophiopogon japonicus can reduce redness, soothe inflammation, and promote a clearer complexion. Its nourishing properties extend to hair care, where it can improve scalp health and strengthen hair follicles.
Holistic and Preventive Health
Perhaps the most compelling advantage of Ophiopogon japonicus is its holistic approach to health maintenance. Rather than targeting isolated symptoms, the herb supports multiple systems simultaneously—cardiovascular, respiratory, immune, and metabolic. This integrative effect makes it an ideal component of preventive healthcare regimens, helping individuals build resilience against chronic illnesses and maintain a balanced state of well-being over the long term.
In summary, the health benefits and essential properties of Ophiopogon japonicus render it a versatile and powerful natural remedy. Whether used to support heart and lung function, enhance immunity, or promote youthful vitality, this herb offers a comprehensive approach to holistic health and disease prevention.
Practical Applications, Usage, and Safety Precautions
Ophiopogon japonicus is a versatile herb that finds its application in various forms—ranging from traditional decoctions to modern extracts and topical formulations. Its incorporation into daily wellness routines can be tailored to individual needs, whether for internal consumption or external use. The following guidelines outline practical methods for using Ophiopogon japonicus, along with recommendations for safe usage and potential contraindications.
Culinary and Herbal Preparations
In traditional Chinese medicine, Ophiopogon japonicus is commonly prepared as a decoction. The dried root is simmered in water for 20–30 minutes to extract its beneficial compounds. For those seeking a milder method of consumption, the powdered form can be added to teas or smoothies. Here are some popular preparation methods:
- Herbal Tea: Use 5–10 grams of dried Ophiopogon japonicus per cup of water. Steep for 15–20 minutes. This tea is especially beneficial for respiratory and digestive support.
- Decoctions: Combine Ophiopogon japonicus with complementary herbs such as Mai Men Dong and Tian Men Dong to create a synergistic formula aimed at nourishing yin and moistening the lungs.
- Powdered Supplements: Standardized capsules or powders offer a concentrated dose of the herb’s bioactives and can be taken daily according to product guidelines.
Medicinal Applications and Dosage Recommendations
For therapeutic use, the form and dosage of Ophiopogon japonicus may vary depending on the specific health concern. It is advisable to consult with a qualified herbalist or healthcare provider to determine the optimal dosage. General recommendations include:
- Decoction: 5–10 grams per serving, taken 1–2 times daily.
- Extracts: Follow the manufacturer’s dosage guidelines; typical dosages range from 300 to 500 mg per day.
- Topical Applications: When used in creams or serums, a small percentage (1–5%) of Ophiopogon japonicus extract is sufficient to achieve skin-soothing benefits.
Topical and Cosmetic Uses
Ophiopogon japonicus is increasingly incorporated into cosmetic formulations due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Its extracts can be found in:
- Facial Creams and Serums: Used to enhance skin hydration, reduce redness, and promote a youthful complexion.
- Masks and Lotions: Combined with other natural ingredients like aloe vera and green tea, Ophiopogon japonicus extract helps soothe irritated skin and improve overall skin tone.
- Hair Care Products: Formulations containing the herb can strengthen hair follicles and improve scalp health.
Practical Tips for Daily Integration
- Morning Ritual: Start your day with a cup of Ophiopogon japonicus tea to invigorate your system and support respiratory health.
- Herbal Blends: Incorporate the herb into traditional formulas alongside other yin-nourishing ingredients to enhance overall vitality.
- Skincare Routine: Use products containing Ophiopogon japonicus extract as part of your daily facial care regimen to combat oxidative stress and support skin renewal.
- Consistent Use: For best results, integrate the herb into your routine on a consistent basis, as its benefits accumulate over time.
Safety Considerations and Contraindications
Ophiopogon japonicus is generally safe for most individuals when used appropriately. However, certain precautions should be observed:
- Pregnancy and Lactation: Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should consult a healthcare provider before using concentrated forms or supplements.
- Medication Interactions: Individuals on medications that affect blood sugar or blood pressure should seek professional advice to avoid potential interactions.
- Allergic Reactions: Although rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions. It is advisable to perform a patch test when using topical preparations.
- Gradual Introduction: Begin with a lower dose, especially if you are new to the herb, to ensure your body adjusts without adverse effects.
By following these usage guidelines and safety precautions, you can effectively integrate Ophiopogon japonicus into your wellness routine and enjoy its multifaceted benefits without undue risk.
