Ginseng is a revered herb known for its powerful adaptogenic properties and long history in traditional medicine. Celebrated for enhancing energy, cognitive function, and overall well-being, ginseng is widely used as a natural remedy to combat stress and support immune health. Its roots are prized for a unique blend of bioactive compounds that contribute to its diverse therapeutic effects, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic benefits. In this comprehensive guide, we explore ginseng’s botanical characteristics, its potent active compounds, the wide range of health benefits it offers, its various applications and safety considerations, and the latest scientific research supporting its efficacy.
Table of Contents
- Plant Characteristics and Identification
- Active Compounds and Chemical Profile
- Health Benefits and Therapeutic Properties
- Applications, Safety, and Usage Tips
- Research Insights and Key Studies
- Frequently Asked Questions
Plant Characteristics and Identification
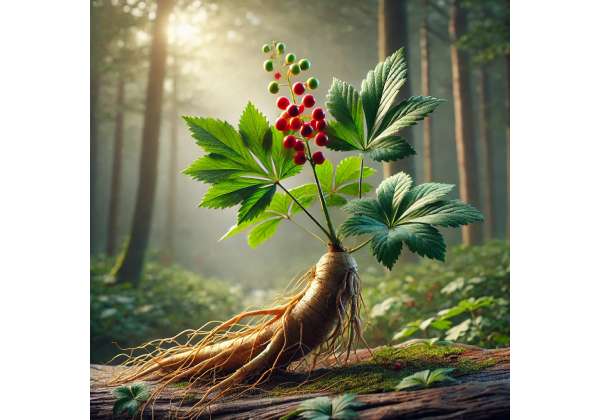
Ginseng is a slow-growing perennial plant that belongs to the genus Panax in the Araliaceae family. The most commonly known species are Panax ginseng (Asian ginseng) and Panax quinquefolius (American ginseng). These plants have been used for thousands of years in traditional medicine systems across Asia and North America. Ginseng plants are easily identified by their forked, fleshy roots, which resemble the shape of a human body—a characteristic that historically led to the belief in their “life-enhancing” properties.
Taxonomy and Morphological Features
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Clade: Angiosperms
- Order: Apiales
- Family: Araliaceae
- Genus: Panax
- Species: Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolius, among others
Ginseng is recognized by its distinctive, bifurcated root system that is often described as resembling a twisted human figure. The roots are typically tan to light brown, with a rough, wrinkled surface, and they contain a concentration of bioactive compounds. The leaves are compound, palmate, and arranged in a rosette at the top of the plant. In early spring, small, yellow-green flowers appear in clusters, though these are generally less valued than the roots for medicinal purposes.
Growth Conditions and Natural Habitat
Ginseng thrives in temperate forest environments with rich, well-drained soils and shaded conditions. Native to the forests of Eastern Asia and Eastern North America, the plant prefers cool, moist climates with dappled sunlight under a canopy of trees. Because of its slow growth and specific habitat requirements, wild ginseng is often rare and highly prized.
- Soil: Rich, loamy, and well-drained
- Light: Prefers partial shade (understory of forests)
- Climate: Temperate regions with distinct seasons
- Water: Requires consistent moisture but well-drained conditions to prevent root rot
Cultivation and Propagation
Cultivating ginseng requires patience and attention to detail. It is typically grown from seed or root division. Seeds need to undergo a period of cold stratification to break dormancy, a process that mimics natural winter conditions. Cultivators often use organic methods to nurture the plants, avoiding synthetic chemicals to maintain the purity of the roots.
- Propagation: Through seeds or by dividing the root clumps
- Growth Period: Plants require several years (typically 4–6 years) before the roots reach optimal potency
- Management: Regular weeding and mulching are essential to mimic natural forest floor conditions
Ecological and Cultural Significance
Ginseng is more than just a medicinal herb—it holds a significant place in cultural traditions. In East Asia, particularly in Korea and China, ginseng is considered a symbol of longevity, vitality, and wisdom. It is often featured in traditional ceremonies and is believed to possess the essence of life. In North America, American ginseng has been a valuable export and is tightly regulated to protect wild populations. The lore surrounding ginseng has contributed to its high market value and its status as a prized natural resource.
Ginseng’s unique appearance, slow growth, and profound historical significance make it a fascinating subject for botanists, herbalists, and cultural historians alike. Its revered status in traditional medicine continues to inspire modern scientific research and its integration into contemporary health practices.
Active Compounds and Chemical Profile
The health-promoting effects of ginseng are largely due to its rich phytochemical composition. Researchers have identified several key active compounds that work synergistically to deliver its powerful therapeutic benefits. Below is a list of the primary bioactive compounds found in ginseng, along with an analysis of their properties.
