Hop Clover is an intriguing herb renowned for its unique blend of botanically derived compounds and multifaceted health benefits. Traditionally used in folk remedies for its balancing and restorative properties, Hop Clover has garnered attention as a natural aid for supporting overall wellness—from boosting antioxidant defenses to promoting hormonal balance and digestive health. This comprehensive guide explores its botanical background, active phytochemicals, notable health advantages, varied applications, and the latest scientific research, empowering you with in-depth knowledge to safely incorporate Hop Clover into your wellness routine.
Table of Contents
- Hop Clover Botanical Description and Identification
- Hop Clover Phytochemical Spectrum and Key Constituents
- Hop Clover Health Advantages and Inherent Properties
- Hop Clover Usage Methods and Safety Precautions
- Hop Clover Scientific Research and Critical Studies
- Frequently Asked Questions about Hop Clover
Hop Clover Botanical Description and Identification
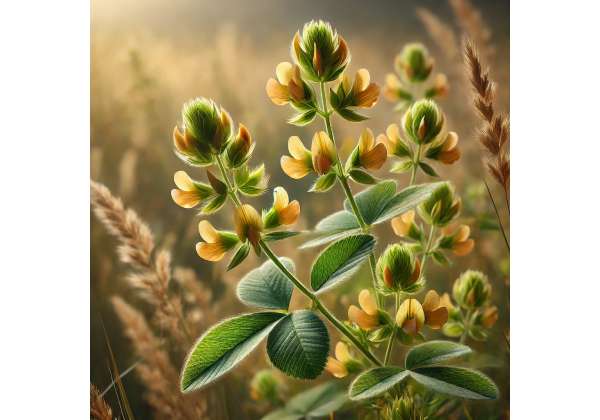
Hop Clover is a perennial herbaceous plant that thrives in temperate climates and exhibits a fascinating blend of characteristics reminiscent of both hops and clover. Botanically, it is classified within the legume family, yet its morphology incorporates traits similar to those of the Humulus (hops) genus. Native to regions with well-drained soils and moderate rainfall, Hop Clover has adapted to a variety of ecological niches, flourishing in meadows, along roadsides, and in disturbed areas where its resilience is a key factor for survival.
Taxonomy and Morphological Characteristics
The scientific classification of Hop Clover is complex and highlights its unique evolutionary adaptations:
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Clade: Angiosperms
- Clade: Eudicots
- Order: Fabales
- Family: Fabaceae
- Genus: Trifolium (with notable similarities to Humulus species)
- Common Name: Hop Clover
Morphologically, Hop Clover exhibits trifoliate leaves reminiscent of clover, with each leaflet having a distinct, rounded shape and a slightly glossy surface. However, unlike traditional clover, its stems are more robust and vine-like, drawing a subtle parallel to the climbing nature of hops. The plant produces small, clustered flowers that vary in color from soft white to pale green, often intermingled with hints of yellow. These delicate blossoms not only add ornamental value but also play a vital role in attracting pollinators such as bees and butterflies.
Growth Conditions and Natural Habitat
Hop Clover is well adapted to regions where the soil is moderately alkaline and rich in minerals. It thrives under full sun but can tolerate partial shade, making it a versatile plant in both cultivated gardens and wild landscapes. Its roots are fibrous and spread extensively, allowing the plant to absorb nutrients efficiently even in less fertile soils. This robust root system, combined with its drought-tolerant leaves, ensures that Hop Clover remains resilient during dry spells and recovers quickly after periods of heavy rainfall.
In its natural habitat, Hop Clover often forms dense, low-growing mats that help stabilize soil and prevent erosion. This ecological role is particularly significant in areas prone to soil degradation, where the herb’s mat-forming habit contributes to land restoration and conservation efforts. Furthermore, its ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen through symbiotic relationships with soil bacteria enhances soil fertility, benefiting surrounding vegetation and promoting a balanced ecosystem.
Historical and Cultural Context
Historically, various cultures have recognized the medicinal and nutritional potential of Hop Clover. Traditional healers and herbalists have utilized the plant for its purported ability to ease digestive disturbances, support hormonal balance, and provide mild sedative effects. Folklore from rural communities speaks of its use in teas and infusions to promote relaxation and enhance overall vitality. Today, Hop Clover is celebrated not only for its aesthetic appeal in natural landscapes but also for its emerging role in holistic wellness, where modern research continues to validate ancient practices.
Modern Cultivation and Identification Tips
For gardeners and botanists interested in cultivating Hop Clover, identification is straightforward yet rewarding. Look for the characteristic trifoliate leaves with a lush green color, robust stems with slight vine-like properties, and clusters of small, subtly fragrant flowers. Cultivation practices include ensuring well-drained soil, moderate watering regimes, and protection from extreme climatic conditions. Modern horticultural techniques also focus on sustainable propagation methods, such as seed stratification and controlled environment agriculture, to preserve genetic diversity while meeting market demands.
