Brachiocephalic artery aneurysm Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
A brachiocephalic artery aneurysm is an abnormal widening of the first major branch that comes off the aortic arch—the vessel that quickly divides into...
Brachiocephalic vein thrombosis Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Guide
Brachiocephalic vein thrombosis is a blood clot in one of the large veins that drains blood from the arm, shoulder, and neck into the...
Bradyarrhythmia Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention Guide
A slow heart rhythm can be a harmless finding in a well-trained athlete, or it can be the first sign that the heart’s electrical...
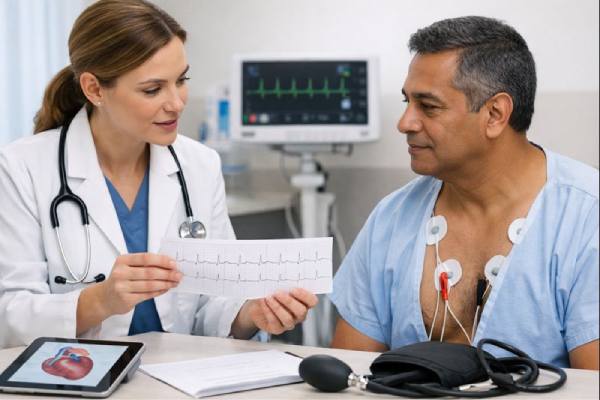
Bradycardia Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Guide
Bradycardia means a slower-than-usual heart rate—typically under 60 beats per minute in adults. Sometimes it is completely normal, especially during sleep or in well-trained...
Bradycardia–tachycardia syndrome symptoms, diagnosis, and best treatments
Bradycardia–tachycardia syndrome is a heart rhythm problem where the heartbeat swings between rates that are too slow and bursts that are too fast. Many...
Bradydysrhythmia Diagnosis and Management for Safer Daily Life
Bradydysrhythmia means the heart is beating too slowly because the electrical system is running slow, blocked, or irregular. A calm, athletic heart rate can...
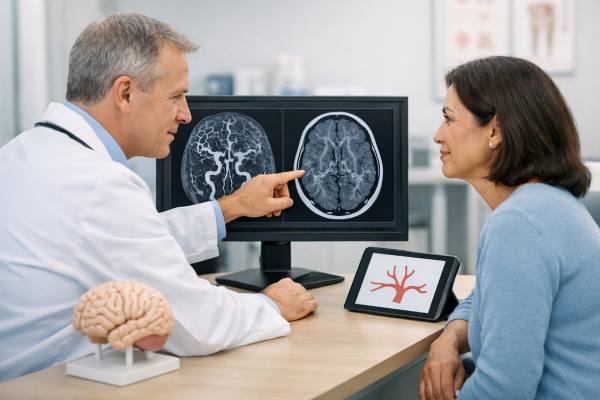
Brain Aneurysm Diagnosis and Imaging Tests: CT, CTA, MRI, and Angiography
A brain aneurysm is a weak, bulging spot in a blood vessel in or around the brain. Many aneurysms never cause symptoms and are...
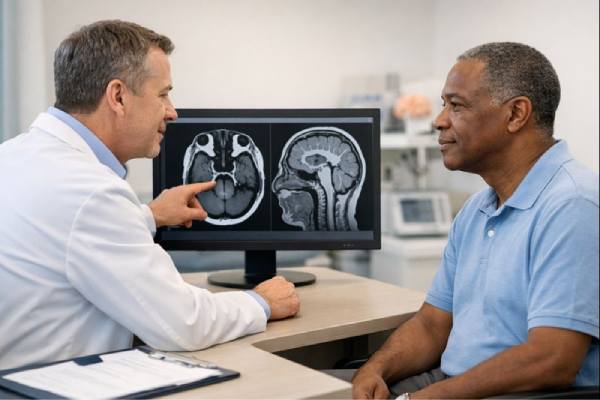
Brainstem Stroke Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Emergency Treatment
A brainstem stroke is a small phrase for a very high-impact event. The brainstem is the body’s “life-support hub,” controlling breathing, heartbeat, swallowing, eye...
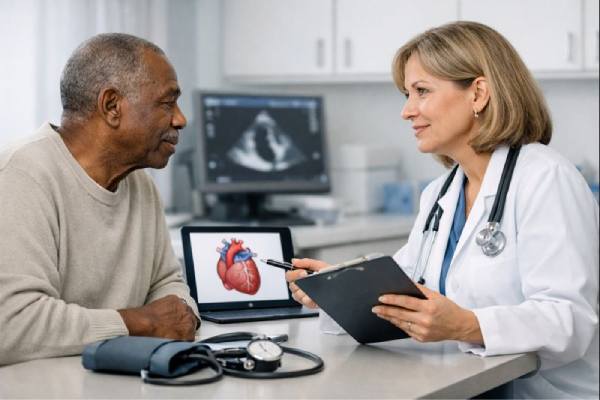
Brown atrophy of the heart: Causes, Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Brown atrophy of the heart is an age-related change in which heart muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) shrink and collect a brown pigment called lipofuscin. It...
Brugada syndrome: Symptoms, ECG Pattern, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Brugada syndrome is an inherited heart-rhythm condition that can raise the risk of dangerous ventricular arrhythmias, often in people whose hearts look structurally normal....
Budd-Chiari syndrome: Overview, Risk Factors, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
Budd-Chiari syndrome is a rare but serious condition in which blood cannot drain normally out of the liver because the hepatic veins (or the...
Buerger’s disease: Thromboangiitis Obliterans Overview, Risk Factors, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Buerger’s disease, also called thromboangiitis obliterans, is a rare inflammatory condition that blocks small and medium blood vessels—most often in the hands and feet....
Bulboventricular foramen defect: What It Is, Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Care Plan
A bulboventricular foramen defect is a rare congenital heart problem seen mainly in “single-ventricle” heart anatomies, such as double-inlet left ventricle or tricuspid atresia...
Bundle branch block: Overview, Risk Factors, Warning Signs, and Management
A bundle branch block (BBB) is an electrical “traffic delay” inside the heart, not a blockage in the blood vessels. The signal that normally...
Zeaxanthin benefits, eye health, macular pigment, dosage, and side effects
Zeaxanthin is a naturally occurring carotenoid pigment best known for its role in protecting the center of your retina (the macula), where sharp, detailed...
Zeolite heavy metal binding, gut support, how to take, and risks
Zeolite is a porous mineral with a cage-like structure that can trap certain molecules and exchange charged particles. That unusual chemistry is why zeolite...