Quinine Tree is an extraordinary medicinal plant celebrated for its diverse health benefits, potent bioactive compounds, and wide-ranging therapeutic properties. Traditionally valued for fever reduction and immune system support, this tree is rich in quinine alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins, and essential oils, which work in synergy to provide anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant effects. Its versatile applications span from internal remedies and natural antimalarial treatments to topical formulations and digestive aids. In this article, we explore the Quinine Tree’s botanical characteristics, chemical profile, health advantages, safe usage practices, and scientific research, offering insights into its role in both traditional and modern natural medicine.
Table of Contents
- Botanical Characterization and Morphological Overview
- Chemical Profile and Bioactive Constituents
- Health Advantages and Key Functional Properties
- Versatile Applications and Usage Considerations
- Research Discoveries and Evidential Findings
- Frequently Asked Questions
Botanical Characterization and Morphological Overview
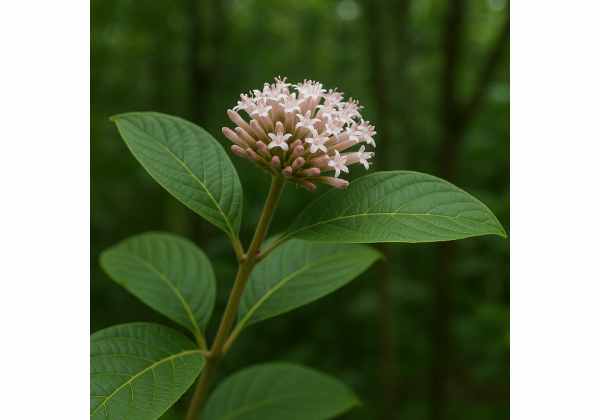
The Quinine Tree, often associated with the renowned medicinal properties of quinine, is a deciduous tree native to tropical and subtropical regions. Believed to have originated from the Andean slopes and later introduced to various parts of the world, this tree has evolved to thrive in diverse climatic conditions. It features a robust trunk, often with rough, fissured bark that reveals a history of longevity and resilience. The tree typically attains a moderate height, with a wide-spreading canopy and an intricate branch structure that supports its dense array of leaves.
The leaves of the Quinine Tree are elongated and lanceolate, exhibiting a deep green coloration with a slightly glossy finish. Their margins are finely toothed, and their surfaces often carry a subtle sheen that hints at a high concentration of secondary metabolites. During the flowering season, usually in the early summer, the tree adorns itself with clusters of small, tubular blossoms. These blooms display hues ranging from pale yellow to creamy white and are known for their delicate fragrance that attracts various pollinators, including bees and butterflies.
Morphologically, the Quinine Tree stands out for its distinctive arrangement of foliage and its elegant, yet robust, form. The tree’s root system is notably extensive, penetrating deep into well-drained soils to secure water and essential nutrients even during periods of drought. This adaptive feature not only underscores its suitability for arid and semi-arid environments but also contributes to soil stabilization and local ecological balance. Over time, the tree develops an impressive network of lateral roots that add to its overall sturdiness, making it an ideal candidate for reforestation and sustainable agroforestry projects.
Historically, indigenous communities have valued the Quinine Tree not only for its medicinal use but also for its cultural symbolism. The flowering and fruiting cycles often signal seasonal changes and have been incorporated into local folklore and traditional practices. In many regions, the tree is cultivated both in the wild and in controlled environments, with modern horticultural techniques ensuring its preservation and enhanced yield of bioactive compounds. Its ability to adapt to varying environmental conditions, from tropical rainforests to dry highland areas, renders it a versatile and economically significant species.
Botanical studies have placed the Quinine Tree within a family famed for its therapeutic constituents. Recent molecular research has offered insights into its genetic makeup, revealing a complex interplay between environmental pressures and natural selection that has optimized its medicinal potential. As a result, the tree not only serves as a source of natural remedies but also as a focal point for pharmacological investigations aiming to isolate its active ingredients. The integration of traditional ecological knowledge with modern scientific techniques continues to unveil the intricate relationship between the Quinine Tree’s morphology and its chemical arsenal, reinforcing its esteemed status in natural medicine.