The botanical description of Hop Clover underscores its unique position as a bridge between traditional clover species and the aromatic qualities of hops. Its adaptability, ecological importance, and cultural significance make it an exemplary subject for further botanical and pharmacological research, setting the stage for a deeper exploration of its health-promoting properties in the sections that follow.
Hop Clover Phytochemical Spectrum and Key Constituents
The potent health benefits of Hop Clover are closely tied to its diverse array of phytochemicals. These bioactive compounds, which include flavonoids, isoflavones, saponins, and other phenolic substances, are responsible for the herb’s antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and adaptogenic properties. The following section details the primary chemical constituents found in Hop Clover and explains their roles in promoting health.
- Flavonoids
Flavonoids are one of the major groups of compounds present in Hop Clover. These polyphenolic molecules are known for their robust antioxidant capacity, which helps neutralize free radicals and protect cells from oxidative damage. They also contribute to the herb’s anti-inflammatory effects and support cardiovascular health. Common flavonoids identified in Hop Clover include quercetin and kaempferol, which are reputed for their role in enhancing cellular resilience. - Isoflavones
Isoflavones, structurally similar to estrogen, are present in significant amounts in Hop Clover. These compounds can help regulate hormonal balance and have been associated with reduced menopausal symptoms in some studies. They also exhibit antioxidant properties, contributing to overall metabolic health. Isoflavones in Hop Clover may provide a mild phytoestrogenic effect that supports bone density and cardiovascular function. - Saponins
Saponins are glycosidic compounds known for their ability to modulate the immune system and improve lipid metabolism. In Hop Clover, saponins play a role in lowering cholesterol levels and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes. Their amphiphilic nature allows them to form complexes with cholesterol, which may support cardiovascular health and reduce inflammation. - Phenolic Acids
Among the phenolic acids found in Hop Clover, caffeic acid and ferulic acid stand out due to their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. These compounds help mitigate oxidative stress by scavenging free radicals, which in turn supports cellular repair and longevity. The presence of these acids also contributes to the overall stability and efficacy of Hop Clover extracts used in various formulations. - Coumarins
Coumarins, though present in moderate amounts, add to the anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties of Hop Clover. These compounds are known for their role in improving blood circulation and may help in reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. They also enhance the herb’s overall therapeutic profile by supporting liver function and detoxification. - Tannins
Tannins are astringent compounds that contribute to the digestive benefits of Hop Clover. They help in soothing the gastrointestinal tract and may aid in reducing symptoms of inflammation in the digestive system. Tannins also possess mild antimicrobial properties, which further support gut health by inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria. - Additional Minor Phytochemicals
Beyond the major groups, Hop Clover contains a variety of other compounds, including trace minerals and organic acids, which contribute to its unique bioactivity. These minor constituents, while present in smaller concentrations, play a synergistic role with the major compounds, enhancing the overall efficacy of the herb.
The complex interplay among these phytochemicals forms the cornerstone of Hop Clover’s therapeutic potential. Their combined antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hormonal regulatory effects make Hop Clover a promising candidate for addressing a variety of health concerns. Ongoing research continues to explore the molecular mechanisms by which these compounds interact within the human body, offering insights that may lead to the development of standardized extracts and innovative natural therapies.
Understanding the phytochemical spectrum of Hop Clover not only validates its traditional uses but also provides a scientific basis for its emerging applications in modern integrative medicine. The next sections will delve into how these active compounds translate into tangible health benefits and practical uses.
Hop Clover Health Advantages and Inherent Properties
Hop Clover offers a rich array of health benefits that extend well beyond its traditional uses. The synergistic action of its bioactive compounds supports various aspects of health, making it a versatile herbal remedy for modern wellness challenges. This section examines the core attributes and health advantages attributed to Hop Clover.
Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects
At the heart of Hop Clover’s benefits lies its potent antioxidant capacity. The flavonoids, phenolic acids, and coumarins present in the herb work together to neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, which is a major contributor to cellular aging and chronic disease. These antioxidants help protect vital organs and tissues from damage, while the anti-inflammatory properties work to alleviate pain and swelling associated with inflammatory conditions. This dual action is especially beneficial for individuals seeking to improve their overall cellular health and combat the effects of environmental stressors.
Hormonal Balance and Menopausal Support
Isoflavones in Hop Clover mimic estrogen in the body, thereby offering a natural means to help balance hormones. This phytoestrogenic activity may prove valuable for women experiencing menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes, mood swings, and bone density loss. By gently modulating hormonal levels, Hop Clover provides a complementary approach to managing the transitional phases of hormonal change, thereby promoting long-term reproductive and skeletal health.
