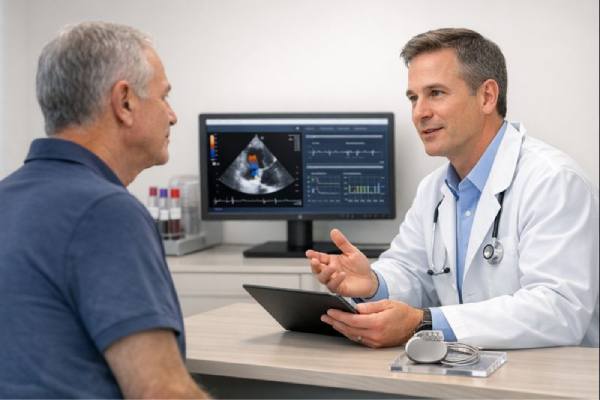
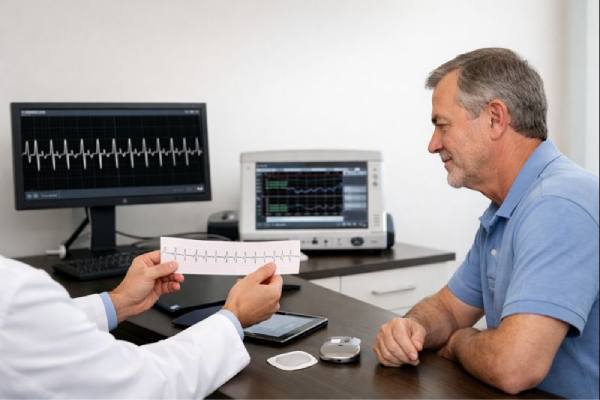
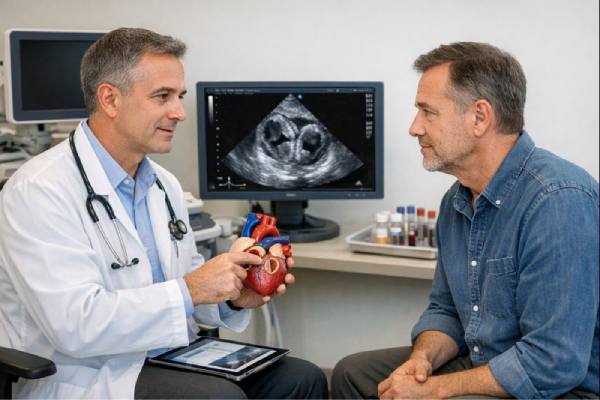
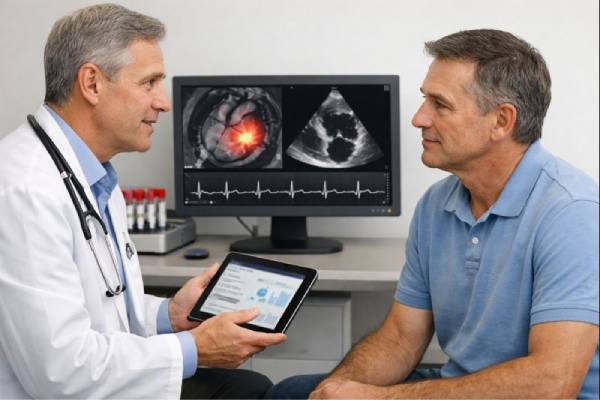
Implant-associated endocarditis: Prosthetic Valve and Device Infections, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
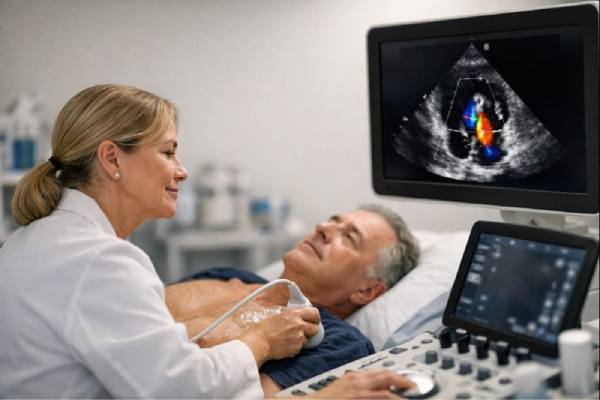
Implant-associated endocarditis is a serious infection that forms on the heart’s inner surface or valves and involves a man-made material inside the heart or...