- Ginsenosides
Ginsenosides are the most extensively studied group of compounds in ginseng and are unique to the Panax genus. These saponins are responsible for many of ginseng’s pharmacological effects, including its adaptogenic, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties. There are over 30 different ginsenosides, such as Rb1, Rg1, and Rg3, each contributing to various aspects of health. For instance, Rb1 is linked to improved cognitive function and stress reduction, while Rg1 may enhance physical performance and endurance. - Polysaccharides
The polysaccharides in ginseng contribute to its immune-modulating effects. These complex carbohydrates help stimulate the body’s immune response by enhancing the activity of macrophages and natural killer cells. They are also thought to exhibit antioxidant properties, protecting cells from oxidative damage and supporting overall immune health. - Peptides
Certain bioactive peptides have been isolated from ginseng, which may play a role in cellular repair and metabolic regulation. These peptides can assist in modulating immune function and promoting tissue regeneration, adding to the overall health benefits provided by ginseng. - Polyacetylenes
Polyacetylenes are a group of compounds with demonstrated anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. In ginseng, they contribute to reducing inflammation and may protect against infections by inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria. Their presence also supports the herb’s potential role in cancer prevention through the modulation of cell proliferation. - Phenolic Compounds
Ginseng contains a variety of phenolic compounds, which act as antioxidants. These compounds help scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, thereby protecting the body’s cells from damage. The antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds is essential in reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disorders and neurodegenerative conditions.
Synergistic Interactions and Bioavailability
The therapeutic efficacy of ginseng is not solely due to individual compounds but rather the synergistic interaction between them. The combination of ginsenosides, polysaccharides, peptides, polyacetylenes, and phenolic compounds creates a multifaceted approach to health. This synergy enhances bioavailability, meaning the body can absorb and utilize these compounds more effectively when they are consumed as part of the whole herb or a standardized extract.
Extraction and Standardization
Modern extraction methods, including ethanol extraction and supercritical fluid extraction, are used to isolate ginseng’s active compounds. Standardized extracts ensure that each dose contains a consistent and effective amount of key compounds, particularly ginsenosides. This standardization is crucial for clinical research and for consumers who rely on ginseng supplements for specific health outcomes.
By understanding ginseng’s chemical profile, researchers can better harness its potential and develop targeted therapies for various health conditions. The intricate blend of bioactive compounds in ginseng forms the basis for its long-standing use as an adaptogen and health tonic.
Health Benefits and Therapeutic Properties
Ginseng is celebrated for its wide-ranging health benefits, which have been validated by centuries of traditional use and modern scientific research. This section explores the various therapeutic properties of ginseng and explains how its unique compounds contribute to overall well-being.
Cognitive Enhancement and Mental Clarity
Ginseng is widely recognized for its positive effects on brain function:
- Improved Memory and Focus: Studies have shown that ginseng supplementation can enhance cognitive performance, including improvements in short-term memory, attention, and learning capacity. Ginsenosides play a key role in protecting neurons and promoting efficient neurotransmission.
- Neuroprotection: The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of ginseng help protect brain cells from oxidative damage. This neuroprotective effect may reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Stress Reduction: As an adaptogen, ginseng helps the body manage stress by regulating the production of stress hormones. This leads to improved mental clarity and a more balanced mood.
Immune System Support
Ginseng’s polysaccharides and other bioactive compounds are known to boost the immune system:
- Enhanced Immune Response: Ginseng can stimulate the production and activity of various immune cells, including macrophages, natural killer cells, and T-cells. This improved immune function helps the body fight off infections and recover from illness.
- Antioxidant Protection: The potent antioxidants in ginseng help reduce oxidative stress, which can compromise immune function. By protecting cells from free radical damage, ginseng supports long-term immune health.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Ginseng reduces inflammatory markers in the body, which can help prevent chronic inflammation—a major contributor to many health conditions.
Energy, Stamina, and Adaptogenic Effects
Ginseng is renowned for its ability to enhance physical performance and boost energy levels:
- Increased Endurance: Athletes and active individuals often use ginseng to improve stamina and reduce fatigue. Ginsenosides help improve oxygen utilization and energy metabolism, resulting in enhanced physical performance.
- Adaptogenic Benefits: As an adaptogen, ginseng helps the body adapt to physical and mental stress. It supports overall homeostasis and can improve resilience against stressors, leading to better recovery and sustained energy levels.