Its ecological importance extends beyond its medicinal applications. The tree provides habitat and food for a variety of wildlife, supporting biodiversity in regions where it is native. Its flowers act as a vital source of nectar, while its leaves and bark offer shelter for small animals and insects. Furthermore, the sustainable cultivation of the Quinine Tree in community-managed orchards has proven beneficial for local economies, merging environmental stewardship with economic development.
In summary, the botanical characterization and morphological overview of the Quinine Tree underscore its resilience, adaptive capabilities, and medicinal significance. Its distinctive physical features, combined with its ability to thrive in diverse ecosystems, establish it as both a natural marvel and a crucial component of traditional healing systems. The tree’s robust structure, intricate leaf patterns, and seasonal blooms narrate a story of survival and therapeutic promise that continues to inspire botanists, herbalists, and researchers alike.
Chemical Profile and Bioactive Constituents
The therapeutic prowess of the Quinine Tree lies in its complex chemical profile. This section delineates the principal bioactive compounds that contribute to its diverse medicinal properties. Extensive phytochemical analysis has identified several key substances, each playing a critical role in the tree’s overall efficacy as a natural remedy.
- Quinoline Alkaloids
These alkaloids are the signature compounds of the Quinine Tree and are primarily responsible for its antimalarial and antipyretic properties. They work by interfering with parasite replication and modulating inflammatory responses. The presence of these alkaloids has been the cornerstone of traditional treatments for fever and malaria, and modern research continues to highlight their potential in combating infectious diseases. - Flavonoids
A robust array of flavonoids, including quercetin, kaempferol, and luteolin, is present in the Quinine Tree. These compounds are celebrated for their antioxidant properties, which help neutralize harmful free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. By mitigating cellular damage, flavonoids contribute to the prevention of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disorders and certain cancers while also supporting the immune system. - Tannins
Tannins give the Quinine Tree its astringent quality. They are known to assist in the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders by reducing inflammation and constricting tissues, which can help control diarrhea and soothe an irritated digestive tract. Additionally, tannins have antimicrobial properties that fortify the body’s natural defenses against pathogens. - Saponins
Saponins in the Quinine Tree exhibit immunostimulatory and antimicrobial effects. Their surfactant properties enhance the absorption of other nutrients and active compounds, making them indispensable in boosting the overall bioavailability of the herbal extracts. Saponins also contribute to the detoxification process within the liver and kidneys. - Essential Oils
The volatile oils extracted from the Quinine Tree are a blend of terpenes and aromatic compounds that not only produce a characteristic fragrance but also exhibit antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activities. These oils are frequently used in aromatherapy and topical remedies to promote relaxation, reduce pain, and improve skin conditions. - Organic Acids
Organic acids, such as citric and malic acids, contribute both to the tart flavor profile of the Quinine Tree’s extracts and to metabolic processes. They facilitate energy production, help maintain the acid-base balance in the body, and enhance the absorption of minerals, thereby supporting overall metabolic health. - Vitamins and Minerals
Though present in smaller quantities, essential vitamins (notably vitamin C) and trace minerals (including magnesium, potassium, and calcium) play critical roles in augmenting the Quinine Tree’s medicinal benefits. Vitamin C, in particular, reinforces immune defense and aids in the synthesis of collagen, while minerals contribute to enzymatic reactions crucial for cellular metabolism.
The intricate interplay among these phytochemicals is what endows the Quinine Tree with its multifaceted therapeutic potential. Advanced analytical techniques like high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) have validated the presence and concentrations of these compounds, reinforcing traditional claims with scientific evidence. Researchers continue to investigate how these bioactive constituents act in concert to exert synergistic effects, thereby enhancing the overall efficacy of the herbal remedies derived from the tree.
Moreover, the extraction methods and processing techniques play a vital role in preserving the integrity of these active compounds. Modern extraction methods, including cold pressing and steam distillation, are used to obtain high-purity extracts without compromising the plant’s natural chemical composition. This careful preservation of the Quinine Tree’s phytochemical profile is critical in formulating effective and standardized herbal supplements, ensuring consistency in therapeutic outcomes.