Incessant ventricular tachycardia: Emergency Symptoms, Electrical Storm Care, Diagnosis, Treatment
Incessant ventricular tachycardia is a dangerous rhythm problem where the heart keeps slipping into a fast beat that starts in the lower chambers and...
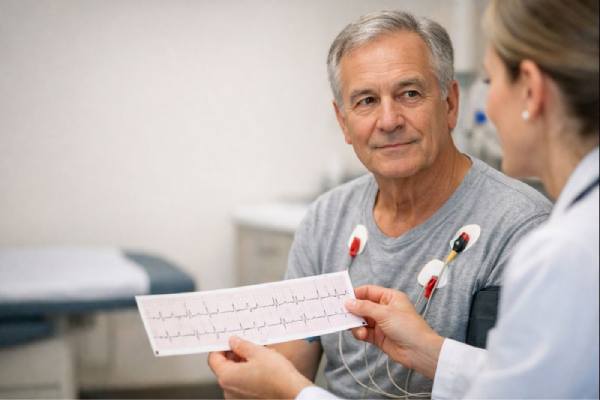
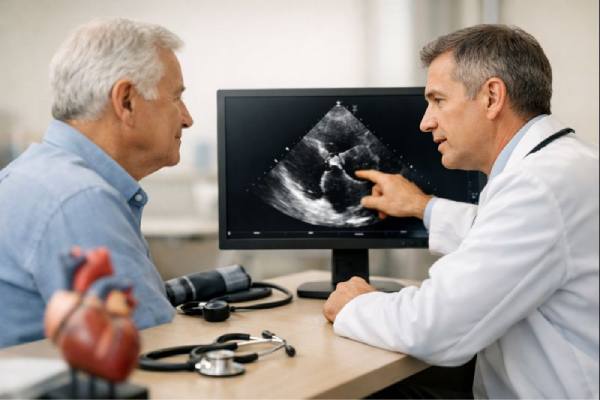
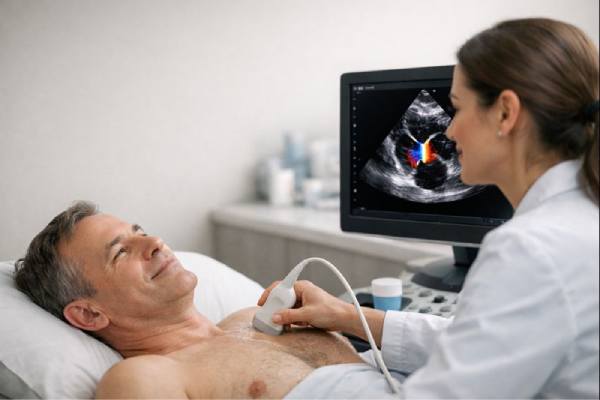
Infective endocarditis: Early Symptoms, Blood Culture Testing, Echocardiography, Treatment Options
Infective endocarditis is a serious infection of the heart’s inner lining and valves. It happens when germs enter the bloodstream and settle on a...
Infective myocarditis: Viral vs Bacterial Causes, Risk Factors, and Management
Infective myocarditis is an illness where an infection triggers inflammation of the heart muscle. (Myocarditis means “inflammation of the heart muscle.”) For many people,...
Infective pericarditis, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options
Infective pericarditis is inflammation of the thin sac around the heart caused by an infection. For some people it starts like a stubborn “flu”...