- Metabolic Support: Ginseng may assist in regulating blood sugar levels and improving insulin sensitivity, making it beneficial for metabolic health and weight management.
Cardiovascular and Circulatory Health
Ginseng offers several benefits for the cardiovascular system:
- Improved Blood Flow: Ginsenosides help dilate blood vessels and improve circulation. Enhanced blood flow supports cardiovascular health and reduces the risk of heart-related issues.
- Antioxidant Protection: The antioxidant properties of ginseng contribute to the health of blood vessels by reducing oxidative stress and preventing the buildup of harmful plaques.
- Reduced Inflammation: By lowering inflammatory markers, ginseng may help protect the cardiovascular system and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
Anti-Aging and Skin Health
Ginseng’s potent antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds contribute to its anti-aging benefits:
- Cellular Protection: Ginseng protects cells from oxidative damage, which is a key factor in the aging process. This protection may help maintain youthful skin and reduce the appearance of wrinkles.
- Improved Skin Appearance: Topical formulations containing ginseng extract are popular in skincare products for their ability to enhance skin elasticity, reduce inflammation, and promote a more radiant complexion.
- Detoxification: Ginseng supports the body’s natural detoxification processes, helping to remove toxins that can accelerate aging and impair skin health.
Overall Wellness and Preventive Care
Ginseng functions as a holistic tonic that supports overall health:
- Enhanced Vitality: Regular consumption of ginseng can boost overall energy and promote a sense of well-being. Its adaptogenic properties help balance the body’s response to stress.
- Preventive Health: Ginseng is often used as a preventive measure to support long-term health. Its diverse range of bioactive compounds helps protect against a variety of age-related and chronic conditions.
- Mood and Mental Health: In addition to cognitive benefits, ginseng may help alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression by modulating stress responses and supporting neurotransmitter balance.
Ginseng’s extensive health benefits make it a versatile natural remedy. Its ability to enhance cognitive function, support the immune system, boost energy, and promote cardiovascular health has solidified its role in both traditional and modern medicine.
Applications, Safety, and Usage Tips
Ginseng is available in multiple forms, making it accessible for various applications in culinary, medicinal, and cosmetic contexts. This section provides practical advice on how to use ginseng effectively and safely to maximize its benefits.
Culinary Applications
In some cultures, ginseng is used as an ingredient in food and beverages:
- Ginseng Tea: One of the most popular ways to consume ginseng is by preparing a herbal tea. Simmer dried or fresh ginseng slices in water for 10–15 minutes to extract its beneficial compounds.
- Soup and Broth: Ginseng is often added to soups and broths to impart a subtle, earthy flavor along with its health benefits. Traditional recipes from East Asia feature ginseng in nourishing broths.
- Smoothies and Functional Foods: Ginseng extract or powder can be blended into smoothies or mixed into health bars and functional beverages to provide an energy boost and enhance overall wellness.
Medicinal Preparations
Due to its well-documented health benefits, ginseng is commonly used in various supplement forms:
- Capsules and Tablets: Standardized ginseng supplements ensure a consistent dosage of active compounds, particularly ginsenosides. These are widely available and are easy to incorporate into daily routines.
- Liquid Extracts and Tinctures: Liquid forms of ginseng are absorbed more quickly by the body, making them suitable for individuals who prefer faster onset of action. These extracts can be added to water or juice.
- Powdered Forms: Ginseng powder is versatile and can be mixed into food, beverages, or smoothies. It is often used in traditional medicine formulations for its concentrated benefits.
Dosage Recommendations
Proper dosing is essential to achieve the desired effects of ginseng without experiencing adverse reactions:
- General Health: A typical daily dose of standardized ginseng extract is between 200 and 400 mg, often divided into two or three doses.
- Cognitive and Energy Boost: Studies suggest that higher doses, up to 600 mg per day, may be more effective for improving mental performance and reducing fatigue.
- Duration: Ginseng is best taken in cycles (e.g., 8–12 weeks on followed by a break) to prevent tolerance and maintain its efficacy over time.
Safety Considerations and Contraindications
Although ginseng is generally well tolerated, certain precautions should be observed:
- Potential Side Effects: Some users may experience mild side effects such as headaches, digestive upset, or insomnia, particularly when taken in high doses.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Due to limited research on the safety of ginseng during pregnancy and lactation, these groups should consult a healthcare provider before use.
- Drug Interactions: Ginseng may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners, antidepressants, and diabetes medications. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you are on prescription drugs.
- Chronic Conditions: Individuals with chronic conditions such as hypertension or hormone-sensitive cancers should exercise caution and seek medical advice before incorporating ginseng into their regimen.