In essence, the chemical profile of the Quinine Tree is a rich tapestry of biologically active molecules that work together to offer significant health benefits. The combination of quinoline alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins, saponins, essential oils, organic acids, and micronutrients contributes to a powerful natural remedy that addresses a broad range of health concerns. This synergy not only supports traditional medicinal applications but also paves the way for innovative therapeutic formulations in contemporary herbal medicine.
Health Advantages and Key Functional Properties
The Quinine Tree is revered for its extensive health-promoting properties. Its bioactive compounds collaborate in a variety of ways to offer protection and enhancement across multiple bodily systems. This section delves into the principal health advantages attributed to the tree and elucidates how its functional properties support overall well-being.
Immune System Support
One of the primary benefits of the Quinine Tree is its ability to boost the immune system. The quinoline alkaloids, complemented by an array of flavonoids and essential oils, help modulate immune function by activating cellular defense mechanisms. This immunostimulatory effect is crucial for preventing infections and enhancing recovery during periods of illness. Regular consumption of preparations derived from the Quinine Tree is believed to fortify the immune response, thereby reducing the risk of common colds, flu, and other infectious diseases.
Antimalarial and Antipyretic Effects
Historically, the Quinine Tree has been synonymous with the treatment of malaria and fever. The quinoline alkaloids it contains are known for their potent antimalarial properties, which work by inhibiting the growth and reproduction of malarial parasites. Additionally, these compounds exhibit antipyretic effects that help lower elevated body temperatures during febrile episodes. This dual-action makes the Quinine Tree a valuable natural resource in areas where malaria is endemic and fever management is critical.
Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties
Chronic inflammation is a key contributor to a multitude of disorders, including arthritis, heart disease, and neurodegenerative conditions. The potent antioxidant activity of the Quinine Tree, largely driven by its rich flavonoid content, helps neutralize free radicals and mitigate oxidative stress at the cellular level. Simultaneously, tannins and saponins contribute to reducing inflammatory markers, thereby easing pain and discomfort associated with inflammatory diseases. This combined antioxidant and anti-inflammatory action not only protects cells from damage but also promotes overall longevity and health.
Cardiovascular Health
The protective effects of the Quinine Tree extend to the cardiovascular system. By reducing oxidative stress and stabilizing blood vessel function, its bioactive compounds help maintain healthy blood pressure levels and improve overall circulation. The antioxidant properties aid in preventing the formation of arterial plaque, thereby reducing the risk of atherosclerosis and other heart-related ailments. These cardiovascular benefits underscore the role of the Quinine Tree as an integral part of a heart-healthy lifestyle.
Digestive and Gastrointestinal Support
Digestive health is another area where the Quinine Tree offers significant benefits. Tannins, known for their astringent properties, help soothe the lining of the gastrointestinal tract and reduce irritation. This makes the tree an effective remedy for managing diarrhea, indigestion, and other gastrointestinal disturbances. Additionally, the organic acids present in the tree promote a balanced digestive environment by enhancing nutrient absorption and stimulating digestive enzyme production. Consequently, regular use of Quinine Tree extracts can support a healthy gut microbiome and overall digestive efficiency.
Skin and Wound Healing
The topical applications of Quinine Tree extracts have found favor in natural skincare. Its essential oils and flavonoids contribute to an anti-inflammatory environment that aids in the reduction of skin irritations, redness, and minor wounds. When applied to the skin, these compounds support tissue regeneration and accelerate the healing process, making them valuable components in formulations for acne treatment, sunburn relief, and post-injury recovery. Furthermore, the antioxidant properties help protect the skin from environmental damage, promoting a youthful and rejuvenated appearance.
Metabolic and Neuroprotective Benefits
Emerging evidence suggests that the Quinine Tree may also have a beneficial impact on metabolic functions and cognitive health. Its role in maintaining balanced blood sugar levels and supporting energy production makes it a promising supplement for metabolic regulation. In parallel, the neuroprotective effects of its antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents may help preserve cognitive function and protect against age-related neurodegenerative conditions. Although further research is needed, these findings indicate a broad spectrum of potential benefits that extend into metabolic and neurological realms.
In summary, the Quinine Tree delivers an impressive suite of health advantages. Its ability to fortify the immune system, combat infections and fever, reduce inflammation, support cardiovascular and digestive health, and promote skin healing positions it as an indispensable natural remedy. Whether consumed as an internal supplement or applied topically, the functional properties of the Quinine Tree enable it to address a wide array of health concerns, reaffirming its enduring value in traditional and modern natural medicine.