Inferior myocardial infarction: Early Symptoms, ECG Findings, Diagnosis, and Urgent Treatment
An inferior myocardial infarction is a type of heart attack that affects the lower (“inferior”) part of the heart. It often happens suddenly, but...
Inferior vena cava obstruction: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Inferior vena cava obstruction happens when the body’s largest vein (the inferior vena cava) becomes narrowed or blocked. This vein carries blood from the...
Inferior vena cava syndrome: Blood Clots, Tumor Compression, and Modern Management
Inferior vena cava syndrome is a pattern of symptoms that appears when the body’s largest “return” vein from the lower half of the body...
Inferior vena cava thrombosis: Warning Signs, Pulmonary Embolism Risk, and When to Seek Care
Inferior vena cava thrombosis is a blood clot in the body’s largest vein that returns blood from the legs and abdomen to the heart....
Infiltrative cardiomyopathy: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Infiltrative cardiomyopathy is a group of conditions in which an abnormal substance builds up inside the heart muscle and makes it stiff. Over time,...
Inflammatory cardiomyopathy: Viral, Autoimmune, and Medication-Related Causes, and Management Explained
Inflammatory cardiomyopathy is a condition where inflammation injures the heart muscle and weakens how well it pumps or relaxes. It often starts as myocarditis...
Inflammatory pericarditis: Symptoms, Chest Pain Patterns, and When It’s an Emergency
Inflammatory pericarditis is irritation and swelling of the pericardium (the thin sac around the heart). For many people it begins suddenly, often after a...
Inflammatory vasculitis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Modern Treatments
Inflammatory vasculitis is a group of conditions where the body’s defense system mistakenly inflames blood vessel walls. When a vessel is irritated and swollen,...
Inlet ventricular septal defect: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
An inlet ventricular septal defect is a type of “hole between the pumping chambers” in a very specific spot—near the heart’s inlet valves. Ventricular...
Innominate artery stenosis: Symptoms, Stroke Risk, and Treatment Options
Innominate artery stenosis is a narrowing in the first major branch off the aortic arch that feeds blood to the right arm and the...
Innominate artery thrombosis: Symptoms, Stroke Warning Signs, and Urgent Treatment
Innominate artery thrombosis is a sudden or progressive blockage in the first major branch off the aortic arch—the vessel that supplies blood to the...
Inoperable coronary artery disease: What It Means, Symptoms, and Management
“Inoperable coronary artery disease” is a phrase doctors use when blocked heart arteries can’t be safely or effectively fixed with procedures like stents or...
Insufficiency of aortic valve: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and When Surgery Is Needed
Aortic valve insufficiency—often called aortic regurgitation (blood leaks backward through the valve)—happens when the aortic valve does not close tightly between heartbeats. Instead of...
Insufficiency of mitral valve: Causes, Risk Factors, and How It Progresses
Mitral valve insufficiency—also called mitral regurgitation (blood leaks backward through the valve)—happens when the mitral valve doesn’t close tightly between the left atrium and...
Insufficiency of pulmonary valve: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Insufficiency of the pulmonary valve (often called pulmonary valve leakage) means the valve between the right side of the heart and the lung artery...
Insufficiency of the tricuspid valve: Risk Factors, Early Signs, and Complications
Insufficiency of the tricuspid valve—often called tricuspid regurgitation (blood leaks backward)—means the valve between the right upper and right lower chambers of the heart...
Interatrial block: Causes, Risk Factors, and Stroke Prevention Basics
Interatrial block is a heart rhythm finding that tells us the electrical signal is taking longer than usual to travel from the right upper...
Interatrial septal aneurysm: Causes, diagnosis, and treatment options
An interatrial septal aneurysm is a “floppy” area in the wall that separates the heart’s upper chambers. It usually sits where a small opening...
Interatrial septal defect: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Modern Closure Options
An interatrial septal defect (often called an atrial septal defect, or ASD) is a gap in the wall between the heart’s two upper chambers....