Scientific Studies and Research Insights
Modern scientific investigations have provided substantial evidence supporting the traditional uses of Ophiopogon japonicus. A range of studies has explored its pharmacological properties, helping to elucidate the mechanisms behind its health benefits. The following highlights summarize key research findings that demonstrate the herb’s therapeutic potential.
- Cardiovascular Benefits and Myocardial Protection (2015)
A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology examined the effects of Ophiopogon japonicus extracts on heart health. The research found that the steroidal saponins, particularly ophiopogonins, improved myocardial function and reduced arterial stiffness. These findings suggest that regular consumption of the herb may help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. - Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Effects (2016)
Research featured in Phytotherapy Research demonstrated that the polysaccharides and flavonoids in Ophiopogon japonicus significantly modulated the immune response. The study reported a reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines, indicating that the herb can alleviate chronic inflammation and enhance immune system resilience. These properties validate its traditional use in nourishing yin and boosting overall immunity. - Respiratory Relief and Lung Moistening Properties (2017)
A clinical trial conducted in China evaluated the efficacy of Ophiopogon japonicus in treating symptoms of dry cough and respiratory discomfort. Participants consuming a decoction containing the herb experienced significant improvements in lung moisture and a reduction in cough frequency. The study attributed these benefits to the herb’s high polysaccharide content, which promotes mucosal lubrication. - Antioxidant Activity and Anti-Aging Effects (2018)
In a study published in the Journal of Natural Products, researchers assessed the antioxidant capacity of Ophiopogon japonicus. The findings indicated that its flavonoids and phenolic acids effectively neutralized free radicals, thereby protecting cells from oxidative damage. This antioxidant activity is closely linked to anti-aging benefits and supports its use in cosmetic and dermatological applications. - Neuroprotective Effects and Cognitive Enhancement (2019)
Emerging research at a leading neuroscience institute investigated the neuroprotective properties of Ophiopogon japonicus. Results from animal studies revealed that the herb’s bioactive compounds reduced oxidative stress in neural tissues and improved memory retention. These preliminary findings suggest that Ophiopogon japonicus could be beneficial in preventing neurodegenerative conditions and enhancing cognitive function. - Metabolic Regulation and Digestive Health (2020)
A clinical trial published in the International Journal of Herbal Medicine focused on the metabolic effects of Ophiopogon japonicus. The study found that regular consumption improved digestive efficiency and stabilized blood sugar levels. Researchers attributed these benefits to the herb’s prebiotic polysaccharides, which promote a healthy gut microbiome and enhance nutrient absorption.
Collectively, these scientific studies underscore the therapeutic potential of Ophiopogon japonicus and provide a robust foundation for its continued use in modern herbal medicine. As research advances, further insights into its mechanisms of action may lead to the development of standardized formulations and novel therapeutic applications.
Frequently Asked Questions about Ophiopogon japonicus
What is Ophiopogon japonicus and why is it used in traditional medicine?
Ophiopogon japonicus, commonly known as dwarf lilyturf or Mai Men Dong, is a perennial herb widely used in traditional Chinese medicine. It is valued for its ability to nourish yin, moisten the lungs, and support cardiovascular and immune health.
How can I incorporate Ophiopogon japonicus into my daily routine?
You can use Ophiopogon japonicus as a decoction, herbal tea, or in supplement form. It is often combined with other yin-nourishing herbs to enhance respiratory, cardiovascular, and digestive functions.
Are there any side effects or contraindications?
Ophiopogon japonicus is generally safe when used as directed. However, pregnant or breastfeeding women and individuals on certain medications should consult a healthcare provider before use. A gradual introduction is recommended to monitor for any adverse reactions.
What health benefits does Ophiopogon japonicus offer?
The herb provides cardiovascular support, respiratory relief, immune modulation, antioxidant protection, and anti-aging benefits. Its bioactive compounds work synergistically to reduce inflammation, improve digestion, and enhance overall vitality.
Which form is most effective for therapeutic use?
Both decoctions and standardized extracts are effective. Herbal teas and tinctures provide a natural method of ingestion, while concentrated capsules offer targeted benefits. The choice depends on individual health needs and preferences.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before making significant changes to your diet or health regimen.
If you found this article informative, please share it on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or your preferred social platform. Follow us on social media for more insights and updates on natural health and wellness tips!