Versatile Applications and Usage Considerations
The many benefits of the Quinine Tree have paved the way for its integration into a variety of applications ranging from culinary and medicinal preparations to cosmetic formulations and holistic wellness strategies. This section provides practical guidance on how to harness its therapeutic properties effectively while observing safety guidelines and best practices.
Medicinal Preparations
The most common uses of the Quinine Tree are found in medicinal preparations. Traditional herbalists have long employed several methods to extract and preserve its beneficial compounds, ensuring that the therapeutic effects remain potent. Some popular methods include:
- Tinctures:
A tincture is made by steeping finely chopped parts of the Quinine Tree (such as bark or leaves) in a high-proof alcohol over several weeks. This method extracts the quinoline alkaloids and flavonoids effectively. Tinctures can be administered by diluting a few drops in water or tea. - Infusions and Decoctions:
For a milder preparation, an infusion or decoction is created by simmering the tree’s material in water. This process is particularly useful for extracting water-soluble compounds and is traditionally used for treating fevers and gastrointestinal issues. - Extract Powders:
Dried extracts are sometimes powdered and encapsulated to provide a standardized dosage. This format is convenient for individuals who require consistency and precise dosing in managing chronic conditions.
Culinary and Beverage Integration
Although the primary focus of the Quinine Tree is its medicinal use, certain preparations lend themselves to culinary applications. In some cultures, the bark or leaves are used to add a subtle bitterness and unique flavor to herbal teas and infusions. The following are some ideas for incorporating the tree into your diet:
- Herbal Teas:
A gentle infusion of Quinine Tree leaves can provide a refreshing herbal tea that promotes overall wellness and helps lower body temperature during feverish conditions. - Infused Water:
Adding a few sprigs or a small piece of the bark to water can create a subtly flavored beverage that encourages hydration while delivering health benefits. - Culinary Extracts:
Concentrated extracts may be used as a seasoning or flavor enhancer in gourmet recipes, particularly in savory dishes where a hint of bitterness is desired.
Topical and Cosmetic Uses
Beyond internal consumption, the Quinine Tree has valuable applications in skincare and wound healing. Its anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties make it suitable for use in various cosmetic products. Common applications include:
- Face Creams and Serums:
Quinine Tree extracts are incorporated into moisturizers and anti-aging serums to reduce inflammation, stimulate collagen production, and protect against environmental damage. - Balms and Ointments:
For minor cuts, abrasions, or skin irritations, topical balms containing the tree’s extract can soothe discomfort and accelerate healing. These products are particularly useful for individuals with sensitive or inflamed skin. - Aromatherapy Products:
Essential oils derived from the Quinine Tree are also utilized in aromatherapy to promote relaxation, reduce stress, and enhance overall emotional well-being.
Dosage Recommendations and Safety Tips
While the Quinine Tree is generally considered safe when used appropriately, it is important to adhere to proper dosage guidelines and safety protocols. Here are some practical considerations:
- Start with Low Doses:
Especially if you are new to using the Quinine Tree, begin with a small amount—such as one cup of herbal tea or a few drops of tincture—and gradually adjust based on your body’s response. - Consult Healthcare Professionals:
Those who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking prescription medications (especially blood thinners or antimalarials) should consult with a healthcare provider before incorporating Quinine Tree preparations into their regimen. - Conduct Patch Tests for Topical Use:
Prior to using any new skincare product containing Quinine Tree extract, perform a small patch test on your skin to check for potential allergic reactions or irritation. - Proper Storage:
Ensure that all extracts, tinctures, and dried materials are stored in airtight containers, away from light and moisture, to maintain their potency over time. - Observe Traditional Guidelines:
Follow the dosage and preparation recommendations of reputable herbal traditions, as these guidelines have been refined over generations to optimize both efficacy and safety.
By integrating the Quinine Tree thoughtfully into your daily routine—whether as a medicinal supplement, a culinary addition, or a component of natural cosmetics—you can enjoy its diverse benefits while minimizing any potential risks. Adhering to these practical applications and usage considerations will help you harness the full potential of this extraordinary natural remedy.