Storage and Handling
Proper storage of ginseng products ensures their potency and longevity:
- Supplements and Extracts: Store in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for maximum shelf life.
- Herbal Tea and Powder: Keep in airtight containers to prevent moisture absorption and oxidation.
- Fresh Ginseng: If using fresh ginseng root, refrigerate it in a plastic bag to maintain freshness until use.
By adhering to these usage and safety tips, you can integrate ginseng into your daily wellness routine with confidence. Whether consumed as a tea, supplement, or added to recipes, ginseng offers a host of benefits when used appropriately and in moderation.
Research Insights and Key Studies
A substantial body of scientific research supports the traditional uses of ginseng, particularly its effects on cognitive function, energy levels, and overall health. Below is a list of key studies that have investigated the therapeutic properties of ginseng.
- Study on Cognitive Function Enhancement (2011)
Journal: Journal of Ethnopharmacology
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, researchers evaluated the impact of ginseng supplementation on cognitive performance in middle-aged adults. Participants received standardized ginseng extract for 12 weeks. The study demonstrated significant improvements in memory recall, attention, and processing speed. Researchers attributed these effects to the neuroprotective actions of ginsenosides, which enhance cerebral blood flow and reduce oxidative stress. This study supports ginseng’s use as a natural cognitive enhancer and its potential role in preventing age-related cognitive decline. - Investigation of Anti-Fatigue and Energy Boosting Effects (2013)
Journal: Journal of Ginseng Research
This clinical trial assessed the impact of ginseng on physical performance and fatigue in athletes. Participants who received ginseng extract reported reduced fatigue levels, increased endurance, and improved recovery times compared to the placebo group. The results were linked to the adaptogenic properties of ginseng, which help regulate energy metabolism and enhance oxygen utilization. The study provides strong evidence for ginseng’s ability to boost stamina and reduce physical fatigue during strenuous activities. - Evaluation of Cardiovascular Benefits (2015)
Journal: Phytotherapy Research
Researchers investigated the cardiovascular effects of ginseng supplementation in patients with mild circulatory disorders. Over a period of 10 weeks, subjects experienced improved blood flow, reduced blood viscosity, and lower blood pressure. The study found that the vasodilatory and antioxidant properties of ginsenosides contributed significantly to these effects. These findings highlight ginseng’s potential in promoting cardiovascular health and preventing heart-related complications. - Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity Study (2017)
Journal: International Journal of Molecular Sciences
This in vitro study explored the antioxidant capacity of ginseng extracts. The results demonstrated that ginseng has a high free radical scavenging activity, effectively reducing oxidative stress in cultured cells. The anti-inflammatory effects were also significant, with ginseng reducing the production of inflammatory cytokines. The study suggests that the combined antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of ginseng play a critical role in its protective effects against chronic diseases. - Impact on Immune Function and Stress Response (2019)
Journal: Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
In this randomized controlled trial, subjects with weakened immune systems were given ginseng supplements for 8 weeks. The study observed an increase in immune cell activity, including enhanced natural killer cell function and improved overall immune response. Additionally, participants reported a reduction in perceived stress levels. These outcomes indicate that ginseng can modulate the immune system and help the body cope with physical and mental stress.
The results of these studies provide robust scientific support for the traditional uses of ginseng. They illustrate how ginseng’s multifaceted bioactive compounds contribute to improved cognitive function, increased energy, cardiovascular support, antioxidant protection, and enhanced immune response.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main health benefits of ginseng?
Ginseng is known for its ability to enhance cognitive function, boost energy levels, support cardiovascular health, and improve overall immune response. Its adaptogenic properties help the body manage stress and combat fatigue.
How is ginseng typically used?
Ginseng is commonly consumed as standardized supplements, liquid extracts, capsules, or herbal teas. It is also used in traditional culinary recipes and functional foods for its health-promoting benefits.
Are there any side effects associated with ginseng?
Ginseng is generally well tolerated; however, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as headaches, digestive upset, or insomnia, especially at high doses. Always consult a healthcare provider if you are taking other medications or have preexisting conditions.
What is the recommended dosage for ginseng supplements?
A typical daily dose of standardized ginseng extract ranges from 200 to 400 mg, often divided into two or three doses. Dosages may vary based on individual needs and the intended health outcome.
Can ginseng be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding?
Due to limited research on its safety during pregnancy and lactation, it is advisable for pregnant or breastfeeding women to consult a healthcare professional before using ginseng supplements.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your diet or health regimen.
If you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or your preferred social platform. Your support helps spread the word about the remarkable benefits of ginseng!