Critical limb ischemia: Revascularization Options, Endovascular vs Bypass
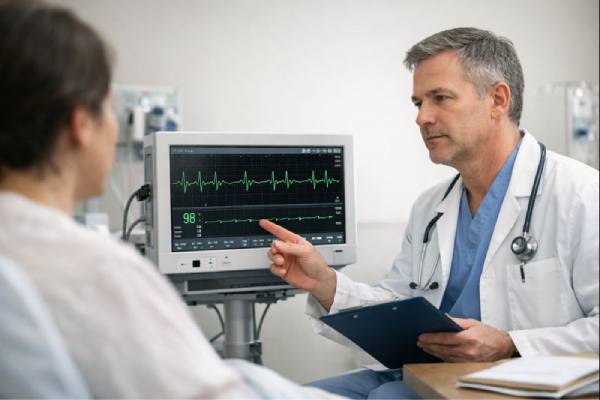
Critical limb ischemia (CLI) describes the most dangerous end of poor leg blood flow, when the foot or toes no longer receive enough oxygen...
Cryoglobulinemic vasculitis: Long-Term Management, Relapse Prevention, and Follow-Up Tests
Cryoglobulinemic vasculitis is a type of vasculitis (blood-vessel inflammation that can damage organs) caused by abnormal blood proteins called cryoglobulins (proteins that clump when...
Cystic adventitial disease: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Surgical Treatment Options
Cystic adventitial disease is a rare cause of reduced blood flow in an artery, most often behind the knee. Instead of plaque building up...
Cystic medial necrosis, Causes and risk factors, Marfan and genetic aortopathy
Cystic medial necrosis is a microscope-level change in the wall of a large artery—most often the aorta (the body’s main artery)—that can make that...
Bacterial endocarditis symptoms and treatment guide for infective endocarditis
Bacterial endocarditis (often called infective endocarditis) is a serious infection of the heart’s inner lining, usually involving one or more heart valves. It starts...
Bacterial myocarditis causes, common risk factors, and Treatment
Bacterial myocarditis is inflammation and injury of the heart muscle caused by bacteria or bacterial toxins. It is far less common than viral myocarditis,...
Bacterial pericarditis symptoms and early signs plus complications
Bacterial pericarditis is an infection of the pericardium—the thin, double-layered sac that surrounds the heart. While uncommon today, it remains one of the most...
Barlow’s syndrome symptoms and early signs plus warning clues
Barlow’s syndrome is a form of degenerative mitral valve disease in which the mitral valve leaflets become thickened and “redundant,” with elongated chordae (the...
Baroreflex failure causes and triggers and who is at risk
Baroreflex failure is a rare but high-impact disorder in which the body loses its fastest, most reliable “autopilot” for blood pressure control. In healthy...
Barth syndrome causes and risk factors including inheritance
Barth syndrome is a rare, inherited condition that mainly affects boys and often shows up early in life with heart weakness, low infection-fighting white...
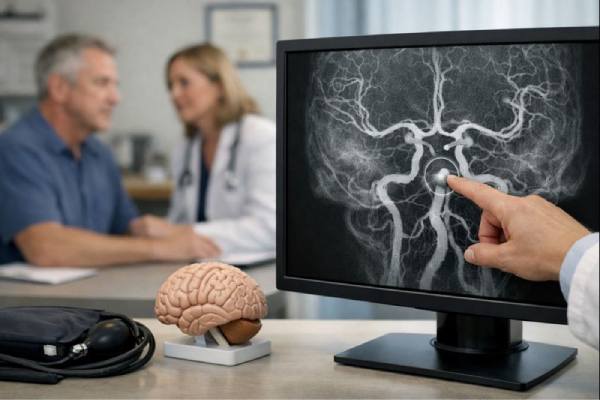
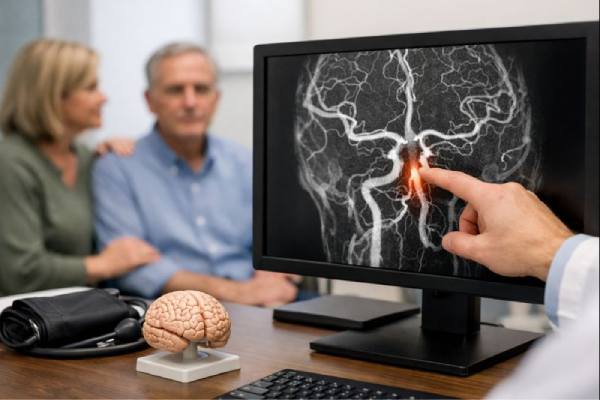
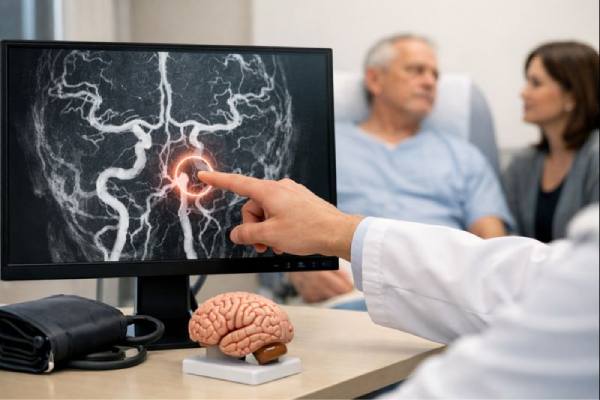
Basilar artery aneurysm diagnosis and tests including CTA, MRA and angiography
A basilar artery aneurysm is a weakened, bulging area in a major blood vessel at the base of the brain. Because the basilar artery...
Basilar artery occlusion symptoms, warning signs, and emergency steps
Basilar artery occlusion is one of the most time-sensitive emergencies in neurology. The basilar artery feeds the brainstem, a compact control center for breathing,...
Basilar artery thrombosis symptoms, warning signs, and emergency response
Basilar artery thrombosis is a life-threatening form of ischemic stroke where a clot forms within the basilar artery itself and blocks blood flow to...
Bayés syndrome symptoms, complications, and stroke warning signs
Bayés syndrome describes a specific electrical problem in the atria (the heart’s upper chambers) that signals higher risk for atrial fibrillation and stroke. It...
Behçet’s disease symptoms and diagnosis guide for patients
Behçet’s disease is a long-term inflammatory illness in which the immune system repeatedly attacks blood vessels and surrounding tissues. It often announces itself with...
Bernheim syndrome prognosis expectations and prevention through blood pressure control
Bernheim syndrome is a classic, much-debated concept in cardiology: the idea that a thickened or enlarged left ventricle can push the heart’s shared wall...