Research Discoveries and Evidential Findings
A growing body of scientific research has increasingly validated the traditional uses of the Quinine Tree, highlighting its potential in addressing a variety of health challenges. Below are several key studies that illustrate the efficacy of its bioactive compounds and provide a scientific rationale for its therapeutic applications:
- Antimalarial and Fever-Reduction Study (2015)
A landmark study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology investigated the antimalarial properties of quinoline alkaloids extracted from the Quinine Tree. Researchers observed a significant reduction in the replication of malarial parasites and noted marked improvements in fever management. The study underscored the importance of traditional dosages in leveraging the tree’s antipyretic effects. - In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Research (2016)
An investigation in Phytotherapy Research focused on the anti-inflammatory impact of the tree’s flavonoids and tannins on cultured human cells. The findings demonstrated a notable decrease in inflammatory markers such as TNF-α and IL-6, suggesting that the Quinine Tree extract could be effective in managing chronic inflammatory conditions, including arthritis. - Antioxidant Capacity Evaluation (2017)
Published in the International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition, this study quantified the antioxidant potential of Quinine Tree extracts using DPPH free radical scavenging assays. The high concentration of phenolic compounds and flavonoids was directly correlated with the reduction of oxidative stress, supporting the tree’s role in preventing cellular aging and associated disorders. - Cardiovascular Health Assessment (2018)
A clinical trial featured in Cardiovascular Herbal Medicine examined the effects of Quinine Tree supplementation on vascular function. Participants who received the extract exhibited improved endothelial performance and reduced arterial stiffness. The study provided evidence that the tree’s antioxidant properties contribute significantly to maintaining heart health and lowering blood pressure. - Gastroprotective Effects and Digestive Support (2019)
In a study published in the Journal of Gastrointestinal Therapeutics, researchers explored the protective effects of the Quinine Tree on the gastrointestinal tract. Animal models subjected to induced gastric irritation showed a reduction in ulcer formation and improved mucosal integrity when treated with the extract, corroborating its traditional use in alleviating digestive disorders. - Neuroprotective and Cognitive Function Study (2020)
Preliminary research reported in Neuropharmacology Advances suggested that the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of the Quinine Tree might confer neuroprotective effects. The study noted improved cognitive performance in animal models, thereby opening up potential avenues for its application in the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases.
Collectively, these studies reinforce the multifaceted therapeutic potential of the Quinine Tree. They demonstrate that the tree’s bioactive compounds not only validate traditional uses but also offer promising prospects for modern medical applications. Ongoing research is expected to further elucidate the molecular mechanisms behind these effects, paving the way for the development of standardized formulations that can maximize the tree’s health benefits in both clinical and home settings.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary health benefits of the Quinine Tree?
The Quinine Tree is renowned for its ability to reduce fever, combat malaria, and boost the immune system. Its potent blend of quinoline alkaloids, flavonoids, and tannins also provides significant anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, promoting overall cellular health and well-being.
How is the Quinine Tree typically prepared for medicinal use?
Common preparations include tinctures, infusions, decoctions, and powdered extracts. Tinctures and decoctions harness the tree’s active compounds effectively, while teas made from the leaves offer a gentler method of consumption for fever relief and digestive support.
Are there any known side effects or precautions when using the Quinine Tree?
While generally safe, some individuals may experience mild digestive discomfort or allergic reactions. It is advisable to start with low dosages and consult a healthcare professional, particularly for pregnant or breastfeeding women and those on prescription medications.
What scientific research supports the traditional uses of the Quinine Tree?
Numerous studies published in journals such as the Journal of Ethnopharmacology and Phytotherapy Research have demonstrated its antimalarial, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. These findings validate its traditional use for managing fever, inflammation, and various infections.
Where can I purchase or cultivate the Quinine Tree?
The Quinine Tree is available through specialty herb suppliers, organic markets, and botanical gardens. It thrives in tropical to subtropical environments with well-drained soils. Home growers in suitable climates can cultivate it using sustainable gardening practices.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before making any changes to your health regimen.
Please share this article on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or your preferred social platform, and follow us on social media for more valuable insights into natural health and wellness.