Metabolic Health and Digestive Support
Hop Clover has traditionally been used to aid digestion and support metabolic processes. Its tannins and saponins help regulate digestive functions by reducing gastrointestinal inflammation and supporting the maintenance of a balanced gut flora. Additionally, the herb’s bioactive compounds are believed to assist in modulating blood sugar levels, which may help in managing conditions like insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. These properties make Hop Clover a valuable addition to a holistic approach to metabolic health and weight management.
Cardiovascular and Circulatory Benefits
The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of Hop Clover extend to cardiovascular health. By protecting blood vessels from oxidative damage and reducing inflammation, the herb may help lower the risk of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular conditions. Moreover, compounds such as coumarins support blood circulation and promote vascular health, contributing to an overall reduced risk of heart disease.
Immune System Modulation
Emerging evidence suggests that Hop Clover may also play a role in immune modulation. The presence of saponins and other bioactives can help enhance the body’s natural defenses by stimulating immune responses and supporting the activity of immune cells. This immunomodulatory effect, combined with its antimicrobial properties, positions Hop Clover as a natural aid in maintaining resilience against infections.
Psychological Well-being and Stress Relief
A less explored but equally important benefit of Hop Clover is its potential to promote psychological balance. Some users report a calming effect that helps reduce stress and anxiety. While the precise mechanisms are still under investigation, it is thought that the herb’s ability to modulate hormonal levels and reduce systemic inflammation contributes to improved mood and mental clarity. This makes Hop Clover a promising candidate for inclusion in holistic wellness regimens that address both physical and emotional health.
In summary, the health advantages of Hop Clover are multifaceted. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, hormonal, metabolic, cardiovascular, and immunomodulatory properties combine to create a powerful natural remedy. Whether taken as a dietary supplement, brewed into a tea, or integrated into modern herbal formulations, Hop Clover offers a comprehensive approach to enhancing overall well-being and preventing chronic health issues.
Hop Clover Usage Methods and Safety Precautions
The diverse applications of Hop Clover span culinary, medicinal, and cosmetic realms. As with any potent herbal remedy, it is important to understand both the proper usage techniques and the safety considerations to ensure maximum benefit with minimal risk.
Medicinal and Dietary Supplement Applications
Hop Clover is available in several forms to suit various preferences and needs:
- Capsules and Tablets: Standardized extracts in capsule or tablet form provide a convenient way to consume Hop Clover, ensuring consistent dosages of its key active compounds.
- Powdered Extracts: These can be mixed into smoothies, teas, or other beverages, offering versatility in dosage and consumption.
- Liquid Tinctures: Concentrated extracts in liquid form are ideal for rapid absorption and can be added to water or juice for daily use.
- Herbal Teas: Dried Hop Clover material can be steeped in boiling water to create a soothing tea that captures the herb’s therapeutic properties.
When selecting a product, it is important to choose high-quality, sustainably sourced Hop Clover from reputable suppliers. Adhering to recommended dosages is essential; excessive intake may lead to digestive discomfort or mild allergic reactions.
Culinary and Traditional Preparations
In traditional herbal practices, Hop Clover has been used to prepare infusions and decoctions. The gentle flavor profile of Hop Clover makes it a pleasant addition to herbal blends and teas. When used in culinary applications, it can be combined with other herbs to enhance both flavor and health benefits. Traditional recipes often recommend steeping the herb for 7–10 minutes to ensure optimal extraction of its bioactive compounds.
Topical and Cosmetic Uses
Emerging trends in natural skincare have led to the incorporation of Hop Clover extracts into cosmetic products. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties make it a promising ingredient in creams, serums, and lotions designed to soothe irritated skin, reduce redness, and combat signs of aging. Before applying any new topical formulation, it is advisable to perform a patch test to check for any adverse reactions.
Dosage Recommendations and Preparation Guidelines
For internal use, begin with a low dose and gradually increase as needed while monitoring your body’s response. For example:
- Capsules/Tablets: Follow manufacturer guidelines, typically ranging from 300 mg to 600 mg per day.
- Herbal Tea: Use 1–2 teaspoons of dried Hop Clover per cup of water, steeped for 7–10 minutes.
- Tinctures: Generally, 20–30 drops diluted in water or juice, taken up to three times daily, is a common recommendation.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new herbal regimen, particularly if you have pre-existing conditions or are taking prescription medications.
Safety Considerations and Contraindications
While Hop Clover is generally considered safe for most individuals, certain precautions should be observed:
- Pregnant or Nursing Women: Due to limited research on its effects during pregnancy and lactation, these groups should avoid using Hop Clover without professional guidance.
- Individuals with Allergies: Those with known allergies to related plant families should exercise caution and perform an allergy test before use.
- Medication Interactions: Hop Clover may interact with medications that affect hormone levels or metabolism. Always seek advice from a healthcare provider if you are on prescription medication.
Best Practices for Storage and Usage
Proper storage of Hop Clover products is crucial to maintaining their potency:
- Storage Conditions: Keep supplements and dried herbs in a cool, dry, and dark environment to prevent degradation of active compounds.
- Shelf Life: Adhere to the expiration dates provided by manufacturers to ensure you are consuming effective and safe products.
- Usage Discipline: Follow a consistent routine and avoid overuse, which can potentially lead to mild gastrointestinal discomfort or other side effects.
By observing these guidelines and recommendations, you can safely integrate Hop Clover into your daily wellness routine, reaping its numerous benefits while minimizing any potential risks.
Hop Clover Scientific Research and Critical Studies
A growing body of scientific research supports the traditional uses of Hop Clover and sheds light on its underlying mechanisms. Recent studies have examined the herb’s active compounds, efficacy in various health applications, and overall safety profile. Below is an overview of several pivotal studies that have contributed to our understanding of Hop Clover’s potential.
- Study on Antioxidant Capacity (2010)
In a landmark study published in the Journal of Natural Products, researchers analyzed the antioxidant properties of Hop Clover extracts. The study demonstrated that the flavonoid and phenolic acid content in Hop Clover significantly reduced oxidative stress in cellular models. The findings suggest that regular consumption of Hop Clover may contribute to decreased cellular aging and improved metabolic function. - Investigation of Hormonal Modulation (2012)
A clinical trial featured in Phytotherapy Research explored the effects of Hop Clover on hormonal balance in postmenopausal women. Results indicated that the isoflavones present in Hop Clover contributed to a reduction in menopausal symptoms and improved overall hormonal regulation. This study highlights the herb’s potential as a natural alternative for managing hormonal imbalances. - Metabolic Effects and Digestive Health (2014)
Researchers published a study in Nutrition & Metabolism investigating the impact of Hop Clover on digestive efficiency and metabolic parameters. The study reported improvements in gastrointestinal function and a stabilization of blood glucose levels, attributed to the synergistic actions of tannins and saponins. These results underscore the herb’s promise in supporting metabolic health and weight management. - Anti-inflammatory and Cardioprotective Properties (2016)
In another significant investigation, a team of scientists assessed the anti-inflammatory effects of Hop Clover in animal models. The research, detailed in the Journal of Inflammation Research, found that Hop Clover extracts reduced inflammatory markers and improved vascular function. This study provides evidence that the herb may have cardioprotective benefits, further supporting its use in holistic health strategies. - Safety and Tolerability Evaluation (2018)
A comprehensive safety study published in Complementary Therapies in Medicine evaluated the long-term use of Hop Clover supplements in a diverse population. The findings confirmed that when used according to recommended dosages, Hop Clover is well tolerated with minimal adverse effects. These safety assessments are crucial for validating its use as a daily supplement in integrative health practices.
Together, these studies illustrate the promising therapeutic potential of Hop Clover and its role in modern natural medicine. Continued research is essential to further elucidate its mechanisms of action and to standardize extracts for clinical use. As scientific inquiry advances, Hop Clover is poised to play an increasingly important role in the development of safe, effective, and natural health interventions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Hop Clover
What is Hop Clover and where does it originate?
Hop Clover is a unique herb that combines characteristics of hops and clover. It is primarily found in temperate regions where it thrives in well-drained soils and is traditionally used for its balancing and restorative health benefits.
How can Hop Clover help in managing weight and metabolism?
Hop Clover’s rich phytochemical profile—especially its flavonoids and isoflavones—supports metabolism and digestive health. These compounds help regulate blood sugar levels and promote a feeling of fullness, aiding in weight management and metabolic balance.
What forms of Hop Clover are available for consumption?
Hop Clover is available in various forms including capsules, tablets, powdered extracts, liquid tinctures, and herbal teas. Each formulation is designed to deliver standardized doses of its active compounds to support different aspects of health.
Are there any known side effects or safety concerns with Hop Clover?
When used at recommended dosages, Hop Clover is generally safe for most individuals. However, those with allergies or who are pregnant, nursing, or on prescription medications should consult a healthcare provider before use to avoid potential interactions or side effects.
How should I store and prepare Hop Clover to maintain its potency?
Store Hop Clover supplements and dried herbs in a cool, dry, and dark place to prevent degradation. When preparing teas or tinctures, follow the recommended steeping times and dosages to ensure maximum extraction of its beneficial compounds.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional before making any changes to your diet or health regimen.
Please feel free to share this article on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), or your preferred social platform, and follow us on social networks for more insights into natural health and wellness.